Data breaches led to the exposure of 6M records in the first quarter of 2023, according to network security stats. Teams using NGFWs, AI-driven security, and automation are saving ~$2M more than those use the traditional tools.
See open source NGFW as a cost-effective network security solution for comprehensive security:
Top 4 open source NGFW comparison
Table 1. Key features
| Tool Name | Packet Filtering | NAT Mapping | DPI | IDPS | Multi WAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zenarmor | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Untangle | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
| PfSense | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Smoothwall | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
For details of key features of open source NGFW and their importance, check the ngfw features.
Table 2. Market presence
| Tool | Github Stars | Rating* | Employee Size** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PfSense | 4.6K | 4.6 out of 289 reviews | 4 | |
| Untangle | 20 | 4.7 out of 44 reviews | 18 | |
| Smoothwall | 0 | 4.6 out of 3 reviews | 153 | |
| Zenarmor | N/A | 5 out of 1 review | 13 |
*Based on data from leading B2B review platforms
**Based on data from LinkedIn
Inclusion criteria:
- Only vendors with at least one review in review platforms were considered.
- Each open source NGFW given in the table provides URL filtering capability as a core feature of next generation firewalls. It allows organizations to control access to specific websites and content. An open source NG firewall equipped with URL filtering capabilities empowers administrators to restrict access to potentially harmful or inappropriate websites, bolstering web and email security within the network.
Ranking: The companies are ordered based on the total count of reviews.
Top 4 NGFWs
1. PfSense
Figure 1. A use case diagram of pfSense features
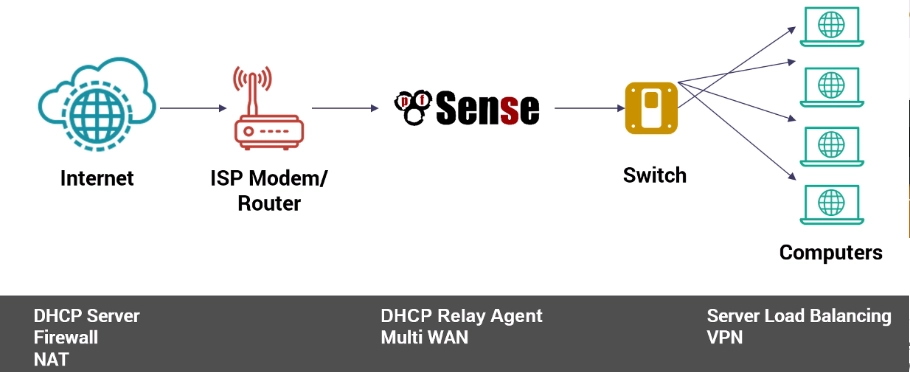
Source: Network Security with pfSense software1
PfSense software offers a complete package with features like packet filtering, network address translation (NAT) mapping, DPI, IDPS, and multi WAN support. Its packet filtering allows for granular control over network traffic, while NAT mapping, as a virtual private network feature, secures communication by masking IP addresses.
DPI enhances threat detection by analyzing inbound and outbound traffic, and IDPS monitors and responds to suspicious activities. Multi WAN support adds redundancy and load balancing for improved network reliability and performance.
2. Untangle
Figure 2. Shows Untangle network security framework
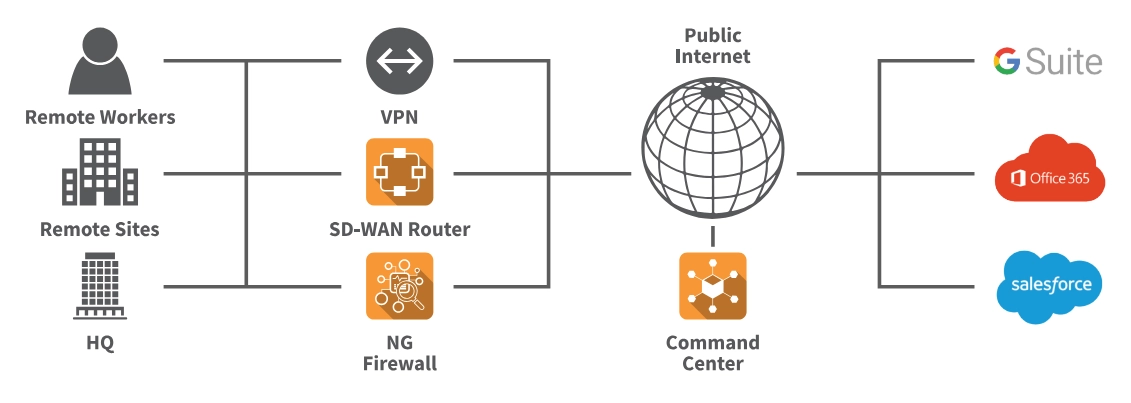
Source: Untangle2
As a Linux based firewall, Untangle focuses on intrusion prevention system, providing robust intrusion detection and prevention system (IDPS) capabilities.
As another key feature, its multi WAN support, representing the ability of connecting to multiple wide area networks (WAN) or internet service providers (ISPs), adds resilience to network configurations, making it a viable option for organizations prioritizing intrusion prevention measures and network reliability. Untangle next generation firewall also offers content filtering.
3. Smoothwall
Smoothwall emphasizes key features of NAT mapping, IDPS, and multi WAN support. Its NAT mapping feature facilitates the translation of private IP addresses to public IP addresses, enabling secure communication between internal and external network devices.
Multi WAN support provides redundancy and load balancing across multiple WAN connections, ensuring continuous network availability and optimizing traffic distribution. Smoothwall’s IDPS feature provides real-time monitoring and analysis of network traffic to detect and respond to suspicious activities or potential security breaches.
4. Zenarmor
Zenarmor is a plugin next generation firewall extension of OPNsense. While lacking certain features like packet filtering, NAT mapping, intrusion detection and prevention system (IDPS), and multi WAN, Untangle’s primary strength lies in its deep packet inspection (DPI) capabilities, enabling granular analysis of network traffic for enhanced intrusion detection systems.
Its proactive approach to threat detection enhances network security by identifying and mitigating emerging threats effectively.
Figure 3. Shows how incoming packets are processed by Zenarmor engine and OPNsense L4 firewall
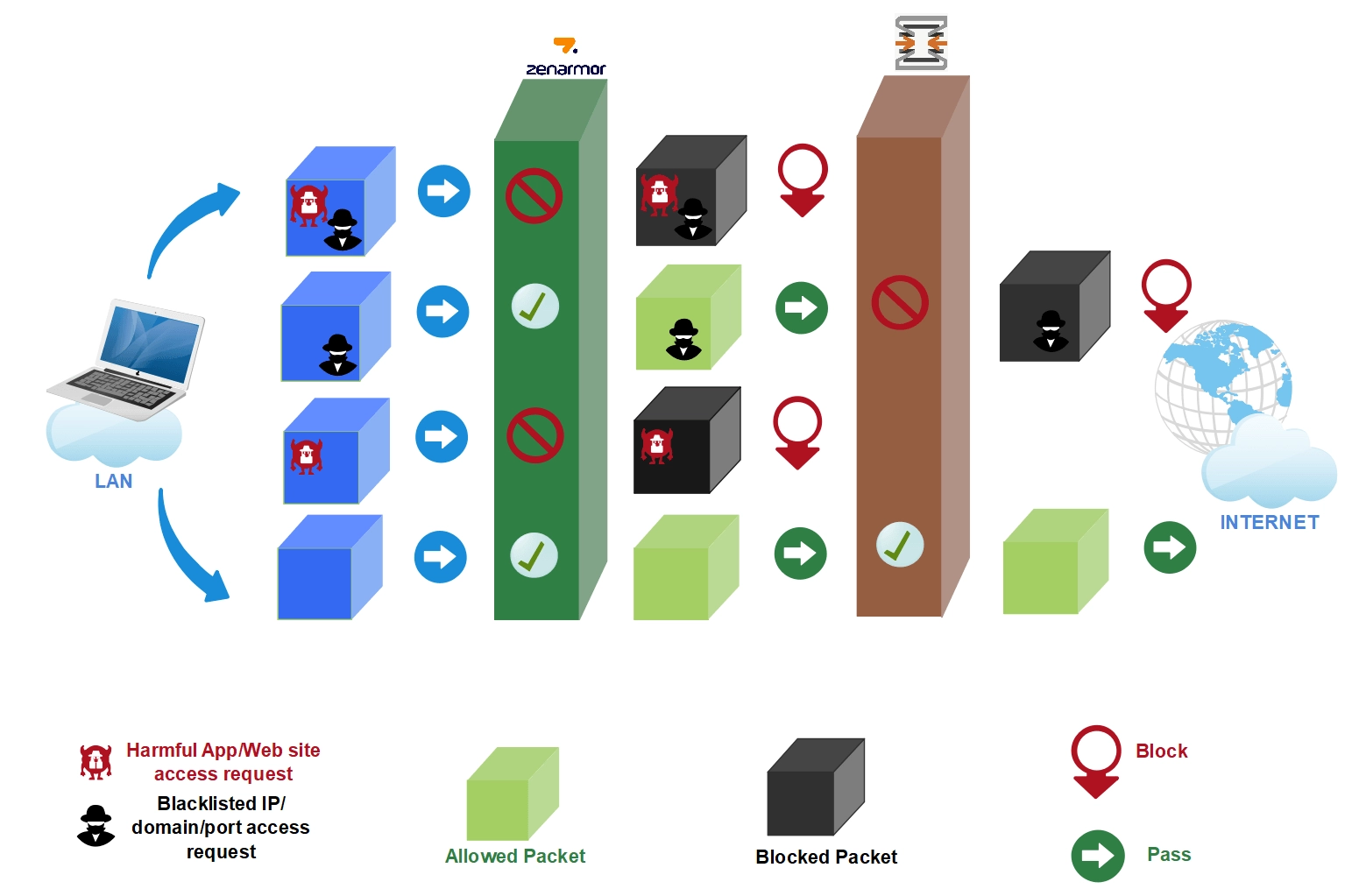
Source: Zenarmor3
Zenarmor is also a next-generation plugin for OPNsense firewalls, which is an open source firewall. It offers advanced key features like application control, network analytics, TLS inspection, web filtering, user-based filtering, centralized management, traffic shaping, and encrypted threats prevention, making it a robust choice for L4 firewall users seeking enhanced security capabilities.
Key features of open source NGFWs
For a detailed analysis of next generation firewalls’ key features, businesses may explore the Top 8 Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW) Features article.
1. Packet filtering:
Figure 4. Shows how packet filtering works
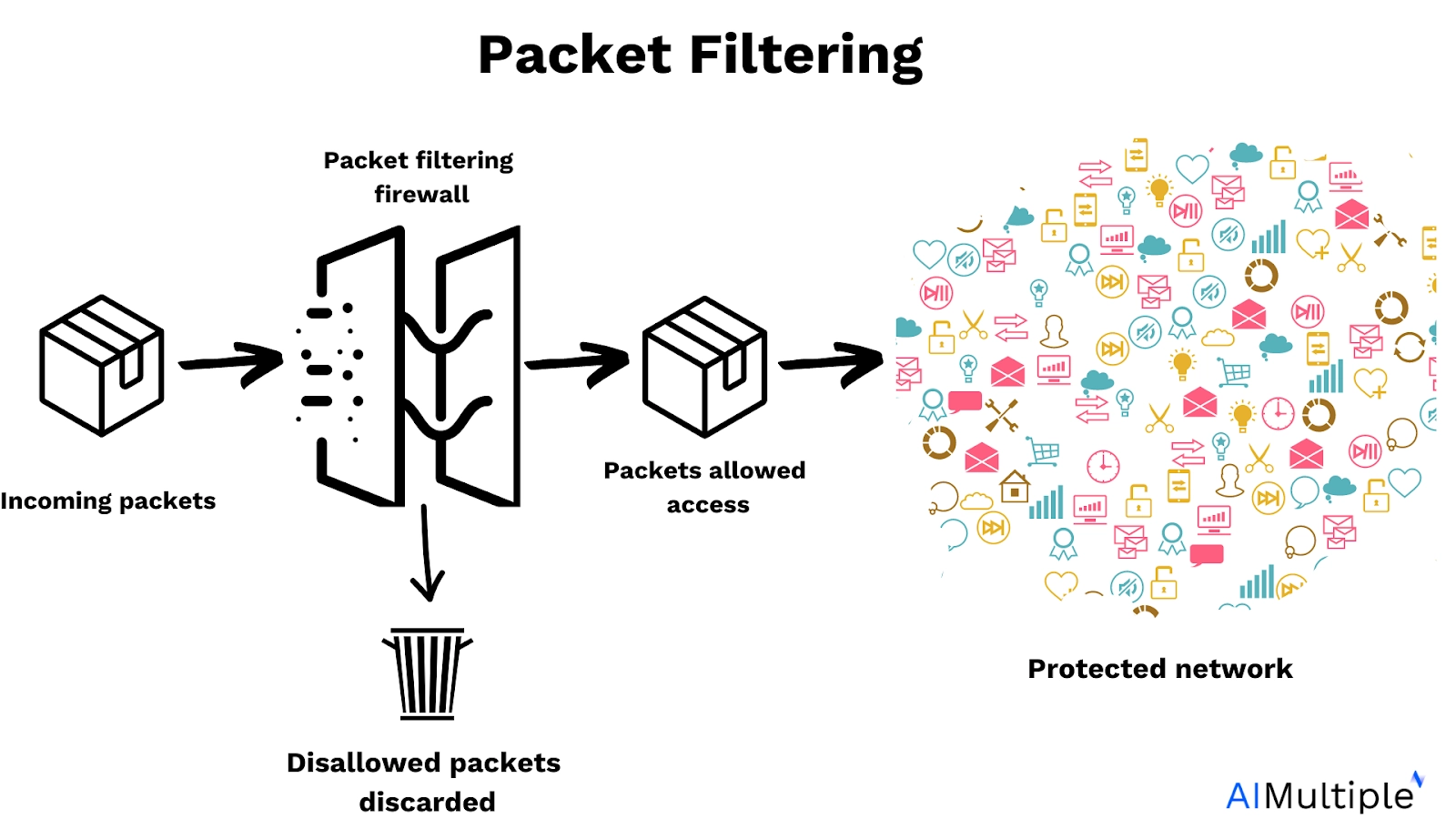
Packet filtering is one of the simplest ways to control network traffic. Firewalls check each packet and decide whether to let it through or block it, using basic rules. It’s a first step in protecting a network, but it doesn’t look at the bigger picture or deeper threats. By analyzing packet headers, including IP addresses, ports, and protocols, open source NGFWs ensure that only authorized traffic traverses the network, safeguarding against potential malware attacks and unauthorized access.
2. Network address translation (NAT):
Network address translation (NAT) plays a pivotal role in securing private networks by mapping local private IP addresses to public IP addresses. This process enables multiple devices within a network to access the internet through a single public IP address, enhancing network security and simplifying network management.
3. Deep packet inspection (DPI):
Deep packet inspection (DPI) represents a sophisticated approach to network traffic analysis, enabling NGFWs to detect, identify, and categorize data packets at a granular level. DPI equipped NGFWs enhance intrusion detection and application awareness by examining data payloads and application layer information, providing a comprehensive defense against cyber threats.
4. Intrusion detection and prevention system (IDPS):
NGFWs integrated with intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) offer real-time threat detection and response capabilities. These systems leverage advanced algorithms to identify suspicious network behavior and thwart potential cyber attacks, safeguarding network integrity and data confidentiality.
5. Multi WAN:
Multiple wide area network (WAN) connection is a key feature of open source NGFWs, enabling organizations to establish redundant and load-balanced connections across multiple Wide area networks (WANs). This feature enhances network reliability, resilience, and performance by ensuring uninterrupted connectivity and optimizing traffic distribution.
To learn more about NGFWs, check out NGFW case studies with use cases and NGFW features.
Businesses may also prefer to use firewall audit software and firewall management tools as a network security system.
FAQs
What is a next-generation firewall (NGFW)?
A next-generation firewall (NGFW) is a sophisticated network security platform that combines traditional firewall functionalities with advanced filtering capabilities. NGFWs are designed to detect and block complex cyber attacks by applying security policies at multiple levels, including application, port, and protocol layers.
What is the difference between open-source firewalls vs commercial firewalls?
Open source firewalls give you freedom to customize and save money. But they often need more time and skill to manage. For teams that need faster setup, built-in features, and expert support, commercial firewalls may be the better fit. The choice between open-source and commercial firewalls depends on factors such as budget, technical expertise, security requirements, and support preferences. You may also explore open source firewall audit tools, open source firewall management services, open-source security automation articles for further cost effective network security solutions.
What is the difference between traditional firewalls and NGFWs?
Traditional firewalls focus on port/protocol inspection at information transport layers (Layers 2 and 4), which are suited for static systems but are less effective against dynamic emerging threats. Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) don’t just block traffic—they study how apps behave and use real-time threat data to catch advanced attacks as they happen. This makes them smarter at spotting threats traditional tools might miss.
Further Reading
- 3-Step Guide to Effective Firewall Audit
- Top 12 Firewall Audit Software & Integration-Based Comparison
External Links
- 1. pfSense. pfSense Features. Accessed: 14/May/2024.
- 2. Untangle. Untangle NG Firewall Simply Powerful Network Security. Accessed: 14/May/2024.
- 3. How does the engine work? What is the relationship between the Zenarmor engine and the OPNsense/L4 firewalls? - zenarmor.com. Zenarmor


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.