Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is one of the earliest areas of artificial intelligence research. Today OCR is a relatively mature technology and it is not even called AI anymore which is a good example of Pulitzer Prize winner Douglas Hofstadter’s quote: AI is whatever hasn’t been done yet.
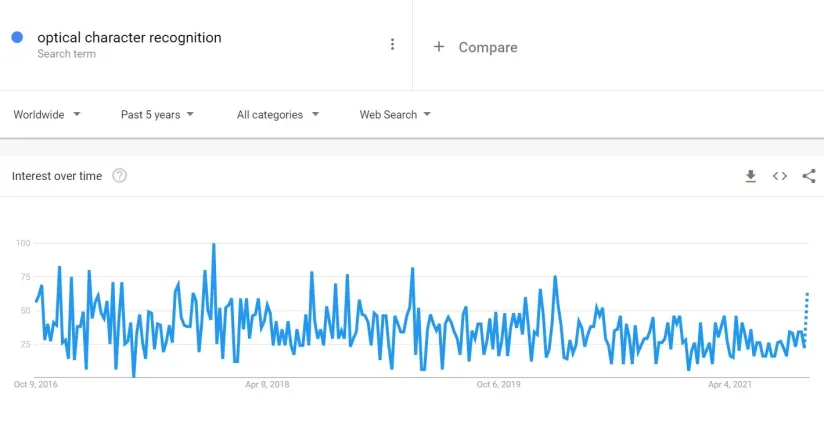
In the featured image, we observe that the interest in OCR is relatively stable in the last three years. This leads some experts to claim that OCR is a “solved” problem and that no further progress is required. However, OCR provides outstanding results only in particular use cases.
In most practical applications, it is still far below human-level accuracy. Modern OCR applications are especially poor in processing documents with poor image quality, some alphabets like less commonly used Arabic fonts such as Nastaliq, handwriting, and cursive handwriting.
The developments in the large language models also help in OCR, in our OCR benchmark, we see that LLM’s achieved the highest score among the OCR tools.
What is OCR?
OCR is a technology that identifies characters from printed books, handwritten papers, or images. With this technology, businesses can rapidly transfer documents into their digital systems, and data analysis tools can process the relevant data. You can read more about OCR in our related article.
Which technology advancements provided today’s OCR technology?
Computer vision
With computer vision technologies, OCR first detects characters one by one. Afterward, it uses image classification to identify each character. If these two steps work successfully, OCR outputs accurate results. However, characters can sometimes be too close to each other and might not be recognized. Thus, OCR requires more than computer vision technologies.
Natural language processing (NLP)
Even though OCR identifies characters, those characters form words, sentences, and paragraphs. Research in NLP has resulted in numerous algorithms that can be used to correct mistakes in character recognition using probabilistic approaches. For example, missing characters can be estimated using context.
Supervised deep learning
OCR leverages deep learning algorithms to improve its performance. While it requires learning from training samples to improve OCR performance, with this technology, OCR tools can:
- Recognize characters with different fonts. Each character can be written in a wide range of forms, and large labelled data set help OCR software identify the characters despite font variations
- Detect errors and correct them. OCR tools can skip characters that cannot be identified. By recognizing patterns in training samples, OCR can detect those errors and correct its mistakes.
What are the limitations of OCR tools?
OCR is not a stand-alone solution in human-machine communication
The main problem with OCR is that it only outputs unstructured characters. This necessitates the combination of other machine learning technologies into OCR. By that, users can obtain structured data from their documents. Our article on data extraction explains how companies can use more advanced technologies to get structured data from documents.
OCRs still can’t match human-level accuracy in most applications.
Errors include misreading letters, skipping over unreadable letters, or combining text from adjacent columns or image captions. While many factors affect the performance of OCR tools, the number of errors depends on the quality and form of the text, including the font used.
However, even with high-quality documents, OCR tools can make mistakes because there are a variety of document formats, fonts, and styles for each character. The limitations that prevent OCR tools from reaching 100% accuracy can be listed as follows:
Document-based Limitations
- Colored backgrounds: Colorful background patterns can be troublesome because they can decrease text recognition
- Blurry or glared texts: Blurry or glared images are challenging to read for humans as well as computers.
- Skewed or non-oriented documents: For situations where the image may be skewed, OCR will have a harder time identifying the characters because the text is not aligned.
Text-based Limitations
- Variety of letters: Letter forms in some alphabets are harder to recognize. For example, as even the printed Arabic characters are in the cursive form, character recognition becomes a challenge. In the below image, you can see how Google Cloud Vision API makes mistakes in recognizing Arabic Letters.
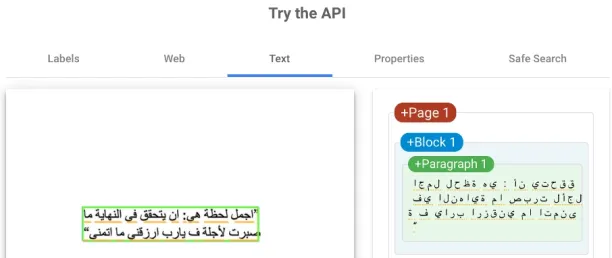
Source: Google Cloud Vision
- Variety of font types & sizes: While it is hard to recognize all different font types, too small/big characters are also tricky to identify.
- Look-alike characters: Some characters look so similar that OCR tools may not distinguish between them. For example, it is hard to differentiate between the number “0” and the letter “O”.
- Handwritten text: As everyone has their own way of writing characters, OCR tools might not recognize all characters with different styles. You can see some characters are recognized with mistakes in the below image.
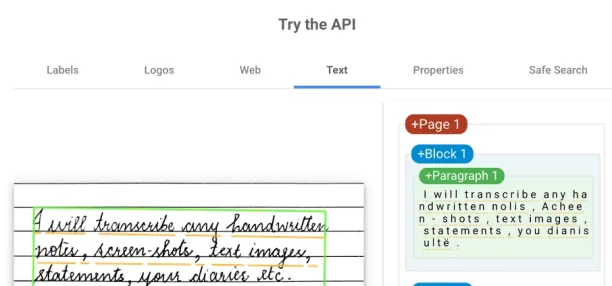
How to measure OCR accuracy?
OCR accuracy can be measured by the portion of characters in a text that the OCR tool can extract without mistakes. For example, 99% accuracy means that 990 out of 1000 characters are correctly recognized.
Is there any active research to surpass these limitations?
Since it was first introduced, OCR has evolved and it is used in almost every major industry now. As it still has areas to be improved, research in OCR has continued. Advances in computer vision and deep learning algorithms contribute to the increased accuracy of this technology.
Right now, OCR tools can reach beyond 99% accuracy in typewritten texts. However, higher accuracy levels are desired as companies still make use of human intervention to check for potential errors.
The current focus of research in OCR technology is mostly on handwriting recognition and cursive text recognition.
Handwriting Recognition
The research on handwriting recognition also leverages the dynamic motion created during the handwriting process to identify characters. While the main problem with handwriting recognition is the variety of character styles, OCR accuracy in this area is constantly but slowly improving.
You can see our handwriting recognition benchmark if you are interested.
Cursive Text Recognition
The joined letters are clearly harder to recognize than printed texts. This situation brings more errors in OCR tools, and the shapes of the letters do not provide enough information to allow the software to perceive them correctly.
You can also check our data-driven list of OCR Software to find the option that best suits your business needs.
Further reading
If you have questions on OCR tools, feel free to contact us:

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.