Recruiters use automation tools to automate basic tasks on platforms like LinkedIn, and these tools are also employed for data scraping. However, scalability can be an issue due to web scraping challenges, as many of these tools rely on cookie-based scraping, which heightens the risk of IP bans.
On the other hand, there are scalable, proxy-based web scraping tools that enhance efficiency in the recruitment process.
This article outlines key concepts related to web scraping in recruitment, focusing on tools used to extract data from various platforms for recruitment purposes.
Web scraping tools for recruiters
| Tool name | Solution type | Purpose | Scrape based on | Price/mo | Free trial |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bright Data | Dedicated API | Data collection platform | Query URL | $499 | 7 days (20 API calls) |
| Smartproxy | General-purpose API | Data collection platform | Query URL | $29 | 7 days |
| Oxylabs | General-purpose API | Data collection platform | Query URL | $49 | 7 days |
| Nimble | General-purpose API | Data collection platform | Query URL | $150 | 7 days |
| Apify | Dedicated API | Data collection platform | Query | $49 | $5 platform credits |
| Octoparse | No-code scraper API | Data collection platform | URL | $99 | Free 10 tasks |
| PhantomBuster | Automation tool | LinkedIn automation platform | URL | $60 | 14 days |
Table features explained:
- Solution type: Explained in the “methods for web scraping recruitment” section.
- Scrape based on: Techniques for scraping the desired web page involve using either a query input or a URL input to scrape data.
Platforms for recruitment data collection and key considerations
- Data types that can be scraped: Profile information, connections, public activity, company information, skills and public contact information
- Considerations for scraping: LinkedIn enforces strict terms of service that limit data extraction and uses anti-scraping measures to identify scraping bots. Some web scraping tools offer built-in proxy infrastructure with dedicated IPs and servers, allowing the user to avoid using their personal account and minimizing the risk of getting banned. Additionally, cookie-based scrapers like PhantomBuster utilize your browser cookies to collect data. However, if LinkedIn detects unusual activity, you may face temporary restrictions or a permanent ban from the platform.
Job Boards (Indeed, Glassdoor, Monster)
- Data types that can be scraped: Profile information, connections, public activity, company information, skills and public contact information
- Considerations for scraping: Job postings may vary in format between different job boards and even within the same platform. It’s important to build parsers that can reliably extract details like job titles, descriptions, salaries, and locations. Since many listings are short-lived, you might need to establish scraping schedules to manage outdated or inactive posts effectively.
GitHub
- Data types that can be scraped: Profile information, repositories, contributions, gists and stars & forks
- Considerations for scraping: GitHub is built-around open-source contributions, making public data widely available. It also provides an official API for accessing this information, though there are rate limits that restrict the amount of data that can be retrieved within a certain time frame.
Dribbble & Behance (Design Portfolios)
- Data types that can be scraped: Profile information, visual portfolio, project tags, client work, skills & tools
- Considerations for scraping: Dribbble and Behance contain both public and private data. While it may be technically possible to scrape private data, doing so without the owner’s explicit permission is typically regarded as unethical.
Most effective ways for web scraping recruitment
1. Dedicated APIs
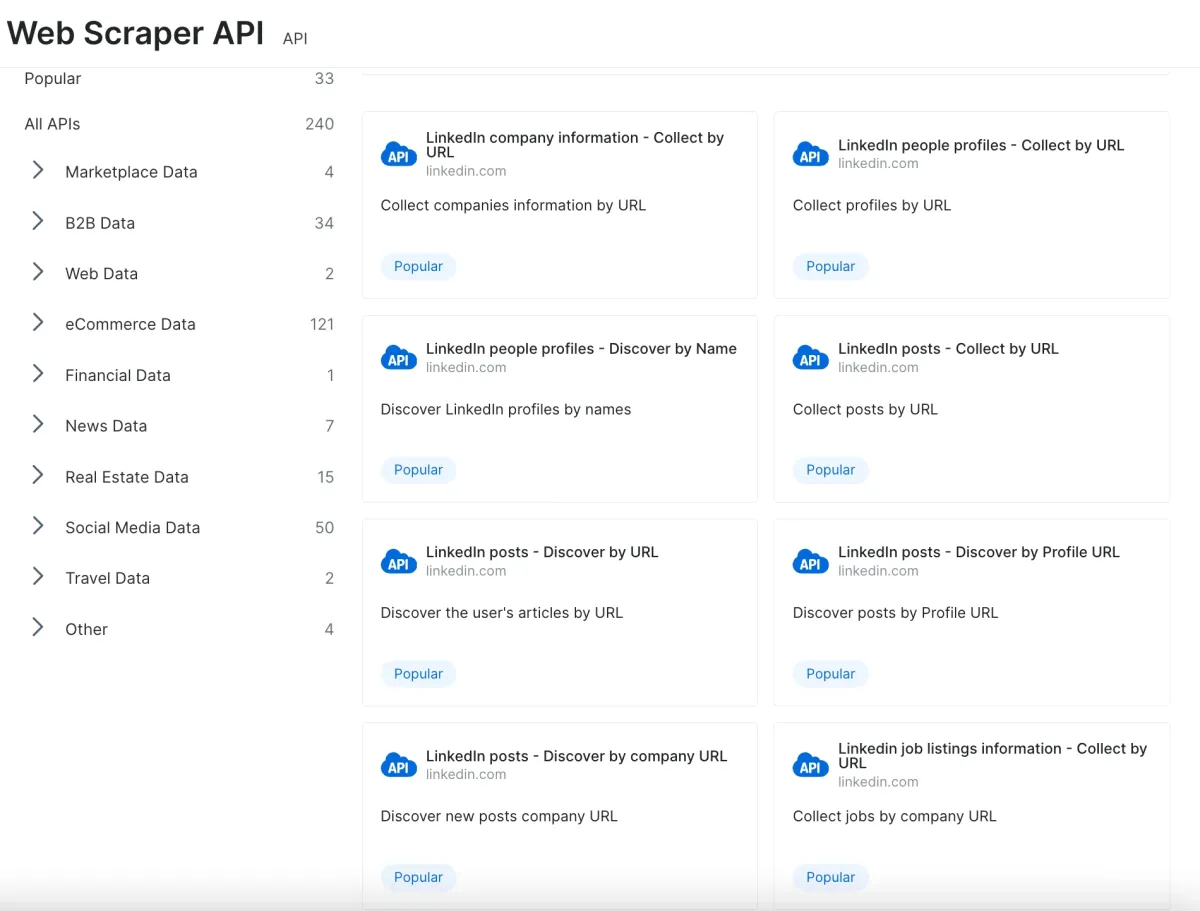
Platforms such as Bright Data and Apify offer APIs designed for particular websites or data categories, like recruitment platforms. These APIs simplify the process of scraping by providing a structured method for requesting and retrieving data. The image below is an example from Bright Data showcasing pre-built dedicated scraper APIs designed for various data types.
2. General-Purpose APIs
Some web scraper providers offer APIs that are built to gather data from a wide range of websites, and these can be customized for particular industries or data types. For instance, Social Media Scraper APIs can be utilized to extract data from platforms like LinkedIn and various job boards.
3. No-Code Scraper APIs
No-code scraping platforms, such as Octoparse and PhantomBuster, provide ready-to-use scraping tools tailored for websites like linkedIn and Indeed. These tools feature user-friendly, point-and-click interfaces that allow users to easily choose the data they wish to extract. The image below demonstrates how the visual data selection process operates.
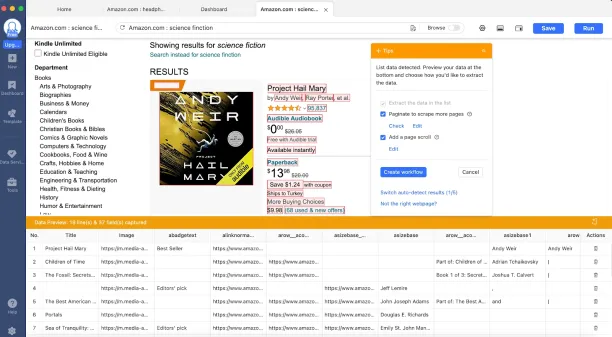
Source: Octoparse
4. Automation tools
There are various automation tools available that allow users to extract data and automate activities on employment websites or social media platforms. You can gather publicly available data such as job postings, company details, or candidate profiles for market research. However, many of these tools are cookie-based. Using automation tools can be risky for websites employ strict anti-scraping techniques since they store session cookies to mimic user behavior without logging in repeatedly.
What are the use cases of web scraping in recruiting?
2 out of 3 recruiters do not have the tools necessary to understand the market and talent pool they are recruiting from. Therefore recruiters can leverage web scrapers for:
Candidate sourcing
1. Building a talent pool
A talent pool is a list of candidates who can be qualified for current or future job openings in an organization. Recruiters can use web scraping service to collect lists of candidates from employment websites in order to create an up-to-date job databases for the organization and build relationships with candidates before they are ready to apply.
2. Targeting candidates in specific geographical regions
Some web scrapers integrate IP proxies to enable access to region-specific online job market data. This enables recruiters to target candidates in a specific region in case the role requires employees to work on-site.
3. Comparing candidate qualifications
Web scrapers can gather data about candidates from targeted platforms such as their profiles on social media accounts andjob aggregator sites. The tools can also be programmed to extract qualification-specific data such as education or skills fields in a candidate’s profile. Recruitment agencies can leverage the collected data to analyze candidates’ qualifications and estimate their match to specific positions.
4. Collecting candidate contact details
Web scraper APIs can collect candidates’ contact details such as email addresses and phone numbers from employment websites to enable recruiters to reach out and contact candidates qualified for open positions.
Job market analysis
5. Understanding salary ranges
Most recruitment websites, such as Glassdoor or Salary.com, provide data about salary ranges for specific roles, years of experience, and geographical regions. Web scrapers can be used to collect salary ranges for the organization’s job openings in order to help recruiters understand candidates’ expectations and optimize their salaries accordingly.
6. Identifying job requirements
Recruiters can understand the education and skill requirements for specific roles by monitoring what their competitors search for in a candidate. Web scrapers can scrape job postings from a business competitor’s job listings and job post details to help recruiters create better job descriptions.

Source: LinkedIn job posting
7. Web scraping job postings
Web scrapers can also gather information from competitors’ websites about training opportunities, flexibility in working hours or vacation days, benefits, and job trends. By understanding competitors’ offerings, recruiters can optimize their job offerings and benefits packages in order to attract candidates and avoid losing them to competition.

Source: LinkedIn job posting
What are the best practices of web scraping for recruitments?
To get the most of web scraping capabilities in the recruiting process, businesses can follow best practices, which include:
- Choosing the right employment platform: There are hundreds of employment websites and platforms today, however, some platforms provide a wider scope than others, while others can be more position-targeted. For example, LinkedIn and Indeed have a wide database for all types of positions around the world, whereas GitHub and Stack Overflow are more focused on programming and tech positions.
- Updating candidate pools: There are ~15M job openings and 35,000 skills listed on LinkedIn alone, and being updated with every hiring. Therefore, it is important to scrape employment websites frequently in order to keep the talent pools up-to-date.
It is crucial to check if the website you want to scrape allows bot scraping, otherwise, you will face legal issues, such as the case of LinkedIn vs. hiQ Labs where hiQ breached the LinkedIn User Agreement, which specifically prohibits automated access and scraping.

![Top 5 HR Analytics Use Cases with Real-Life Examples ['25]](https://research.aimultiple.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/use-cases-of-HR-analytics-190x107.png.webp)
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.