IT process automation tools can save time and effort, but 76% of IT leaders struggle with the complexity of the IT landscape, making it hard to choose the right tool.1
AIMultiple break downs IT process automation tools by shortlisting and comparing top tools:
| Tools* | Category | Rating** |
|---|---|---|
| ActiveBatch | WLA | 4.5 based on 350 reviews |
| RunMyJobs by Redwood | WLA | 4.7 based on 226 reviews |
| Stonebranch | WLA | 4.5 based on 93 reviews |
| Fortra's JAMS | WLA | 4.4 based on 217 reviews |
| AutoSys Workload Automation | WLA | 4.5 based on 49 reviews |
| BMC Control-M | WLA | 1.6 based on 162 reviews |
| Automate by Fortra | RPA | 4.6 based on 159 reviews |
| AutomationEdge | RPA | 4.3 based on 208 reviews |
| IBM RPA | RPA | 4.5 based on 607 reviews |
| UiPath RPA | RPA | 4.6 based on 9636 reviews |
| Kissflow | BPA | 4.3 based on 776 reviews |
| Laserfiche | BPA | 4.7 based on 1659 reviews |
| Nintex platform | BPA | 4.2 based on 1242 reviews |
| Salesforce Platform | BPA | 4.4 based on 2957 reviews |
* Tools are sorted in alphabetical order in their relevant categories with the exception of sponsors which are placed at the top and linked to their websites.
**Based on reviews on B2B review platforms. More information is available under each product’s section.
Selection criteria
We refined IT process automation tool comparison based on these three key factors:
- Workforce presence: 10+ employees listed on LinkedIn.
- Number of reviews: At least one review.
- IT process automation focus: We excluded vendors not mentioning IT process automation on their websites, as not all RPA or BPA tools suit IT automation tasks.
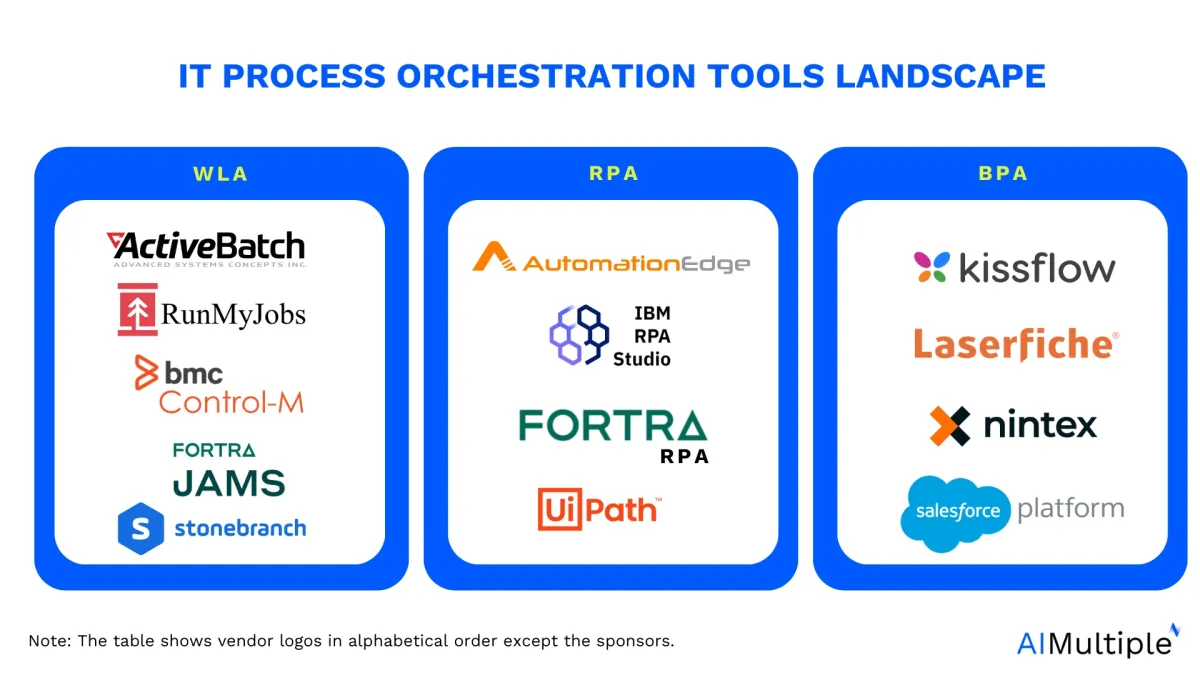
Shortlisted IT process automation tools
| Tools* | Pros** | Cons** |
|---|---|---|
| ActiveBatch | User-friendly Integration capabilities Automation and orchestration features | The learning curve Documentation issues |
| RunMyJobs by Redwood | User-friendly Easy documentation Workload balancing | Lack of public course & material to learn |
| Stonebranch | Ease of setup File transfer management | Manual update process of software |
| AutoSys Workload Automation | Easy orchestration Dependency triggering Easy development of JILs | Lack of dependency triggering Lack of configuration based JILs |
| BMC Control-M | Batch orchestration Easy administration Change management | Limitations for geographical user interface Requires technical expertise |
| Fortra's Jams | Automated alerting | Limited dashboard options for viewing status |
| Automate by Fortra | Easy script creating | Buggy browser updates |
| AutomationEdge | Strong customer support | Time-consuming email verification |
| IBM RPA | Data analysis Workflow automation | Complex interface |
| UiPath RPA | User-friendly Various features and functionalities Easy management of automation workflows | Learning curve Pricing |
| Kissflow | Ease of use and flexibility Efficient document management | Absence of a scripting engine for customization |
| Laserfiche | Automation capabilities User-friendly interface | Limited customization option No standardized Laserfiche course accessible |
| Nintex platform | User-friendly interface Interactive process maps Strong customer support & training | Lack of advanced analytics Limited workflow automation features & integration capabilities |
| Salesforce Platform | Email Automation Efficient reporting Enriched dashboards | Complicated reporting |
Statements in the pros and cons sections are based on top B2B review platforms.
1.) ActiveBatch
ActiveBatch is a comprehensive IT automation platform designed to centralize and automate IT processes. It offers a visual workflow designer, enabling organizations to automate complex workflows, schedule jobs, and manage tasks seamlessly.
Unique features
- Flow Control Job Steps that enable management of jobs within workflows with drag-and-drop functionalities
- REST API Adapter for easy integration with internal systems.
- Script support in any language of the operating system to run and modify scripts.
- Job step library providing platform-neutral, production-ready functions for efficient process orchestration.
Pros & cons
In all the reviews we collected, ActiveBatch is identified as easy to use by 16%. On one user review the tool’s pros and cons are listed as:
- Pros:
- User-friendly
- Integration capabilities
- Automation and orchestration features
- Cons:
- The learning curve
- Documentation issues
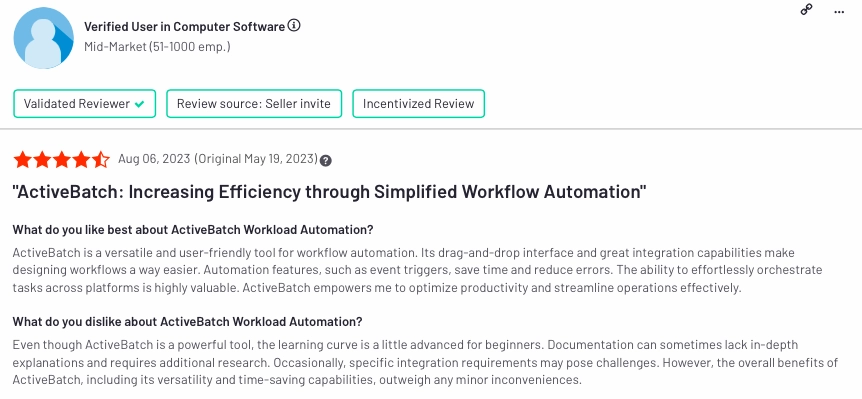
2.) RunMyJobs by Redwood
RunMyJobs by Redwood is an IT process automation platform that specializes in job scheduling and workload automation. It aims to simplify and optimize business processes by automating routine tasks and workflows.
Unique features
- Object-oriented programming features to help isolate changes, enhance script readability, and simplify maintenance.
- A secure gateway to handle all application-level communication, streamlining integration and bolstering network security.
- Support for over 25 scripting languages to complete with built-in syntax highlighting and parameter replacement.
- Easy navigation with a clear job tree, role-based customization, and quick action buttons.
- SAP Integration with over 1,000 pre-built job templates for a broad range of SAP modules, including S/4HANA, BW, BusinessObjects, and Datasphere as SAP Endorsed App – Premium Certified and the only non-SAP WLA listed by the SAP ECS team.
Pros & cons
In all Redwood RunMyJobs‘ reviews, the tool was described as easy to use with 5%. A user review explains pros and cons of RunMyJobs as:
- Pros:
- User-friendly
- Easy documentation
- Workload balancing
- Cons:
- Lack of public course:
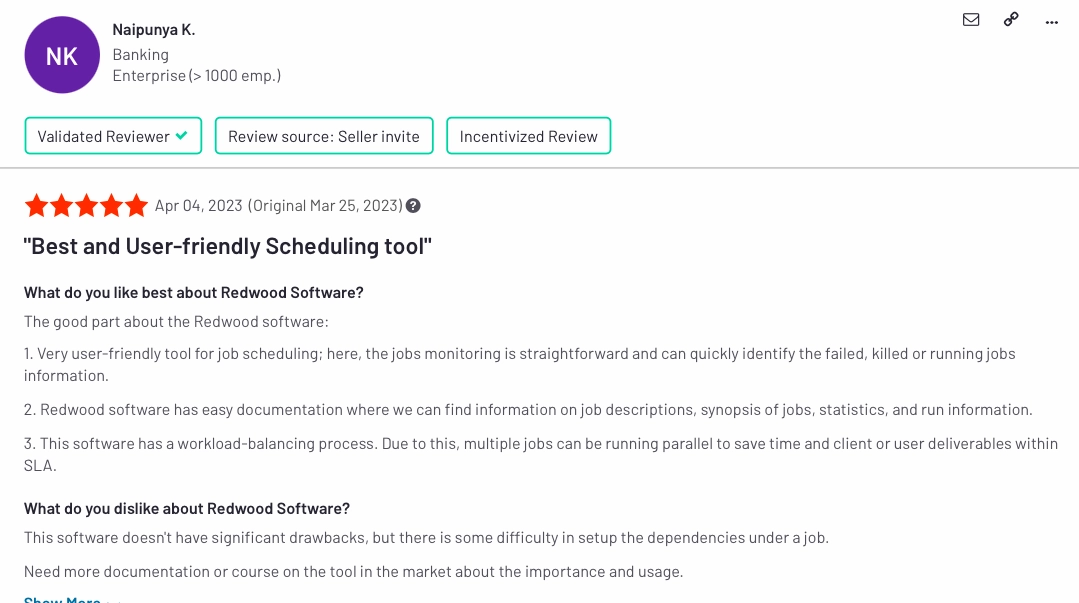
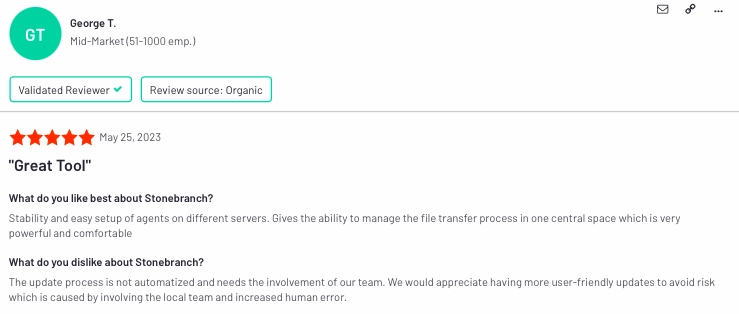
3.) Stonebranch
Stonebranch provides a universal automation platform for orchestrating IT processes across diverse environments. It enables organizations to automate, manage, and control IT tasks, ensuring efficiency and reliability in complex, hybrid IT landscapes.
Pros & cons
According to data collected on Stonebranch, the most positive word is detected as ease of use in 6% of all reviews. Other pros and cons are listed in Figure 6:
- Pros:
- Ease of setup
- File transfer management
- Cons:
- Manual update process of software
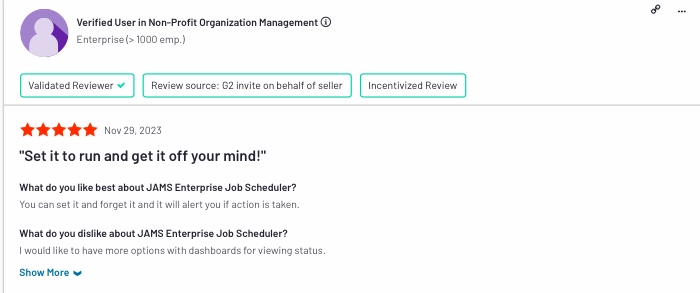
4.) Fortra’s Jams
Fortra’s JAMS is a powerful workload automation (WLA) tool designed to streamline and optimize business processes. With robust capabilities, it offers a comprehensive solution for automating and managing workflows efficiently. The platform stands out with its advanced scheduling and monitoring features, providing organizations with the tools needed to orchestrate complex tasks seamlessly.
Pros & cons
In Forta’s Jams comments, the most positive word for the tool was support team with 7%. Other pros and cons can be found in one user review in Figure 5:
- Pros:
- Automated alerting
- Cons:
- Limited dashboard options for viewing status
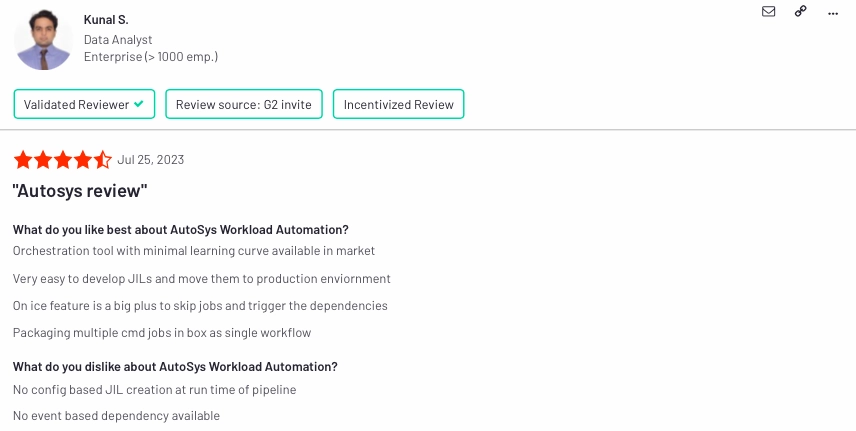
5.) AutoSys Workload Automation
AutoSys Workload Automation is a prominent WLA tool that excels in automating and orchestrating workflows. Known for its reliability and scalability, AutoSys offers a range of features to schedule, monitor, and manage diverse tasks.
Pros & cons
- Pros:
- Easy orchestration
- Dependency triggering
- Easy development of JILs
- Cons:
- Lack of dependency triggering
- Lack of configuration based JILs
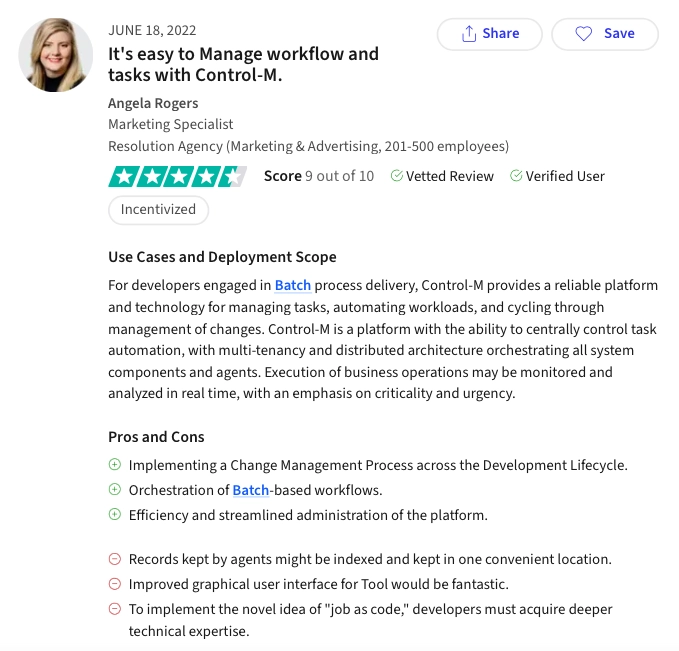
6.) BMC Control-M
BMC Control-M is a leading enterprise-grade workload automation solution, recognized for its versatility in managing and automating business processes. Control-M empowers organizations to optimize their workflows, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure the successful execution of critical tasks.
Pros & cons
In Control-M‘s data we gathered, User friendly appeared the most by 15%. Some other pros and cons can be explained as:
- Pros:
- Batch orchestration
- Easy administration
- Change management
- Cons:
- Limitations for geographical user interface
- Requires technical expertise
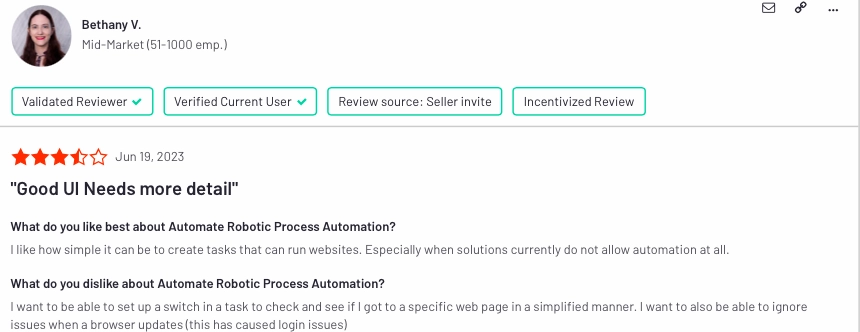
7.) Automate by Fortra
Automate by Fortra is an IT process automation solution that streamlines business processes through task automation. It offers a visual workflow designer, allowing organizations to automate tasks without the need for extensive coding.
Pros & cons
Automate’s most positive comment is ease of use with 14% as our analysis suggests. Other positive and negative aspects are:
- Pros:
- Easy script creating
- Cons:
- Buggy browser updates
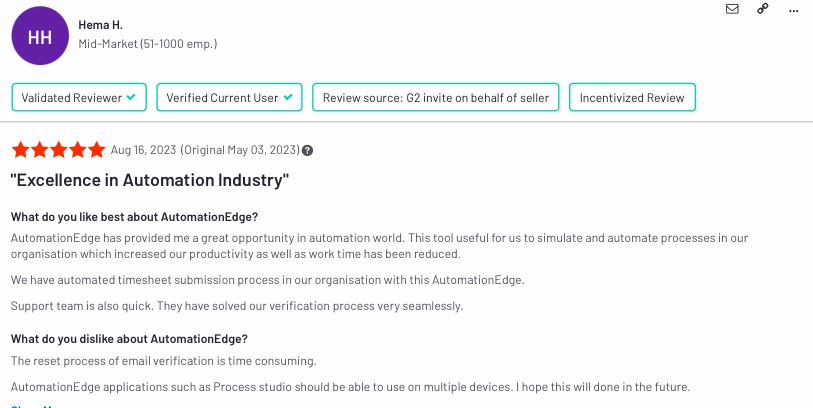
8.) AutomationEdge
AutomationEdge is a leading robotic process automation (RPA) tool that excels in IT process automation. AutomationEdge simplifies business processes by automating tasks efficiently. The platform features a visual workflow designer, eliminating the necessity for intricate coding.
Pros & cons
AutomationEdge is mostly cited as easy to use in 10% of all review data. Here is a specific user review on a review platform describing pros and cons (Figure 8):
- Pros:
- Strong customer support
- Cons:
- Time-consuming email verification
9.) IBM RPA
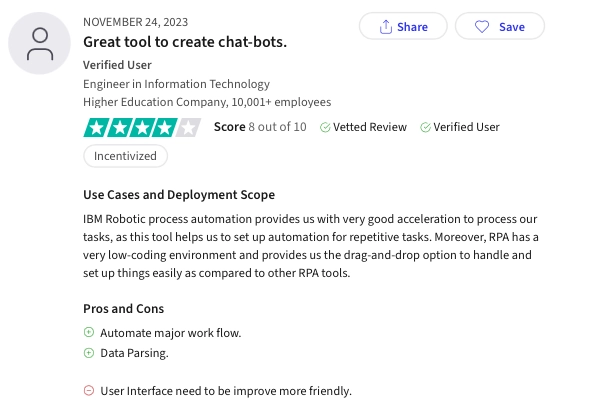
IBM RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is part of the IBM Automation platform, providing tools to automate routine tasks and workflows. It focuses on improving operational efficiency by automating manual processes across different business functions.
Pros & cons
IBM RPA is an easy to use tool according to 21% of all reviews we gathered. Some other positive and negative comments can be explained as:
- Pros:
- Data analysis
- Workflow automation
- Cons:
- Not very straightforward user interface
10.) UiPath RPA
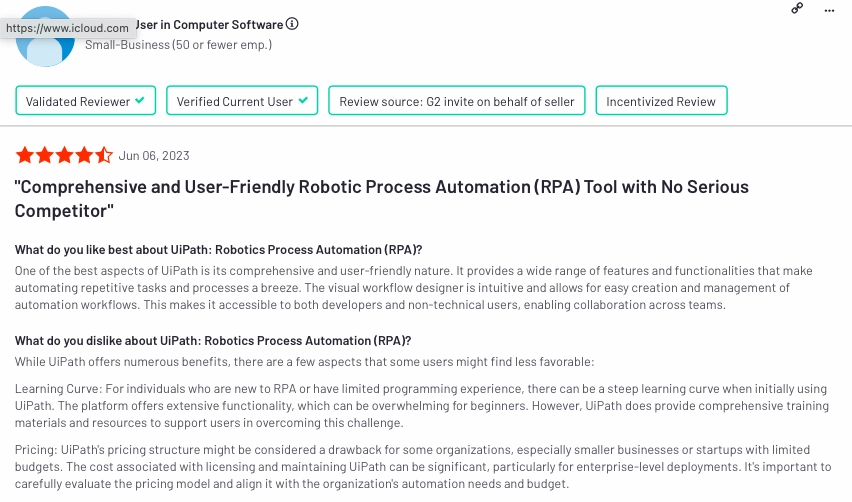
UiPath is a leading Robotic Process Automation (RPA) platform, specializing in automating repetitive, rule-based tasks. It utilizes software bots to mimic human actions, enhancing efficiency and accuracy in various business processes.
Pros & cons
UiPath RPA data shows that 14% of users find the tool easy to use.
- Pros:
- User-friendly
- Various features and functionalities
- Easy management of automation workflows
- Cons:
- Learning curve
- Pricing
11.) Kissflow
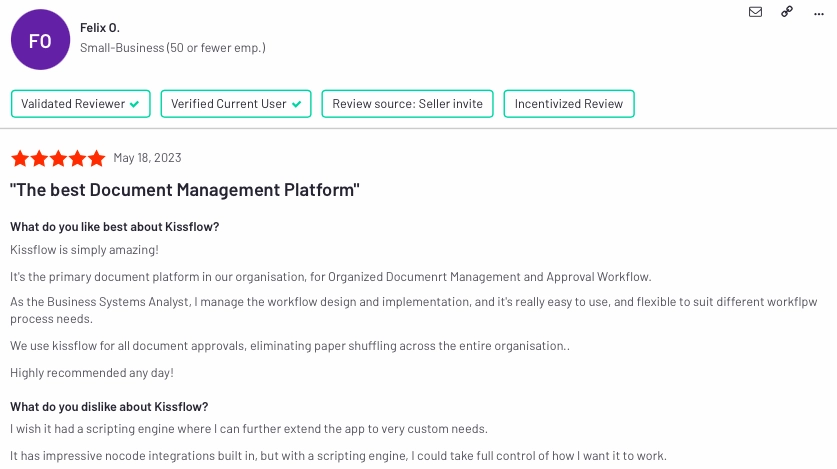
Kissflow is a cloud-based digital workplace platform that includes process automation capabilities. It allows users to design and implement workflows, automate routine tasks, and collaborate seamlessly within an organization.
Pros & cons
14% of all Kissflow users evaluate Kissflow‘s platform as easy to use. Some other qualities include:
- Pros:
- Ease of use and flexibility
- Efficient document management
- Cons:
- Absence of a scripting engine for customization
12.) Laserfiche
Laserfiche is a comprehensive document management and business process automation (BPA) tool that operates as an on-premises or cloud-based solution. Laserfiche users can streamline document storage, automate workflows, and enhance collaboration across organizations.
It provides robust features for designing and implementing workflows, enabling the automation of routine tasks and fostering seamless collaboration within the digital workplace.
Pros & cons
Top quality in all reviews we analyzed for Laserfiche is ease of use with 4%. Other negative and positive comments cover:
- Pros:
- Automation capabilities
- User-friendly interface
- Limited customization option
- Cons:
- No standardized Laserfiche course accessible
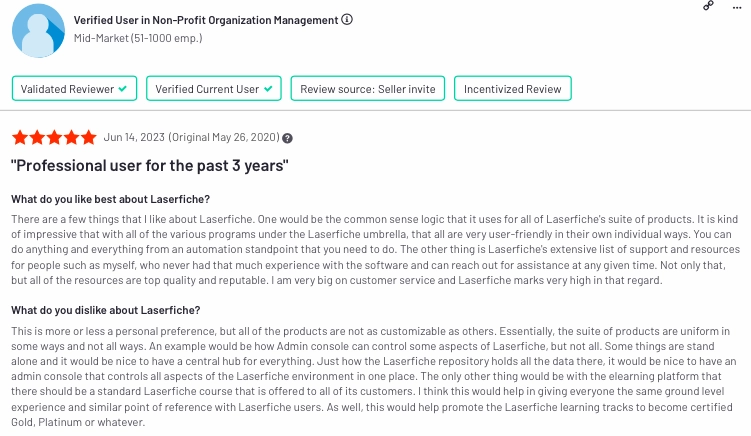
13.) Nintex platform
Nintex is a digital process automation platform that enables organizations to automate and optimize business processes. It offers tools for workflow automation, document generation, and forms, simplifying the automation of various business processes.
Pros & cons
- Pros:
- User-friendly interface
- Interactive process maps
- Strong customer support & training
- Cons:
- Lack of advanced analytics
- Limited workflow automation features & integration capabilities
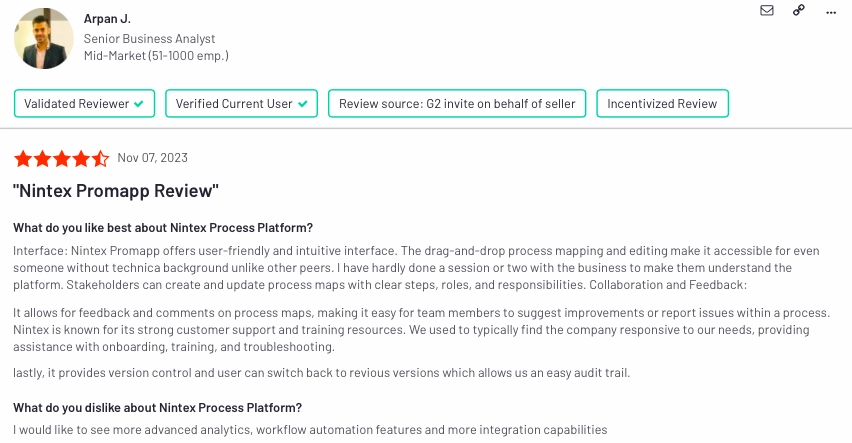
14.) Salesforce Platform
Salesforce Platform provides a robust set of tools for building customized business applications and automating workflows. It empowers organizations to automate processes related to customer relationship management (CRM) and beyond.
Pros & cons
Salesforce‘s review data shows that 12% of comments focus on ease of use. Other pros and cons can be listed as in Figure 14:
- Pros:
- Email automation
- Efficient reporting
- Enriched dashboards
- Cons:
- Complicated reporting
What are different types of ITPA tools?
Within the realm of IT Process Automation (ITPA), various tools cater to distinct aspects of organizational needs. Such tools include:
1.Business Process Automation (BPA)
BPA tools are instrumental in optimizing and automating end-to-end business processes. Through the creation of cohesive workflows, these tools seamlessly integrate tasks, facilitating a streamlined and efficient progression of activities.
A business process automation platform plays a crucial role in improving operational efficiency, reducing errors, and enhancing overall business agility by automating complex and interconnected business processes. Some of the tools considered under BPA cover:
- Workflow Automation: Automating the sequence of tasks that make up a specific process or workflow. This could include tasks such as provisioning and de-provisioning user accounts, software deployment, or system monitoring.
- Orchestration: Coordinating and managing the execution of multiple automated tasks to achieve a larger business process. Orchestration involves integrating different systems and ensuring they work together seamlessly. Some of the orchestration tools to manage and improve IT processes include:
2. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA tools bring a touch of automation through software robots or ‘bots’ that emulate human actions in rule-based, repetitive tasks. These tools are specifically designed to handle routine, mundane activities across various applications.
By doing so, RPA enhances speed, accuracy, and scalability in processes, freeing up human resources for more strategic and creative endeavors. RPA transforms the automation landscape by introducing a layer of intelligence and adaptability to rule-driven processes.
3. IT Automation Tools
IT automation focuses on optimizing and streamlining IT operations. These tools cover a spectrum of functions, from automating routine tasks to managing IT services and infrastructure. The overarching goal is to enhance efficiency, reduce manual intervention, and ensure the smooth functioning of IT processes, ultimately contributing to a more agile and responsive organizational IT environment.
IT automation software include tools like workload automation tools (WLA), IT service management tools (ITSM) and other RMM automation tools.
Learn all workload automation use cases and case studies to start deploying it in different industries and business functions, such as:
- Hyperautomation in Retail: Top 10 Use Cases & Benefits
- HR Workload Automation 5 Use Cases & 6 Best Practices
- Workload Automation in Supply Chain: Unlock 26 Benefits
FAQ
What is IT process automation (ITPA)?
IT Process Automation (ITPA) refers to the use of technology to create repeatable instructions and processes to replace or reduce human interaction with IT systems. The goal of IT process automation is to streamline and simplify routine tasks and workflows within an organization’s IT environment. This can lead to increased efficiency, reduced errors, and improved overall operational effectiveness.
Explore IT process automation use cases to learn how to deploy ITPA tools.
What is the difference between IT automation and IT process automation?
There is a distinction between IT automation and IT process automation, although the terms are mostly used interchangeably. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
IT Automation:
1. Broad term: IT automation is a more general term that encompasses any use of technology to perform tasks in an IT environment without manual intervention.
2. Not necessarily sequential: IT automation may involve the use of scripts, tools, or software to perform specific tasks but might not follow a structured, sequential workflow.
IT Process Automation (ITPA):
1. Focused on processes: IT process automation specifically focuses on the automation of structured and repeatable processes within the IT domain.
2. Structured workflows: ITPA is more concerned with the orchestration and automation of end-to-end processes, involving multiple tasks and possibly multiple systems.
What are the benefits of IT process automation?
IT process automation (ITPA) offers several benefits to organizations, contributing to improved efficiency, reliability, and overall operational effectiveness. Here are some key advantages:
1. Improves efficiency:
– Faster execution: Automated processes can complete tasks much faster than manual methods, leading to quicker overall process execution.
– Resource optimization: Automation allows organizations to allocate resources more effectively, reducing the need for manual intervention in routine tasks.
2. Enhances accuracy:
– Reduced human error: Automation minimizes the risk of errors that can occur with manual processes, leading to more accurate and reliable results.
– Consistency: Automated processes ensure that tasks are performed consistently according to predefined rules and standards.
3. Reduces costs:
– Creating time for higher value tasks: By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, organizations can reduce labor costs and free up personnel for more strategic and value-added activities.
– Operational cost savings: Efficiency gains from automation can lead to overall cost reductions in IT operations.
4. Allows scalability:
– Flexible scaling: Automation enables organizations to scale their operations more easily to accommodate growth without a proportional increase in manual effort.
– Handling complexity: As IT environments become more complex, automation helps manage the increased workload without a linear increase in staffing.
– Ensures compliance and security: Consistent compliance: Automated processes can be designed to adhere to regulatory requirements and internal policies consistently.
– Enhanced security: Automated security processes can respond rapidly to threats, reducing the likelihood of security breaches.
5. Advances visibility and control:
– Real-time monitoring: Automation often includes monitoring capabilities, providing real-time insights into the status of processes and systems.
– Centralized control: Centralized management of automated processes allows for better control and coordination across the IT infrastructure and effective project management strategies.
– Event-driven automation: Automation triggered by specific events allows for rapid response to incidents, minimizing downtime and potential disruptions.
6. Accelerates customer experience:
– Faster service delivery: Automated processes enable quicker delivery of services and responses to customer requests, leading to improved satisfaction.
What are the challenges of IT process automation?
While IT process automation (ITPA) offers numerous benefits, there are also challenges and considerations that organizations may face during implementation. Here are some common challenges associated with IT process automation:
1. Complexity of implementation:
1. Learning curve: Implementing automation tools and frameworks often requires a learning curve for IT staff, particularly if they are not familiar with scripting or programming languages.
2. Integration challenges: Integrating automation into existing IT systems and workflows can be complex, especially in heterogeneous environments with diverse technologies.
4. Maintenance overhead: Automated processes require ongoing maintenance to ensure they remain effective and aligned with evolving business needs. This can involve updating scripts, handling changes in system configurations, and addressing compatibility issues.
5. Security Concerns: Automated processes can become targets for cyberattacks if not properly secured. Organizations must implement robust security measures to protect automated workflows.
6. Over-Automation: Automating without a clear understanding of the underlying processes or without evaluating the necessity of automation for a particular task can lead to inefficiencies and wasted resources.
7. Monitoring and auditing: Monitoring and auditing automated processes can be challenging, and organizations must invest in tools, such as process intelligence and process mining that provide visibility into automated workflows to identify and address issues.
What is business process automation and how it is related to IT process automation?
Business process automation (BPA) involves the use of technology to automate complex business processes. Process automation tools include robotic process automation (RPA), workflow automation software and business process automation software.
IT process automation (ITPA) is a subset of business process automation that specifically focuses on automating tasks and workflows within the IT domain.
While business process automation can encompass a broader spectrum of organizational activities, IT process automation targets tasks and workflows within the information technology realm, contributing to improved operational performance and resource optimization.
Critical capabilities for ITPA tools
Here are key capabilities of IT process automation tools:
1. Integration and Compatibility: An ideal ITPA tool must integrate with a variety of IT systems, applications, and platforms. This way, businesses can ensure seamless communication and data exchange between different tools and systems in the IT environment.
2. Scripting and Coding Support: This is the support for scripting and coding to create custom automation scripts or extend automation capabilities.This feature allows organizations to tailor automation processes to specific needs and integrate with existing scripts or code.
3. Event-Driven Automation: It refers to the ability to trigger automation processes based on specific events or conditions. This feature enables responsive and dynamic automation, allowing actions to be taken in real-time in response to changes in the environment.
4. Monitoring and Reporting: Tools should provide monitoring capabilities to track the status and performance of automated processes, along with reporting features for analysis. This way, they offer visibility into the execution of automated tasks, ease troubleshooting, and support continuous improvement.
5. Security Features: Incorporation of security measures to protect automated processes and ensure compliance with security standards. ITPA security features safeguards against potential vulnerabilities and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
6. Error Handling and Exception Management: Mechanisms for identifying, handling, and resolving errors or exceptions that may occur during the execution of automated processes. This feature improves the reliability and resilience of automation by addressing issues promptly.
7. Scalability: It is the capability to scale automation processes to handle increased workloads and growing IT environments. A scalable IT process automation tool ensures that automation remains effective as the organization expands, preventing bottlenecks.
8. Version Control: It refers to the ability to manage and track different versions of automation workflows. It is essential for collaboration, facilitating rollback in case of issues, and ensuring version consistency in complex automation environments.
9. Audit Trail: Logging and auditing features to maintain a record of actions performed by automated processes. This feature supports compliance, troubleshooting, and accountability by providing a transparent history of automation activities.
Transparency statement
AIMultiple collaborates with various technology vendors, including Redwood, offering solutions like Active Batch and RunMyJobs.
Further reading
Find out more on IT automation:
Explore other automation tools useful for IT teams:
- Top 10+ Data Warehouse Automation Software
- Top 11 Batch Scheduling Software: Vendor Benchmark
- Top 10+ Data Warehouse Automation Software
Check out our comprehensive and data-driven IT automation software and workload automation tools lists if you want to compare other solutions.
For more questions on IT process automation, we would like to help:
External sources
- 1. “The Impact of Automation on IT Operations.” Freeform Dynamics Ltd. July 2017. Access December 6, 2023.
- 2. ActiveBatch Workload Automation Reviews 2025: Details, Pricing, & Features | G2.
- 3. RunMyJobs Reviews 2025: Details, Pricing, & Features | G2.
- 4. Stonebranch Reviews 2025: Details, Pricing, & Features | G2.
- 5. JAMS Reviews 2025: Details, Pricing, & Features | G2.
- 6. AutoSys Workload Automation Reviews 2025: Details, Pricing, & Features | G2.
- 7. Control-M Reviews & Ratings 2025. TrustRadius
- 8. Automate® Reviews 2025: Details, Pricing, & Features | G2.
- 9. AutomationEdge Reviews 2025: Details, Pricing, & Features | G2.
- 10. IBM Robotic Process Automation Reviews & Ratings 2025. TrustRadius
- 11. The UiPath Platform™ Reviews 2025: Details, Pricing, & Features | G2.
- 12. Kissflow Reviews 2025: Details, Pricing, & Features | G2.
- 13. Laserfiche Reviews 2025: Details, Pricing, & Features | G2.
- 14. Nintex Reviews 2025: Details, Pricing, & Features | G2.
- 15. Salesforce Lightning Platform Reviews & Ratings 2025. TrustRadius

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.