Agentic AI for cybersecurity functions as an autonomous decision-maker for SecOps and AppSec. It can take proactive actions, automate software development processes, or automate pentesting.
For example, AppSec AI agents like Aptori can integrate into your IDE and CI/CD pipeline to run automated pentests to identify if your APIs are free from vulnerabilities.1
Examples of AI agents in cybersecurity
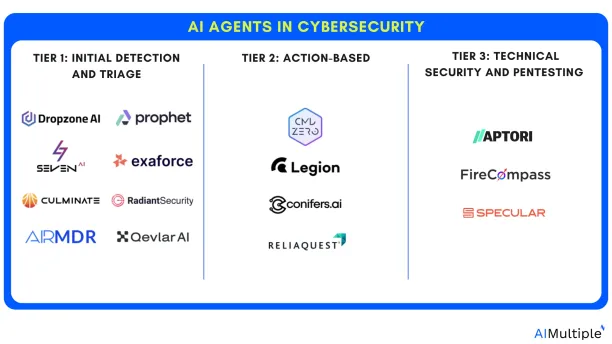
- Tier 1 agents handle the initial detection and triage of a potential security threat.
- Tier 2 agents take proactive actions like:
- isolating affected systems
- removing malware
- patching vulnerabilities
- restoring compromised data
- Tier 3 agents leverage security tools for threat hunting and in-depth analysis. These agents often have capabilities like:
- automated threat detection
- complex vulnerability scanning
- pentesting
- malware analysis
Agentic AI for cybersecurity
Unlike traditional security systems that depend on pre-defined rules and manual interventions—often too slow or narrow to address modern threats—agentic AI leverages its ability to learn dynamically from its environment.
It enhances cybersecurity activities by:
- Continuously monitoring and addressing threats in real-time
- Automating repetitive SOC tasks with minimal human intervention
- Offering contextual decision support
Architecture of AI Agents integrated with AI Inference, for their interaction with LLMs and enterprise data for SOC automation:
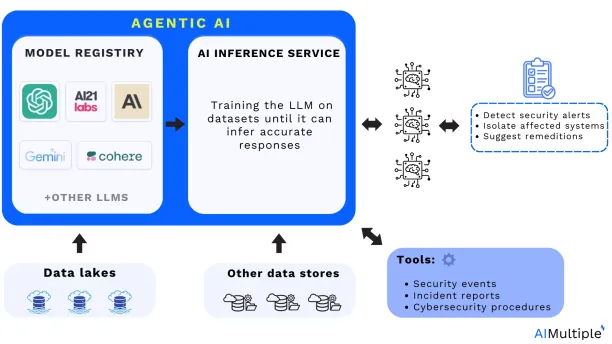
Adapted from: Cloudera2
Read more: AI in SOAR.
> Real-life use cases: Agentic AI in SecOps
1. Triage and investigation
Agentic AI detects security alerts before they reach human analysts. It automates the triage and investigation processes, imitating human SOC workflows and decision-making. AI agents in initial triage and investigation can leverage:
Alert deduplication: Identifying duplicate events to reduce noise.
Alerts grouping: Clustering alerts related to a specific asset (e.g., endpoint, server).
Alert enrichment: Adding critical context for more effective investigations, including:
- IOC (indicator of compromise) enrichment:
- Check if an IP address on a blacklist
- Compare file hashes to malware databases
- Machine enrichment: (e.g. provides data about affected systems)
- Account enrichment: (e.g. provides data about user identities)
Real-life example: AI agents leveraging triage and investigation
Challenges — A digital insurance company’s early security configuration required manual alert management, which was resource-intensive.
This created several challenges, including:
- High volume of security alerts
- Time-consuming processes
- Need for continuous 24/7 monitoring
Solutions — The company deployed cybersecurity AI agents and integrated these agents with existing systems like AWS, Google Workspace, and Okta.
The following outcomes have been achieved:
- Reducing the manual burden allowed SOC analysts to prioritize higher-value tasks.
- Detailed investigation reports provided a granular level of analysis, increasing the visibility into IOC (indicator of compromise).
- Reduction in false positives improved accuracy in threat detection, allowing the team to focus on major risks.3
2. Adaptive threat hunting
Agentic AI can be used in cybersecurity systems to detect and respond to threats in real-time.
For example, these agents can identify unusual network behavior and isolate impacted devices autonomously to prevent a compromise without human intervention.
While leveraging threat hunting, AI agents take several actions, including:
Decomposing the alert:
- Indicator classification: Categorizing the alerts into various types of indicators:
- Atomic Indicators: Basic elements like IP addresses, domain names, email addresses, and file hashes.
- Computed Indicators: Information derived from data analysis, such as malware file sizes or encoded strings.
- Behavioral indicators: Patterns of behavior, including tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) employed by threat actors.
Searching for atomic (e.g. IP address) and computed indicators ( e.g. behavioral anomalies):
- Creating queries to search historical data across SIEMs, or other relevant tools for the identified IOCs.
- Accessing numerous systems and requesting all relevant platforms simultaneously to collect data from many sources.
Analyzing behavioral indicators:
- Mapping computer network protocol for control systems by connecting behavioral indicators and using frameworks like MITRE ATT&CK.
- Searching historical alerts and data across connected systems.
Real-life example: AI agents leveraging threat hunting
Challenges — The University of Kansas Health System had difficulties in coordinating incident response, some of the key challenges include:
- Lack of visibility
- Limited incident response
- Employee resource constraints
Solutions — The University implemented a security platform with agentic AI capabilities to improve visibility and automate incident response threat-hunting.
The following outcomes have been achieved:
- Visibility across systems increased by over 98%
- Detection coverage has improved by 110% within six months.
- Automated incident response processes filtered and resolved 74,826 out of 75,000 alerts, escalating only 174 for manual review.
- True positives among escalated alerts totaled 38, reducing noise and enabling focused responses.4
3. Response actions
Generating infrastructure as code: Using code to manage and provision computing resources instead of manual processes, examples include:
- Generating OpenTofu and Pulumi templates for remediation, ready for DevOps review.
- Configuring components like operating systems, middleware, and applications.
Performs endpoint actions: Entering a response action command in the console’s input area.
Security controls: Updating blocklists or firewall rules as new security incidents emerge.
Real-life example: AI agents leveraging response actions
Challenges — APi Group, a distribution organization, faced the following cybersecurity challenges:
- Diverse technology stacks
- Visibility across the ecosystem
Solutions — To address the above challenges, APi Group implemented ReliaQuest’s agentic AI platform to enhance threat detection for its Microsoft environments.
The following outcomes have been achieved:
- Reduced response times by 52% through automation and integrated playbooks.
- Achieved a 47% increase in visibility across Microsoft 365, Cisco, and Palo Alto stacks.
- Expanded MITRE ATT&CK coverage by 275%, enabling better prioritization of resources.5
Agentic AI and security operations (SecOps) explained
Security operations (SecOps) is a collaborative approach between IT security and IT operations teams focused on proactively identifying, detecting, and responding to cyber threats.
The problem:
SecOps face serious fatigue since teams deal with vast data from diverse systems and rapidly evolving threats while navigating complex organizational structures and compliance requirements.
How agentic AI helps:
AI is especially effective at “reasoning tasks” such as analyzing alerts, conducting predictive research, and synthesizing data from tools.
Thus, AI agents in SecOps can help automate tasks that require real-time analysis and decision-making, such as phishing, malware, credential breaches, lateral movement, and incident response.
For example, these tools can be trained on MITRE ATT&CK knowledge bases to mimic the expertise of human analysts or use incident response playbooks to:
- enrich alerts
- detect impacted systems
- isolate/triage infected systems
- create incident reports
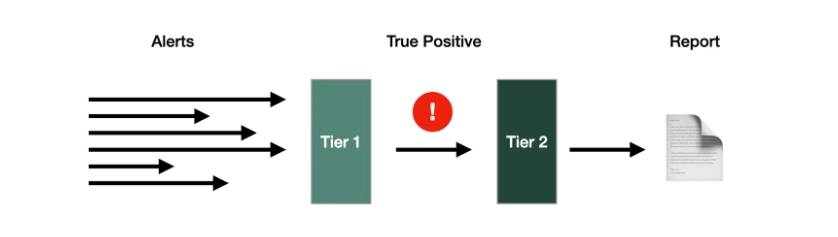
Source: 6
> Real-life use cases: Agentic AI in AppSec
4. Risk identification
Agentic AI serves as a vigilant sentinel, continuously analyzing your environment for threats and potential vulnerabilities in applications and code bases. AI agents can execute external and internal discovery to identify threats:
External discovery:
- storing and classifying data about your apps and APIs.
- scanning for exposed web servers.
- discovering open ports on internet-facing IP addresses.
Internal discovery:
- Evaluating runtime configurations, identifying issues, and prioritizing.
- API accessibility & functionality visualization
- App-API visualization and usage
- Agentless AWS & Azure API workload monitoring
- App traffic volume & pattern analysis
Real-life example:
Tools like Ghost integrate into CI/CD pipelines to provide continuous visibility and risk analysis during application development.7
5. Application test creation and adaptation
AI agents generate tests automatically depending on user interactions with the application. As testers or developers use the tool to capture test cases, the AI monitors and creates test scripts.
If the application’s UI changes (for example, an element’s ID changes or the layout changes), the AI agent may identify these changes and customize the test scripts to avoid failure.
6. Dynamic application test execution
Agentic AI continuously executes tests in varied contexts (e.g., across multiple browsers and devices) without human interaction. The AI agents can schedule tests and analyze application behavior autonomously to ensure complete testing coverage.
They can also dynamically customize test parameters, such as copying different user data inputs or changing network conditions, to allow for a more thorough application analysis.
7. Autonomous reporting and predictive suggestions
AI Agents can examine application testing data autonomously, finding failure patterns and determining core causes.
For example, if numerous tests fail due to the same problem, the AI Agent will combine the findings and highlight the underlying issue to the development team.
Based on previous test data, the AI agents can predict potential future failures and recommend application testing methodologies to address these issues.
8. Autonomous remediation
Agentic AI automates the remediation process, for example, if the AI agent detects that certain tests are redundant or do not adequately cover specific risks, it can optimize the test suite by deleting unrelated tests and prioritizing those that focus on more relevant areas.
The AI agent can also detect when a test fails due to minor errors (such as a minor UI change) and “remediate” the test script to comply with the revised application, eliminating false positives and requiring less manual involvement.
9. Automated pentesting
Agentic AI automates the penetration testing process, including the identification of vulnerabilities, generation of attack plans, and execution. Some key practices of AI agents in pentesting initiatives include:
Real-time adversary simulation:
- Conducting simulations like network, application, and social engineering attacks.
- Executing penetration tests such as DAST (dynamic application security testing).
Reconnaissance:
- Scanning the internet, including the deep, dark, and surface web, to detect exposed IT assets (e.g., open ports, misconfigured cloud buckets).
- Integrating OSINT (open-source intelligence) and threat intelligence to map attack surfaces.
Real-life example:
Tools like FireCompass provide semantic testing for APIs, creating tailored attack scenarios that automate pentesting efforts.8
Agentic AI and application security (AppSec) explained
Application security entails protecting apps during their full lifecycle, which covers design, development, deployment, and continuous maintenance.
The problem:
As hosted apps became increasingly important as key revenue drivers for public-scale enterprises, so did their security—this created recent trends such as:
- Wide usage of Cloud, SaaS applications has moved security earlier in the SDLC to minimize risks before they reach production.
- With the increase in cloud-native programming, more migration to third-party platforms such as AWS has occurred, thus the attack surface for apps becomes more exposed to vulnerabilities.
As a result of increasing attack surface and potential, attackers developed new and inventive methods of compromising apps.
How agentic AI helps:
Agentic AI can help enhance AppSec by integrating and automating various stages of the application lifecycle to enhance security, including monitoring your CI/CD pipelines or automating your pent testing.
Benefits of agentic AI for cybersecurity
By implementing an agentic AI strategy, SOCs may gain tremendous benefits in terms of operational efficiency and team morale. Here are four major benefits of this technology:
1. Improved security orchestration automation and response (SOAR): Streamlines security processes, automating workflows and orchestrating responses.
2. Reduced alert fatigue: By filtering out irrelevant alerts and automating responses, AI reduces analyst workload and helps focus on critical issues.
3. Adaptability to evolving threats: Learns from new data and adapts to changing attack methods, staying ahead of emerging threats.
4. Reducing mean time to response (MTTR): By minimizing the manual bottleneck of triage and investigation, Agentic AI accelerates remediation, reducing MTTR.
5. Enhancing analyst retention: Improves analyst retention by performing routine triage and investigation work, transforming the function of SOC analysts.
Challenges of agentic AI in cybersecurity
1. Lack of transparency and interpretability
- Opaque decision-making: AI-driven security operations and systems can be difficult to interpret, especially when they modify security policies or decisions on their own. Test engineers and developers may struggle to comprehend why certain actions were made or to confirm the AI’s decisions.
- Trust and reliability: Without explicit explanations, it might be difficult for teams to trust the AI’s recommendations or revisions, leading to resistance to implementing agentic AI solutions.
2. Data quality concerns
- Data reliance: AI agents need diverse data to learn how to perform actions effectively. Insufficient or biased data can result in false actions or incorrect forecasts.
- Edge cases in system configurations: If an organization’s IT infrastructure includes bespoke configurations or rare software combinations, an AI agent may misinterpret normal behaviors as anomalies or fail to detect genuine threats.
3. Maintaining reliability
- False positives and negatives: Agentic AI can incorrectly classify data related to SecOps or AppSec, resulting in false positives (reporting bugs when none exist) or false negatives (failing to detect actual issues). These errors may compromise trust in the system and require manual intervention to validate results.
- Adaptability problems: Although agentic AI is designed to adapt to changes, certain complex or unexpected changes in the application (for example, major UI redesigns or backend architecture changes) may still cause security operations to fail, necessitating human intervention to update the AI’s models.
4. Complexity of implementation
- Difficulty in securing API integration: AI agents frequently interface with external systems; therefore, protecting APIs is critical. API tokenization and validation are all measures that help to ensure a reliable interaction.
- Training and deployment: Agentic AI models should be trained on large datasets and diverse scenarios to be effective, which can be resource-intensive and time-consuming.
5. Human oversight requirements
- Continuous monitoring: While agentic AI aims to reduce human involvement, it still requires monitoring and maintenance to ensure that it functions properly. Security teams need to verify the AI’s results, adjust models as needed, and get involved when the AI encounters complex or unexpected scenarios.
- Highly skilled personnel requirements: Managing agentic AI necessitates expertise in AI, machine learning, or application security. Organizations may have difficulty finding or training staff with the required skills.
What is agentic AI: The path from LLMs
Agentic AI, also known as autonomous AI or self-directed AI, refers to artificial intelligence systems that can operate autonomously to achieve specific goals.
Unlike traditional AI systems, which require human input and guidance, agentic AI systems can make decisions, conduct actions, and learn from their experiences without ongoing human interaction.
This is an important shift from the current most typical application of AI, which frequently involves LLMs and humans interacting with AI via prompts.
- LLMs specialize in processing and generating language or ideas based on user prompts. It uses techniques like
- prompt engineering to process writing instructions to guide AI models to produce specific responses.
- Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to improve the accuracy of generative AI models with facts fetched from external sources.
- AI agents, by contrast, are action-oriented systems. They autonomously perform tasks such as scanning networks to find unusual activity or managing workflows with minimal human oversight.
For more: Agentic AI: 5 steps from chatbots to secure enterprise AI agents.
Conclusion
Agentic AI has the potential to enhance cybersecurity operations by improving response times and alleviating the burden on security teams.
However, challenges such as a lack of transparency, data quality concerns, and false positives/negatives can increase the overall difficulty of deploying agentic AI solutions effectively.
Successful implementation of agentic AI in operations requires skilled personnel, ongoing monitoring and updates, effective false-positive validation processes, and attention to other key challenges.
Further reading
External Links
- 1. AI-Powered Penetration Testing (Pen Testing) Automation. Aptori
- 2. AI-Driven SOC Transformation with Cloudera: Enhancing Security Operations with Agentic AI | Blog | Cloudera.
- 3. ”Transforming Security Operations“. Dropzone AI. Retrieved on December 2024
- 4. University of Kansas Health System Grows Visibility by 98% with GreyMatter - ReliaQuest.
- 5. APi Group Increases Visibility by 47% - ReliaQuest.
- 6. AI SOC Analysts: LLMs find a home in the security org - Scale Venture Partners. Scale Venture Partners
- 7. Ghost Security- Platform.
- 8. FireCompass Agentic AI Platform. FireCompass


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.