The global supply chain management market is projected to reach nearly $31 billion by 2026, reflecting its growing importance across various industries.1 Yet despite this rise, recent disruptions, such as the COVID-19 pandemic and ongoing geopolitical tensions, have exposed deep vulnerabilities in supply chains, resulting in costly delays and operational inefficiencies.
AI in supply chain operations offers tools to mitigate these challenges by enabling more intelligent forecasting, faster decision-making, and greater end-to-end visibility.
Explore 13 supply chain AI use cases designed to optimize performance, lower costs, and improve adaptability.
Supply chain automation use cases
Modern supply chain automation is not possible without AI. AI enables supply chain automation technologies, such as digital workers, warehouse robots, autonomous vehicles, and robotic process automation (RPA), to perform repetitive, error-prone tasks automatically.
Through AI, the following supply chain tasks can be automated:
1. Back-office automation
AI in supply chain automates repetitive administrative tasks such as invoice processing, purchase order management, and data entry. These tasks often slow down supply chain operations. Artificial intelligence leverages data analytics, conversational AI, and RPA to process large datasets, thereby reducing manual errors and improving response times.
This enables supply chain professionals to focus on higher-value tasks, such as supplier negotiations and demand planning.
2. Logistics automation
In the logistics industry, AI models help optimize freight scheduling, last-mile delivery, and real-time tracking. AI algorithms process vast amounts of real-time data from logistics networks to select optimal routes, forecast delays, and enhance supply chain visibility.
This improves delivery performance and reduces costs. Machine learning models can also support predictive analytics, enabling more accurate shipment planning.
3. Warehouse automation
AI-powered robots and automated systems can efficiently handle tasks such as picking, sorting, and packaging in distribution centers. These systems reduce reliance on human workers and operate around the clock.
Machine learning helps fine-tune warehouse layouts and workflows to optimize efficiency. This enhances efficiency and supports resilient supply chains by maintaining operations during labor shortages or demand surges.
4. Automated quality checks
Computer vision systems enable visual inspection systems that detect product defects in real time. These systems use machine learning to analyze data from camera feeds or sensors.
This reduces dependence on manual checks and improves consistency.
5. Automated inventory management
Supply chain AI solutions enable real-time visibility into inventory levels by using connected sensors, AI algorithms, and demand forecasting.
AI models analyze historical data and relevant input data, such as sales trends or customer needs. This allows supply chain managers to automate reordering and align inventory plans with demand patterns. It also helps in identifying risks related to stockouts or overstocking.
6. Inventory optimization
Machine learning models support inventory optimization by forecasting demand and adjusting inventory levels in response to market trends and business needs.
AI in supply chain processes can simulate scenarios, evaluate risk management strategies, and recommend changes to inventory policies. This helps reduce excess stock and lowers operating costs while ensuring product availability.
Scenario planning with generative AI
Supply chain planners often need to test multiple outcomes before making changes to their networks. Generative AI tools use machine learning to process vast amounts of data and provide summaries that support data-driven decisions.
For example, if a port closes or a supplier fails, the AI system can model how these changes affect delivery times, inventory levels, and operating costs. Generative AI helps supply chain leaders evaluate options without needing to create reports manually, thereby enhancing decision-making and supporting supply chain resilience.
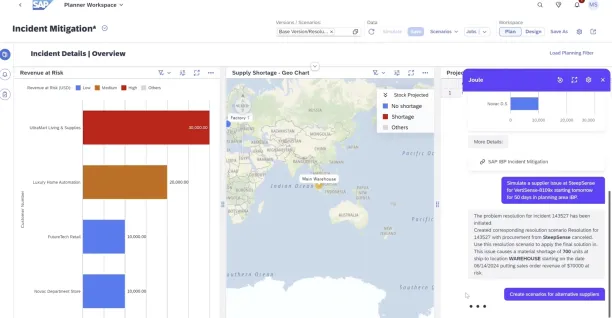
Figure 1: SAP Joule’s root cause analysis for delays and suggestions for improvements.2
Demand and supply planning use cases
7. Region-specific forecasts
AI algorithms analyze historical data, demand patterns, and regional events to generate accurate region-specific forecasts. These forecasts support supply chain planners in localizing supply chain planning and aligning logistics operations with regional variations.
This improves supply chain resilience and meets diverse customer needs across global supply chain networks.
8. Bullwhip effect prevention
The bullwhip effect occurs when small changes in demand lead to large fluctuations upstream in the supply chain. AI in supply chain mitigates this by using real-time data and predictive analytics to enhance visibility and coordination.
AI models support better demand planning and communication between supply chain partners, reducing variability.
9. Enhanced supplier relationship management
Artificial intelligence enables supply chain leaders to evaluate supplier performance effectively using data analytics. AI models analyze data sets including delivery history, quality scores, and compliance records. This helps identify risks and improve decision-making.
For ongoing communication, AI tools can automate routine updates and flag exceptions, improving collaboration with supply chain partners and enhancing efficiency across supplier networks.
Sustainability use cases
Sustainability is a growing concern for supply chain managers, as most of an organization’s indirect emissions are generated through its supply chain. AI can help improve supply chain operations to make them greener and more sustainable.
10. AI-powered circular supply chains
Reverse logistics is becoming more critical as supply chain organizations aim to meet sustainability goals and comply with regulations. AI technology helps predict return volumes and sort returned goods for reuse, recycling, or resale. These processes are optimized using machine learning models that evaluate relevant data from distribution centers and customer behavior.
AI tools determine whether to repair, recycle, or resell a returned item based on its condition and current market trends. This reduces waste, enhances efficiency, and supports cost-effective operations. Supply chain planners utilize AI to enhance circular flows without disrupting overall supply chain operations.
11. Carbon accounting and emissions tracking
New regulations require companies to track and report carbon emissions from their supply chain. AI in supply chain is used to calculate Scope 3 emissions, which come from suppliers and logistics activities. These tools process data sets from energy use, transportation, and material sourcing to estimate emissions and suggest ways to reduce them.
Supply chain professionals utilize AI to monitor emissions in real-time, identify high-impact areas, and propose changes that align with sustainability targets. This enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and improves compliance. AI supports cost-effective carbon management strategies that fit into existing supply chain solutions.
Other use cases
12. Risk management and disruption prediction
Supply chain managers are facing increasing pressure to manage risks associated with geopolitical events, natural disasters, and cyber incidents. Artificial intelligence is used to predict and respond to such disruptions.
AI models monitor real-time data from multiple sources, including news, weather, customs, and social platforms. These systems analyze relevant data to identify risks across logistics networks and supply chain partners.
Supply chain organizations utilize predictive analytics to develop mitigation strategies before problems impact operations. Generative AI can summarize risks and recommend actions for supply chain planners to mitigate them. This enhances decision-making, improves supply chain visibility, and helps maintain resilient supply chains.
13. Digital twin and AI integration
Digital twin technology creates a real-time model of supply chain operations. AI models are used in conjunction with digital twins to simulate and monitor real-world systems, including factories, warehouses, and distribution centers. This supports data-driven decisions by providing a virtual space to test changes without interrupting real processes.
These AI tools fine-tune inventory plans, forecast demand, and evaluate logistics scenarios to optimize operations.
Supply chain managers use the system to analyze data, identify risks, and validate supply chain planning choices. It improves supply chain visibility and enhances supply chain resilience across global supply chain networks.
Real-life examples of supply chain AI applications
Amazon: AI-driven supply chain optimization
Amazon has significantly enhanced its logistics capabilities, achieving a 75% increase in speed through the use of artificial intelligence. According to Scot Hamilton, VP of Planning and Routing Technology, AI helps Amazon deliver products faster by forecasting demand and optimizing operations.
- Cyber Monday 2023: AI predicted demand for over 400 million items daily, using historical data to pinpoint where orders would originate.
- Warehouse restocking: AI ensures high-demand items are stocked in nearby facilities, reducing delivery times.
- Sequoia Robotics: This robotic inventory system has increased inventory identification and storage speed by 75%, reduced human effort and injury by 15%, and decreased processing time by 25%.
- Environmental and cost benefits: In 2020, AI-led improvements saved over $1 billion and cut 1 million tons of CO2 emissions in transportation and logistics.
Minimizing packaging waste using AI
To reduce its environmental footprint, Amazon introduced the Packaging Decision Engine (PDE) in 2019, an AI solution designed to optimize packaging.
- Packaging optimization: PDE evaluates millions of items daily to suggest the most suitable packaging.
- Workflow:
- Items pass through a computer vision tunnel, which checks for defects and measures dimensions.
- The AI combines data from item metadata and customer feedback to recommend ideal packaging.
- A vector score helps determine and store the best packaging approach for future use.
This system has enabled Amazon to eliminate over 2 million tons of packaging materials globally since 2015, enhancing both efficiency and sustainability.
Preventing damaged product deliveries
Returns due to damaged or incorrect items are a major logistical challenge for Amazon. Common causes include:
- 23%: Incorrect items sent
- 22%: Items looking different from what was expected
- 20%: Product damage
To address this, Amazon implemented Project P.I. (Private Investigator), an AI initiative leveraging generative AI and computer vision.
- Traditional checks: Previously required five employees to conduct a six-point visual inspection.
- AI upgrade: Project P.I. automates defect detection, verifying accurate specifications such as size and color before shipping.3
Nestlé: Smarter inventory management through AI-powered analytics
Nestlé has transformed its inventory forecasting by shifting from manual, judgment-based planning to AI-driven analytics platforms. Historically, the company relied on Excel-based calculations to predict demand, which were often impacted by subjective human inputs and prone to error. Mistakes in forecasting led to costly issues like stockouts, lost sales, and customer churn.
To overcome these inefficiencies, Nestlé adopted AI and machine learning models that use real-time demand signals to enhance forecasting accuracy. These models can:
- Measure the impact of advertising and pricing on demand
- Simulate “what if?” scenarios (e.g., how a 2% price drop would affect sales)
- Support demand shaping and sensing across a vast product portfolio
This approach replaces reactive forecasting, empowering Nestlé to make data-informed, strategic decisions. SAS Institute advisor Charles Chase, who helped implement this system, emphasized blending data science and industry knowledge on an exception basis to drive lean, value-added forecasting.
At the start of their transformation, 80% of forecasts were manually adjusted, while only 20% used data science and domain expertise. Over time, this balance has shifted due to the integration of AI tools and partnerships with platforms like Coupa (see the video below). However, challenges such as data quality and model understanding have remained focal areas for improvement.
Enhancing collaboration and process efficiency with Large Language Models
Nestlé also recognized the value of generative AI, specifically large language models (LLMs), in transforming communication and workflow automation across its enterprise.
A persistent issue in manufacturing and supply chain is poor internal communication, often leading to project delays and disengaged employees. Nestlé’s response to this issue is to build its own LLM, branded NesGPT, paired with a user-friendly chatbot interface.
NesGPT was developed to:
- Support communication between departments: Minimize communication gaps by providing employees across various functions, including sales, marketing, legal, and product innovation, with the necessary support.
- Enhance supply chain optimization: Identify potential stockouts and optimize pricing strategies.4


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.