We focus on RPA use cases in finance, such as automated record-keeping and financial control. Some of those use cases are:
Why is RPA important in finance?
RPA’s usage is growing in the finance department because it is effective in handling repetitive, mundane, back-office tasks. In addition, they can easily be integrated with machine learning models to take on more complex tasks.
Finance departments always push other business units to be lean and cost-efficient. Robotic process automation allows finance departments to achieve that so they can be an example to other businesses.
RPA bots can handle most activities in tasks such as payroll, record keeping, financial reporting, invoice processing and accounts payable and receivable.
In the finance function, RPA’s benefits include:
- Reducing operational costs
- Increasing compliance by reducing human error rate
These benefits allow:
- Finance teams to focus on more strategic tasks such as business planning and investor relations.
- Companies to grow with less difficulty as automated systems can easily be scaled.
- Companies to achieve cost savings while enhancing operational efficiency and improving customer satisfaction.
What are the first finance processes to automate?
Robotic process automation bots are taught to follow prescribed protocols and procedures with precision, enabling increased compliance and cost efficiencies. Therefore, RPA bots can handle:
Accounts Payable (AP) and Accounts Receivable (AR) Automation
RPA bots can automate most of the accounting tasks, such as accounts payable and receivable because they include repetitive tasks, such as:
- Managing outgoing documents: Auto generating invoices and orders to be sent out. Offers received from suppliers can be used to generate orders. Customer contracts can be used to generate invoices.
- Managing incoming documents
- Extracting data from invoices or orders received from suppliers and customers in numerous different formats
- Matching invoices to purchase orders
- Matching orders to offers
- Invoice routing for approvals
- Invoice filling and retrieval
- Processing payments
For example, Thermo Fisher Scientific implemented RPA for automating invoice processing, reducing processing time by 70%. This automation allowed the company to efficiently handle 824,000 documents annually, leading to a significant boost in productivity.1
Financial Controls
- RPA bots produce dependable data because they follow standard procedure and do not skip steps by accident so they reduce compliance issues in automated processes. A Fortune 500 tech company from global tech applied RPA to automate financial report generation which helped them to reduce errors and improved auditing capabilities with the detailed logs. The firm also managed to reduce turn around time and efforts by 70%.
- RPA bots can also be used to aggregate compliance related data from various sources into a single system. Using this aggregated data, the finance function can implement necessary monitoring and alerting functionality to identify oversights and errors in a timely manner. TreasuryOne deployed RPA software to automate back-office operations, including performing settlements and sending out deal confirmations, which led to a reduction in errors.
Combing RPA with Natural Language Processing (NLP) modules from RPA marketplaces, reporting activities can be at least partially automated. Examples include:
- Record-to-report
- Investor reporting such as annual reports etc.
- Regulatory reporting (e.g. for tax purposes including income tax). This is especially useful since regulatory reporting errors can be costly from a reputational and financial perspective and increased automation can reduce errors.
Financial Planning
RPA in financial planning allows businesses to provide forecasts at a faster rate and constantly have an updated view of the latest capital expenditures, investments, and financial statements. Some of these activities include:
- Forecasting: Analyzing latest financial trends in the business and researching the market to build accurate forecasts.
- Comparing results vs plans: Forecasts need to compared with actuals to improve future forecasting accuracy and to measure the performance of the business and identify improvement points. This activity involves loading accounting balances (i.e. difference between the sum of debit entries and the sum of credit entries) into financial planning systems and creating variance reports. These variance reports compare actual results with forecasts in detail.
Both activities involve gathering data inputs, formatting the data and aggregating them in an easy-to-understand format for all stakeholders.
What is the automation potential in finance?
According to Accenture, up to 80% of financial operations can be automated, potentially freeing a substantial portion of employee time for strategic initiatives, customer satisfaction, and other critical areas.2
A McKinsey research report analyzed all finance operations processes to identify their automation potential as seen below. Averaging automation potential across all functions, they claim that ~42% of finance operations can be fully automated. 3
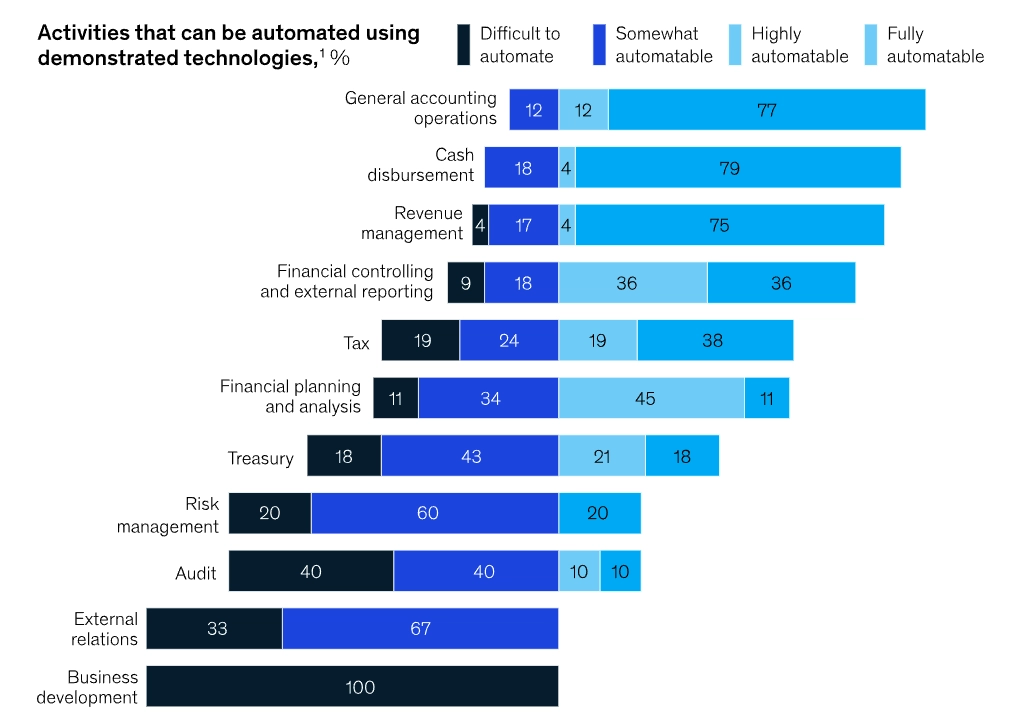
RPA in financial institutions can address complex accounting processes and enhance financial planning by integrating with existing systems. This leads to improved accuracy in financial reporting and better risk management.
As a result, finance teams experience increased productivity, reduced operational costs, and greater accuracy in financial statements. The deployment of RPA helps finance professionals focus on higher value work and strategic tasks on their valuable time.
What are the primary processes in the finance department?
An organization’s finance team’s responsibilities are split into:
Accounting
- Record keeping and report preparation of all transactions and financial events
- Accounts payable including managing vendor data and creating accounting entries as we previously mentioned in AP automation.
- Accounts receivable includes managing timely collection of payments to the company as well as recording and accounting for such payments. For more, feel free to read about order management for businesses.
- Payroll, tracking overtime, paid leave, taxes, pensions, etc.
- Financial controls, making sure that processes follow legal guidelines and compliance regarding fraud and theft.
Explore more on RPA in accounting.
Investor relations
Investor relations prepares necessary reports for investors and external shareholders:
- External reports such as financial statements (income statement, statement of comprehensive income, balance sheet, statement of cash flows, and statement of stockholders’ equity) and the notes to the financial statements.
- Quarterly and annual reports to stockholders.
- Regulatory reports such as financial reports to governmental agencies including quarterly and annual reports to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
- Documentation pertaining to the issuance of common stock and other securities.
Strategic finance management
- Financial planning is the analysis of a company’s current cash flows, its targets and market dynamics to plan future financial decisions.
- Risk management is the process of identification, analysis, and acceptance or mitigation of uncertainty in investment decisions.
- Treasury ensures that the business has the funds it needs to manage its day-to-day business obligations, while also helping develop its long term financial strategy and policies.
- Capital management (CM) ensures maximum efficiency in managing a company’s cash flow. This involves budgeting and financing.
What is the future of RPA in finance?
Maintenance of RPA bots can be difficult since the people who developed them may no longer be working on the project and the code base may be hard to understand.
Therefore, when market conditions or regulatory reporting (e.g. internal control over financial reporting ICFR) requirements change, businesses may face a difficult process of updating RPA bots. Read more about RPA’s challenges in our article: 21 RPA Pitfalls/ Challenges & A Checklist to Tackle Them
RPA bots are expected to dominate transactional tasks in the finance sector in the short term. However, we also expect them to take part in more complex strategic ones. Read our article about RPA marketplaces to see how RPA companies are integrating AI models into their bots.
To learn more about
- What RPA will look like in the future, you can read our article Future of RPA: In-depth Guide to RPA Innovation
- RPA case uses and applications: Feel free to read our article about Top 100 RPA Use Cases with Real-Life Examples

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.