Cyber attacks are projected to cost nearly $10 trillion globally in 20241 and data breaches average $5 million each.2 These highlight the importance of the compliance to industry-specific security policies to strengthen cyber security. Firewall compliance with industry standards like ISO 27001, GDPR, NIST, SOX, and NERC CIP ensures that organizations meet regulatory requirements and mitigate the risk of cyber incidents.
Explore the concept of firewall compliance, key industry standards such as ISO 27001 & HIPAA, use cases, and implications for different industries.
Firewall security standards (Industry specific)
Firewall management software help organizations automatically audit compliance with industry security standards to secure firewall configuration. See the top 12 firewall management tools and the top security standards for which these software generate compliance reports:
Table 1. Compliance of security standards of top 10 firewall audit softwares
| Vendor | GDPR | HIPAA | ISO 27001 | NERC CIP | NIST | SOX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tufin Orchestration Suite | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| AWS Firewall Manager | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
| SolarWinds Network Configuration | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
| Qualys VMDR | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Cisco Defense Orchestrator | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Network Perception View | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Palo Alto Network Panorama | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| AlgoSec Firewall Analyzer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| FireMon Security Manager | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Titania Nipper | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
Inclusion criteria:
- All listed vendors have at least one user review in B2B review platforms.
- All listed vendors have at least 200 employees.
- All listed vendors provide firewall audit and compliance products, alongside other network security solutions.
- All listed vendors provide automated firewall audits for the compliance of PCI DSS.
Ranking: Products are ranked based on their total number of employees except for the sponsored products ranked at the top.

Key security standards
General
1. National institute of standards and technology (NIST)
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) enhances cybersecurity by developing trusted cryptographic tools and resources, validated strong algorithms, and forward-thinking standards to protect data, including against future quantum computing threats.
Widely recognized in the cybersecurity industry, NIST’s frameworks, such as the cybersecurity framework (CSF) and the risk management framework (RMF), provide organizations with comprehensive strategies for managing cybersecurity and privacy risks within their operational contexts.3
2. International organization for standardization (ISO 27001)
ISO 27001 is the globally recognized standard for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an information security management system (ISMS) in organizations of any size or sector.
Compliance with ISO/IEC 27001 ensures that an organization has a systematic approach to managing risks related to data security, incorporating best practices and principles for risk management, cyber resilience, and operational excellence.4
3. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR requires organizations to conduct thorough data audits, justify their data processing activities legally, and ensure transparency by providing clear information in privacy policies.
It also mandates robust data security measures, including encryption and awareness training, to protect personal data throughout its lifecycle and requires organizations to appoint a Data Protection Officer if necessary to ensure accountability and compliance.5
Firewalls play crucial role in the GDPR compliance.
Financial services
4. Payment card industry – data security standards (PCI-DSS)
Compliance with PCI-DSS is paramount for businesses handling payment card data. PCI-DSS outlines requirements for securing cardholder data, including firewall configurations, access control, encryption, and monitoring. Firewall compliance plays a vital role in protecting cardholder data by enforcing strict firewall rules, conducting firewall audits, and maintaining secure network segmentation.
5. Payment services directive 2 (PSD2)
PSD2 is a European Union directive that regulates payment services and electronic payment transactions. It mandates strong customer authentication and security measures for online payments and is primarily applicable in the European financial sector.
6. Financial industry regulatory authority (FINRA)
FINRA is a regulatory organization in the United States that oversees securities firms and brokers. It sets standards and regulations related to securities trading, investor protection, and market integrity.
7. Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX)
SOX compliance focuses on financial reporting integrity and requires controls over financial data. Firewall compliance under SOX involves securing access to financial systems, protecting sensitive financial information, and implementing robust firewall security controls to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
Defense industry services
8. Defense office of regulatory affairs (DORA)
DORA regulations apply to defense contractors and government agencies, emphasizing secure network configurations, access controls, and firewall management. Compliance with DORA standards ensures robust firewall security, protects sensitive data, and maintains compliance with government security policies.
9. Defense information systems agency security technical implementation guides (DISA STIG)
DISA STIGs provide configuration guidelines and security controls for network devices, including firewalls, to meet military cybersecurity requirements. Adhering to DISA STIGs strengthens firewall compliance, enhances network security posture, and aligns with military-grade security standards.
Other industries
10. North American electric reliability corporation critical infrastructure protection (NERC CIP)
NERC CIP standards focus on securing critical infrastructure in the energy sector. Firewall compliance in NERC CIP involves protecting control systems, implementing secure remote access through virtual private networks (VPNs), and conducting firewall audits to mitigate risks and ensure operational resilience.
11. Health insurance portability and accountability act (HIPAA)
HIPAA sets standards for protecting health information and requires secure network environments. Firewall compliance under HIPAA involves securing electronic protected health information (ePHI), implementing firewall rules to control access, and conducting firewall audits to ensure data security and regulatory compliance.
12. Federal information security management act (FISMA)
FISMA mandates cybersecurity requirements for federal agencies and contractors, including firewall compliance, risk assessments, and security controls. Compliance with FISMA standards is essential for government entities to protect sensitive data, comply with regulatory mandates, and maintain a strong security posture.
What is firewall compliance?
It refers to the adherence of firewall configurations, rules, policies, and security practices to industry standards, regulatory requirements, and best practices. It involves ensuring that firewalls are effectively deployed, configured, monitored, and maintained to protect networks from unauthorized access, malicious activities, and network security threats.
Firewall audit is one of the cornerstone strategies for fortifying network, company, and application security. Firewall audit software are tools specifically designed to assess and evaluate the configurations, policies, rules, and overall security posture of firewalls. Being able to configure a wide variety of hardware and software based firewalls with a single interface facilitates audits and firewall management.
Key components of firewall compliance
Firewall rules and standards are two main components of firewall compliance. Together, firewall rules and standards contribute to firewall compliance by ensuring that firewalls are configured, managed, and audited in a secure, compliant, and effective manner to protect networks, data, and resources from unauthorized access, threats, and vulnerabilities.
Firewall rules
Firewall rules, also known as rule sets or rule bases, are specific configurations within a firewall that dictate how the firewall should handle incoming and outgoing network traffic. Firewall rules determine whether traffic should be allowed, blocked, or redirected based on the defined criteria, effectively controlling network communication and access.
Main firewall rules include:
1. Deny all
This rule instructs the firewall to block all incoming and outgoing traffic by default unless specifically allowed by other rules. It follows the principle of “block everything unless explicitly permitted,” providing a strong first line of defense against unauthorized access and potential threats.
Example rule:
Source: Any
Destination: Any
Action: Deny
2. Least privilege
It, based on the principle of least privilege, restricts network access to the minimum level necessary for users or systems to perform their legitimate tasks. In firewall configuration, this rule limits access to specific services, ports, or resources based on the principle of granting only the essential permissions required for operation.
Example rule:
Source: 192.168.1.10 (IP address of User X)
Destination: 192.168.2.20 (IP address of the database server)
Protocol: TCP
Port: 3306 (MySQL database port)
Action: Allow
3. Explicit allow
This rule permits specific traffic or connections based on predefined criteria. Unlike the deny all rule, the explicit allow/deny rule selectively allows desired traffic, such as access to specific services, applications, or IP addresses. This rule ensures that only authorized traffic is allowed while blocking all other traffic not explicitly stated.
Example rule:
Source: 0.0.0.0/0 (All IP addresses)
Destination: 172.134.1.100 (IP address of the web server)
Protocol: TCP
Port: 443 (HTTPS)
Action: Allow
4. Explicit deny
It emphasizes a strict security posture by explicitly denying all traffic that is not expressly permitted. This rule applies to both incoming and outgoing traffic, ensuring that only authorized communications are allowed while blocking all other attempts to access network resources.
Example rule:
Ingress Traffic Example:
Source: Internet Blacklist IPs
Destination: Company Network
Action: Deny
Egress Traffic Example:
Source: Company Network
Destination: Internet Blacklist IPs
Action: Deny
5. Stateful inspection
It is a sophisticated firewall feature that examines the context and state of network connections to make intelligent decisions about traffic flow. Unlike simple packet filtering, stateful inspection evaluates the entire communication session, including the source, destination, port numbers, and packet sequence, to determine if the traffic is legitimate and conforms to expected behavior.
Best practices for firewall auditing and compliance
Best practices for firewall policies and rules include:
1. Regular firewall audits
Conduct periodic firewall audits using comprehensive open source or closed sourced audit tools to assess firewall configurations, firewall rule base, access controls, and security policies.
2. Security posture assessment
Perform risk assessments and vulnerability scans to evaluate the organization’s security posture, identify potential threats, and prioritize remediation efforts.
3. Compliance checks
Ensure adherence to firewall security standards, regulatory requirements, and internal security policies through rigorous compliance checks and audits. Firewall audit software with automatic compliance reporting streamlines compliance checks by generating comprehensive reports, which reduces the workload on IT teams and minimizes the risk of non-compliance.
Figure 1. Firewall compliance reporting example from Tufin
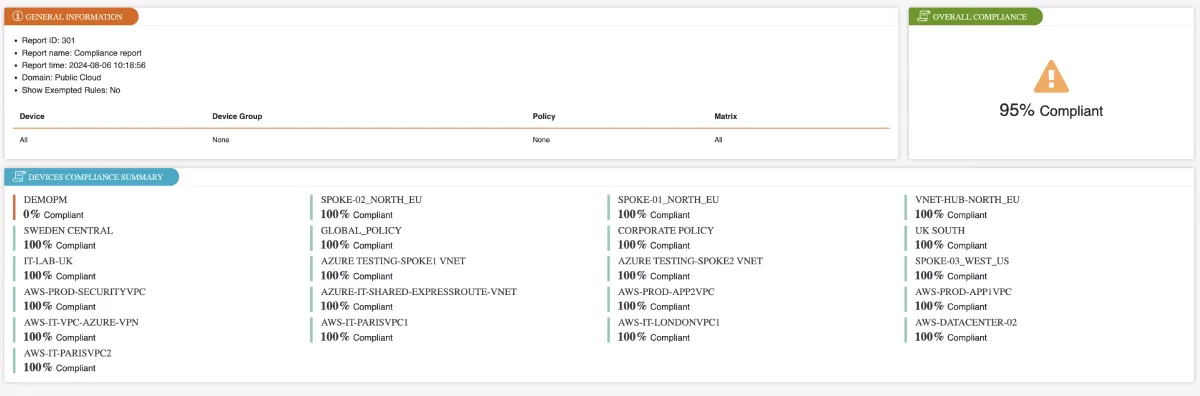
4. Log monitoring and analysis
Monitor firewall logs and analyze network traffic patterns to detect security incidents, anomalies, and unauthorized activities.
5. Policy enforcement
Enforce strict access controls, security policies, and best practices to mitigate risks associated with inbound and outbound traffic, internal network access, and data breaches.
The crucial role of firewall in audits & compliance
Firewall audits play a pivotal role in assessing the effectiveness of firewall configurations, identifying vulnerabilities, and ensuring compliance with security standards and industry regulations. By conducting regular firewall audits, organizations can gain insights into their security posture, detect anomalies in network traffic, and mitigate risks associated with outdated rules, misconfigurations, or unauthorized access attempts.
If you are looking for a firewall audit solution, you may find the firewall audit software article useful.
FAQs
What is the difference between firewall rules and firewall standards?
Firewall rules refer to the specific configurations within a firewall that dictate how traffic should be managed, controlled, and allowed or blocked. However, firewall standards encompass guidelines, requirements, and best practices that define the overall framework for configuring, managing, auditing, and ensuring compliance with firewalls.
Are there any industry-specific firewall standards?
Yes, there are industry-specific firewall standards such as PCI-DSS for payment card data security, PSD2 for financial services, FINRA for financial institutions, SOX for financial reporting, NERC CIP for energy sector critical infrastructure, HIPAA for healthcare data, FISMA for federal agencies, and DORA and DISA STIG for defense systems.



Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.