No-code AI simplifies access to artificial intelligence by enabling non-technical users to build and deploy AI models without programming skills. It accelerates the development of AI solutions, reduces costs, and allows businesses and individuals to customize applications easily.
Ideal for small businesses, entrepreneurs, and professionals in fields like marketing, education, or healthcare, no-code AI tools help simplify testing, integration, and iterative improvements.
Explore no-code AI’s transformative potential, its key benefits, and how it differs from AutoML.
What is no-code AI?
No-code AI, also known as codeless AI, is a rapidly growing category within the artificial intelligence landscape that seeks to make AI accessible to a broader audience, including those without technical expertise. This approach leverages no-code development platforms, which feature intuitive, visual, and often drag-and-drop interfaces, allowing users to deploy AI and machine learning models without writing any code.
These platforms simplify the traditionally complex processes of AI development and implementation, empowering non-technical users to classify and analyze data, and build accurate predictive models in a fraction of the time it would take with traditional coding methods.
No-code AI tools are diverse, ranging from dedicated no-code AI solutions to automation platforms, such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA) software, which integrate AI functionalities into their no-code user interfaces.
By lowering the technical barriers, no-code AI facilitates the rapid development and deployment of AI-powered applications, making it an invaluable tool for small businesses, startups, educators, and professionals in various industries without the overhead of a specialized technical team.
No-code AI reduces the time to build AI models to minutes, enabling companies to easily adopt machine learning models in their processes.
Despite rising interest, no-code AI adoption lags behind other AI trends, such as learning machine learning or autoML. No-code AI solutions have not yet overpowered data scientists.
Increasing the maturity and flexibility of existing solutions and widespread integrations will drive more adoption. Therefore, businesses that can capitalize on this emerging market before competitors can stay ahead.
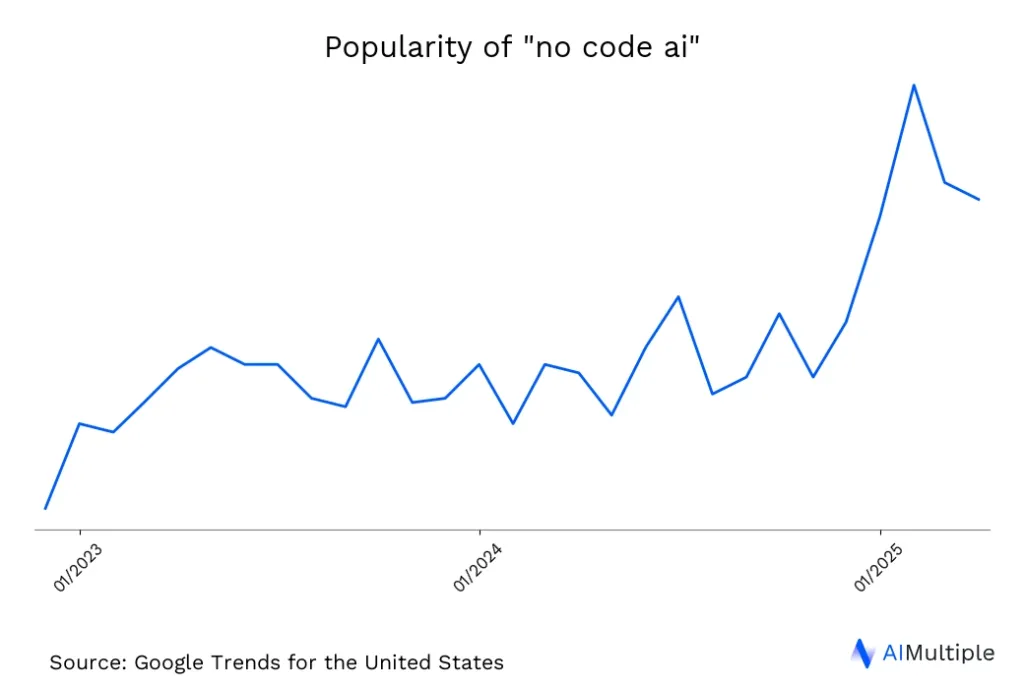
Figure 1: Online interest in no code AI.
No-code AI across industries
Finance: Financial institutions can use no-code AI tools for predictive analytics, sentiment analysis, fraud detection, and customer data analysis. These tools help create accurate predictive models and perform tasks like analyzing historical data, building linear regression models, or integrating AI for risk assessment without writing code.
Healthcare: No-code AI solutions support healthcare providers to analyze structured and unstructured data for patient diagnostics, image classification (e.g., X-rays or MRIs), and predictive analytics. This no-code approach accelerates AI adoption in medical research and operational efficiencies.
For example, AI healthcare tools enable providers to identify optimal treatments by analyzing patient data, such as genetics, lifestyle, and medical history, to develop tailored care plans. This approach improves treatment efficacy, minimizes side effects, and reduces costs by avoiding unnecessary procedures.
Retail and eCommerce: Retailers and eCommerce businesses can use no-code AI for customer segmentation, sentiment analysis from text data, predictive models for sales forecasting, and personalized marketing through generative AI tools.
For example, website personalization with AI and machine learning allows customizing the online shopping experience based on customer behavior and preferences, such as purchase history and browsing patterns. It offers personalized product recommendations and marketing messages, enhancing customer relationships and loyalty.
Another example of using no-code AI in retail is self-checkout systems. Self-checkout systems helps simplify transactions by enabling customers to complete purchases independently. These systems help automate tasks such as item scanning and payment processing for a smooth checkout experience.
Manufacturing: No-code AI platforms enable manufacturing companies to perform tasks like object detection, anomaly detection, and predictive maintenance using computer vision and automated machine learning. These tools can also analyze business data and optimize processes without needing data science expertise.
For example, no-code AI tools enable manufacturers to optimize processes for sustainable production. Process mining tools help identify and eliminate bottlenecks by analyzing performance across regions, down to individual steps, including duration, cost, and personnel.
These insights allow manufacturers to streamline workflows and build consistent systems, such as ensuring timely and accurate deliveries despite operating multiple factories in different regions.
Marketing and advertising: Marketers can analyze data to create targeted campaigns using generative AI models for content creation, image generation, and natural language processing with no-code tools. These tools allow them to handle customer data efficiently and deploy AI solutions with just a few clicks.
Education: Educational institutions can leverage no-code AI to develop AI assistants, analyze data for student performance, and integrate AI into learning platforms. Check out generative AI and conversational AI use cases in education to learn more.
For example, ChatGPT helps teachers enhance their workflow by offering support in grammar checks, writing evaluation, and grading. Teachers can use ChatGPT for proofreading lesson plans, providing feedback on student writing, and teaching grammar and writing skills.
Additionally, ChatGPT assists in grading by analyzing content, structure, and coherence in student work, offering automated feedback and helping create grading rubrics aligned with learning objectives.
Technology and startups: Startups can benefit from no-code AI tools to prototype AI models quickly, enabling users to test generative AI models with computer vision and end-to-end processes.
For example, a tech startup can use no-code AI tools to build a smart chatbot for automating customer support. They can train the chatbot to handle FAQs, troubleshoot common issues, and escalate complex queries to human agents. Using no-code platforms, the team can integrate the chatbot with their website and CRM systems without writing code.
Logistics and supply chain: Businesses in logistics can use no-code tools for demand forecasting, route optimization, and inventory management by analyzing structured and unstructured data.
For example, AI-powered bots with computer vision can automate repetitive inventory tasks, such as real-time scanning. These bots can streamline inventory management in warehouses and retail stores, to improve efficiency and accuracy.
Examples of no-code AI
| Tool | Type | Use Cases | Business Types Benefited |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bardeen | Automation & workflows | Browser automation, AI agents for repetitive tasks. | Sales, execs, project managers |
| ChatGPT Custom GPTs | LLM-based | Custom AI assistants. | Content creation, education, internal support |
| Flowise | LLM-based | Build LLM apps, chatbots, agents, RAG pipelines. | Startups, AI developers, consultancies |
| Levity | No-code data & predictive AI | Document classification and image recognition. | Operations, HR, customer support |
| MagickML | LLM-based | Chaining LLMs and APIs for workflows and agents. | Operations, customer service, prototyping |
| Make.com | Automation & workflows | Natural language-based workflow automation. | IT, marketing, e-commerce |
| MonkeyLearn | No-code AI analytics | Text analysis. | Marketing, support, product teams |
| Obviously.AI | No-code data & predictive AI | Predictive analytics from datasets. | Sales, marketing, finance |
| Peltarion | No-code data & predictive AI | Deep learning for NLP and image recognition. | Healthcare, finance, enterprise AI |
| Zapier AI | Automation & workflows | Workflow automation. | Operations, admin, SMBs |
To make no-code AI actionable, here are some leading platforms and tools that non-technical users can explore today across different AI capabilities, including language models, vision, automation, and analytics:
LLM-based platforms
- ChatGPT Custom GPTs (OpenAI): Create tailored AI assistants with specific behavior, tone, or knowledge. Set up using natural language instructions and file uploads.
- Flowise: A drag-and-drop visual builder for creating LLM-based apps (e.g., chatbots, agents, RAG pipelines) using LangChain under the hood. Ideal for prototyping.
- MagickML: A visual no-code interface for chaining LLMs and APIs to build conversational AI, workflows, and tools. Designed for non-programmers with agent support.
No-code data & predictive AI tools
- Levity: Trains models for document classification, sentiment analysis, or image recognition. Integrates with Zapier and Slack.
- Obviously.AI: Upload your dataset and generate predictions (e.g., customer churn, sales forecasting).
- Peltarion: Offers visual model building for deep learning tasks like NLP or image recognition. Tailored for enterprise AI use cases.
No-code AI analytics & dashboards
- MonkeyLearn: Offers text analysis tools (e.g., keyword extraction, sentiment detection) with an intuitive dashboard and integrations for spreadsheets and apps.
Automation & workflows
- Bardeen: A browser automation platform that combines AI agents and no-code automation for repetitive tasks like reporting, email sorting, and scheduling.
- Make.com (formerly Integromat): Offers LLM modules to automate workflows like generating emails, creating documents, or routing requests based on natural language inputs.
- Zapier AI: Lets you build AI-enhanced automations with tools like OpenAI, allowing logic-based workflows (e.g., summarizing emails, drafting replies, classifying messages).
Key benefits of no-code AI solutions
No-code AI solutions reduce entry barriers for individuals and businesses to start experimenting with AI and machine learning. These solutions help businesses adopt AI models quickly and at a low cost, enabling their domain experts to benefit from the latest technology.
It combines business experience with AI
Data science is still an emerging field and most data scientists have less business experience than domain experts. According to a data science survey conducted by data science competition platform, Kaggle which is a crowdsourcing solution for AI projects, the most common age of respondents is 24 and the median is 30.
With these no-code solutions, business users can leverage their domain-specific experience and quickly build AI solutions.
It’s fast and low cost
Building custom AI solutions requires writing code, cleaning data, categorizing, structuring data, training, and debugging the model. These take even longer for those who are not familiar with data science. Studies claim that low code/no-code solutions have the potential to reduce the development time up by 90%.
One of the most obvious benefits of automation and no code technologies is savings. Companies need fewer data scientists when they can have their business users build machine learning models.
It helps data scientists focus
For businesses that already have a data science team, requests of other employees shift the data science team’s focus to easy-to-solve tasks. No-code solutions minimize these distracting requests since they enable business users to tackle such requests themselves.
Learn more about the benefits of no code technology.
What are the differences between AutoML and no code AI?
AutoML and no-code AI are both tools designed to simplify the development of AI and machine learning (ML) models, but they serve different user groups and purposes, with key distinctions:
Target audience
AutoML: Primarily aimed at data scientists and technical users who have expertise in data science and machine learning.
No-Code AI: Designed for non-technical users, such as business analysts, educators, and marketers, who need to build ML models without programming knowledge.
Complexity vs. simplicity
AutoML: Offers transparency and control over the entire ML pipeline, including data preprocessing, feature engineering, model selection, and hyper-parameter tuning. This complexity allows data scientists to customize and refine models for specific needs.
No-Code AI: Simplifies the process by abstracting the details of the ML pipeline. Users interact with easy-to-use visual interfaces for quick model development without technical complexity.
Flexibility vs. ease of use
AutoML: Provides greater flexibility for advanced customization and fine-tuning, making it suitable for complex projects requiring precise control.
No-Code AI: Prioritizes ease of use and accessibility, making it ideal for straightforward use cases but less customizable for advanced or nuanced requirements.
Best for
AutoML: Experienced users who want to manage repetitive tasks in ML development while retaining the ability to tweak specific aspects of the pipeline.
No-Code AI: Non-technical users who need to quickly develop AI solutions, such as predictive models or data analysis, without diving into the technical details.


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.