As businesses move towards remote and hybrid work environments,1 implementing zero trust network access (ZTNA) solutions can support businesses’ cybersecurity efforts. ZTNA open source tools offer a cost-effective way to authorize at each layer to secure remote access to resources.
For businesses
- Without a network security budget, these tools provide an accessible ZTNA solution.
- With a budget, enterprise-grade ZTNA tools are worth considering.
Explore the top 5 ZTNA open source solutions, key considerations for selecting a ZTNA solution, and reasons to implement ZTNA open source tools:
Top 5 ZTNA open source software
| Software | Github Star | User Ratings* | # of Employee** | ZTNA architectures | ZTNA category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenVPN | 10,200 | 4.6 out of 203 reviews | 163 | Identity Defined Network | authorization |
| Pomerium | 3,900 | 4.8 out of 11 reviews | 19 | Reverse Proxy | identity, posture, and context |
| OpenZiti | 2,200 | 4.3 out of 5 reviews | 71 | Software Defined Perimeter | web application authentication |
| Pritunl Zero | 570 | 4.3 out of 36 reviews | 1 | Host-based Firewall Control | privileged access management |
| Ferrumgate | 11 | N/A | 6 | Privileged Access Management | unified platform |
Inclusion criteria: Only software with at least 10 Github stars are considered.
Ranking is done based on the GitHub stars of each tool.
1. OpenVPN
OpenVPN possesses core zero trust network access (ZTNA) capabilities, segregating policy enforcement from network access. Using the OpenVPN tunneling protocol, network access does not equate to application access, ensuring only authenticated and authorized users can reach specific applications.
OpenVPN implements multiple security checks, such as digital certificates and HMAC signatures, before establishing network connections, thereby minimizing the attack surface and preventing discovery by unauthorized applications.2
2. Pomerium
Pomerium offers a zero trust architecture by continuously verifying each action against identity, posture, and context rather than relying on a one-time verification process.3 It employs a self-hosted reverse proxy to maintain control over data and avoid the security risks associated with third-party vendors decrypting traffic.
Pomerium’s zero trust approach also addresses the limitations of traditional tunneling solutions by ensuring that security checks are ongoing, thereby reducing the risk of lateral movement and compromised credentials.4
3. OpenZiti
OpenZiti offers a comprehensive set of open-source tools designed to integrate zero trust principles directly into applications, enabling the creation of zero trust overlay networks with smart routing capabilities.
The project emphasizes the importance of software agility and provides SDKs to embed zero trust principles seamlessly into various applications, bridging the gap for apps that cannot inherently implement zero trust. It offers a trust overlay network, providing secure access control for users connecting to web applications and services.5
4. Pritunl Zero
Pritunl Zero is an open-source BeyondCorp server offering zero trust security for privileged access to SSH and web applications, providing single sign-on compatibility with major providers like OneLogin, Okta, Google, Azure, and Auth0.
With role-based access policies, users and services can be managed efficiently, allowing access via any web browser without the need for VPN clients, and configuration is quick without network modifications, ensuring easy scalability and high availability.
Pritunl Zero also offers (secure shell) SSH management and multi-factor authentication and serves as a free alternative to other platforms like Gravitational Teleport, ScaleFT, and CloudFlare Access with added SSH support and features.6
5. Ferrumgate
By utilizing a software-defined perimeter, Ferrumgate provides a solution for secure remote access, cloud security, privileged access management, identity and access management, endpoint security, and IoT device protection through its Zero Trust virtual networks.
Ferrumgate’s features include support for various single sign-on methods, easy deployment without network changes, detailed activity insights, and integration with IP and Fqdn intelligence providers for enhanced security measures.7
Key considerations for selecting a ZTNA approach
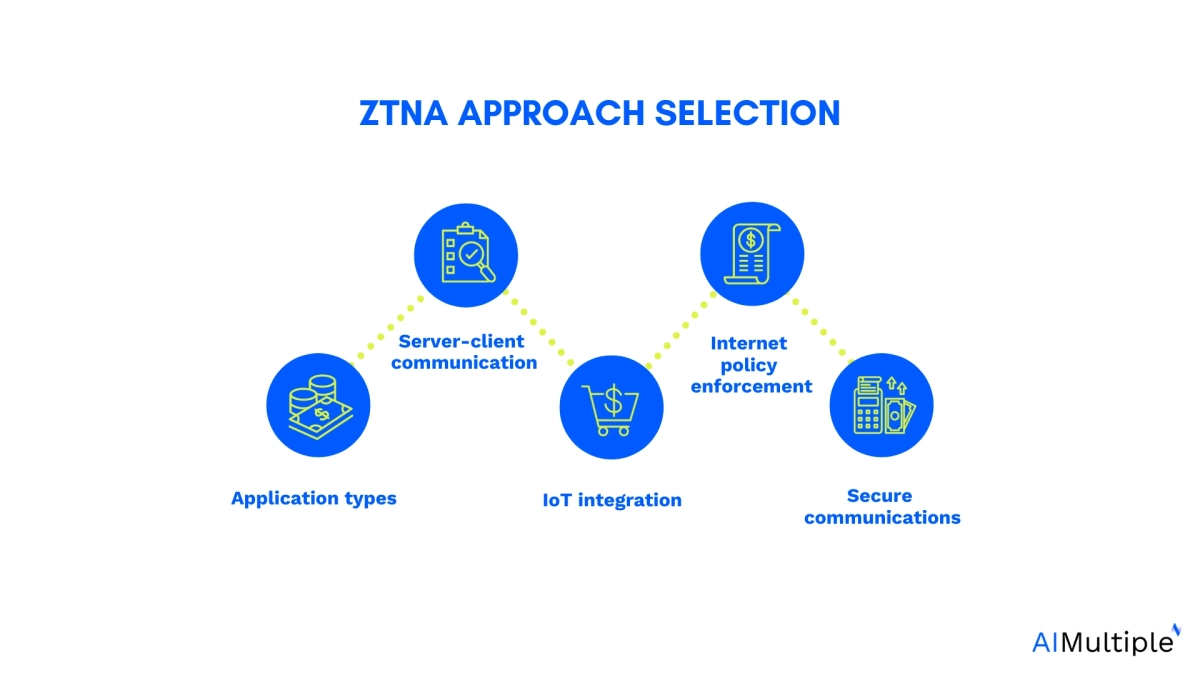
When evaluating zero trust network access (ZTNA) solutions, it is crucial to ensure that the chosen architecture meets your business’s needs without increasing operational complexity. Here are five essential considerations to guide your decision-making process:
1. Application types
Assess the diversity of private applications requiring access, from legacy mainframe to modern Web3 applications, and confirm if the ZTNA solution supports various application protocols comprehensively.
2. Server-client communication
Evaluate if any private applications mandate the server to initiate communication with the client, ensuring the chosen ZTNA approach facilitates such server-initiated traffic for application functions.
3. IoT integration
Determine if the ZTNA solution can integrate with IoT applications, considering their role as potential entry points to the IT infrastructure and addressing security concerns.
4. Internet policy enforcement
Explore if the ZTNA solution extends beyond private application access to enforce internet policies, enhance defense-in-depth strategies, and secure internet and SaaS applications effectively.
5. Secure communications across data centers
Consider whether the ZTNA solution can secure communications within or across data centers, including identity provision and policy enforcement for API communications and inter-data center application access.
Reasons to implement ZTNA open source tools
Easy configuration and deployment
ZTNA open source solutions boast easy configuration and deployment, requiring minimal network modifications. This simplicity reduces downtime and increases productivity, allowing businesses to quickly set up and configure their systems, enhancing operational efficiency.
Extending zero trust networking
ZTNA solutions can extend zero trust networking across various industry applications, connecting APIs, OT, IoT, mobile, desktop, containers, VMs, browsers, reverse proxies, modems, firewalls, edge servers, and clouds using SDKs and endpoints. This extensibility eliminates the need for traditional VPNs, MPLS, permitted IPs, and bastions, streamlining network security.
Cost-effectiveness
ZTNA open source tools provide a budget-friendly alternative to proprietary solutions, reducing licensing costs and allowing for greater customization and flexibility. By leveraging community-driven development, organizations can implement robust security measures without incurring significant expenses.
ZTNA architectures
Zero trust network access may be reached by various ZTNA architectures.8
- Privileged Access Management: Agent-based architecture where the vendor’s product centrally manages credentials for access to target servers.
- Host-based Firewall Control: Agent or remote-management based architecture where the vendor manages host-based firewalls built into device operating systems to control access.
- Identity Defined Network: Agent-based architecture where all traffic traverses network relays coordinated by centralized policy-based management.
- Software Defined Perimeter: Appliance and proxy-based architecture utilizing a reverse proxy appliance at the network edge, governed by a centralized policy-based controller.
- Reverse Proxy: Agent-based architecture where the reverse proxy sits between users and applications, enables agentless ZTNA by intercepting and inspecting user traffic before securely forwarding it to internal or cloud apps, ensuring authentication, access control, and data protection without exposing the backend servers.
FAQs
Why is ZTNA open source important in modern security?
ZTNA open source solutions play a critical role in addressing the security challenges posed by remote access and the proliferation of unmanaged devices. ZTNA works on the idea that no one is trusted by default—not even inside the network. It checks every access request closely. This helps reduce the damage if a system is hacked and keeps threats from spreading.
Implementing ZTNA enhances the security posture of organizations, providing a robust defense against evolving cyber threats.
How can I evaluate ZTNA solutions fit for my organization?
When selecting a ZTNA solution, it is crucial to evaluate whether the architecture meets the business’s needs, can extend beyond initial use cases, and accommodate various current and future needs. Not all ZTNA architectures are alike, each having distinct advantages and disadvantages. ZTNA helps reduce the risks that come with remote access. Unlike VPNs, it doesn’t give broad access to the whole network.
What is zero trust network access (ZTNA)?
Zero trust network access (ZTNA) changes how remote access works. Instead of trusting anyone inside the network, it checks every user and device—every time. This makes it safer than older tools like VPNs, especially for today’s remote work.ZTNA works by hiding apps behind a secure wall called a software-defined perimeter (SDP). Instead of exposing the whole network, it only shows what each user needs. This reduces the chance of attacks and keeps the rest of the system out of reach.
Further Reading
If you need further help in finding a vendor or have any questions, feel free to contact us:
External Links
- 1. Top Remote Work Statistics And Trends – Forbes Advisor. Forbes
- 2. Zero Trust With OpenVPN Protocol for Network Access = Our ZTNA-Capable Solutions. OpenVPN
- 3. Pomerium | Zero trust, identity-aware proxy | Pomerium.
- 4. Pomerium | Zero trust, identity-aware proxy | Pomerium.
- 5. Open Source Zero Trust Networking – OpenZiti is an open source zero trust network applying zero trust principles directly into applications through SDKs or to existing networks using tunnelers.
- 6. Pritunl Zero - Enterprise Zero Trust.
- 7. Open Source Zero Trust Access - FerrumGate.
- 8. The no-bullshit ZTNA vendor directory .


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.