In the EU alone, adoption of smart meters have reached up to 72%. 1 Such adoption rates may positively impact the meter-to-cash process by facilitating more accurate consumption data and reliable service. However, potential challenges could arise in
- Managing the increased volume of data
- Addressing data privacy concerns
- Ensuring the seamless integration of diverse smart grid technologies.
Utility providers must optimize their the meter-to-cash cycle to avoid these potential complexities, which allows them to improve customer experience, increase data quality and achieve reliable revenue recognition.
What is meter-to-cash process?
The meter-to-cash process, also known as M2C process, refers to the end-to-end workflow in utility services, encompassing activities from measuring energy consumption through meters to generating invoices and receiving payments from customers.
This process is crucial for most utility companies, ensuring accurate billing, efficient cash flow management, and maintaining transparent documentation throughout the billing cycle. Automation and technology play key roles in optimizing the meter-to-cash process, reducing errors, and improving overall operational efficiency in the utility industry.
Which processes are involved in meter to cash process?
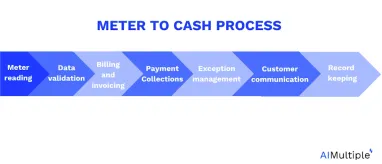
The meter-to-cash process involves several key processes, including:
- Meter reading: Field workers or automated systems capture readings from utility meters measuring energy consumption (e.g., electricity, gas, water).
- Data validation: The captured meter readings undergo validation to ensure accuracy and reliability, checking for anomalies or errors.
- Billing and invoicing: Based on validated meter readings, billing and invoicing processes generate customer invoices, calculating charges according to consumption and applicable rates.
- Payment collection: Processes for collecting payments from customers, which may include various payment methods such as online payments, checks, or direct debits.
- Exception management: Handling exceptions or discrepancies in meter readings, billing, or payments, ensuring timely resolution and accurate financial transactions.
- Customer communication: Communication processes to inform customers about billing, provide details on consumption, and address any concerns or inquiries.
- Record keeping: Maintaining accurate records of meter readings, billing transactions, and customer interactions for documentation, auditing, and regulatory compliance.
- Analytics and reporting: Utilizing analytics tools to gain insights into consumption patterns, billing performance, and key performance indicators for informed decision-making.
What are the pain points of M2C process and how to optimize them?
Optimizing meter-to-cash processes involves leveraging technology and strategic approaches to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Here are key strategies:
| Pain Point | Recommended Technology | Best Practice |
|---|---|---|
| Identity Verification Challenges 🛡️ | Blockchain technology 🌐 | Implement advanced authentication methods such as biometrics or multi-factor authentication. |
| Data Privacy Concerns 📊 | Anonymized or tokenized data 🔒 | Develop robust data protection protocols and comply with relevant privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA). |
| Meter Accuracy 📏 | Smart metering 📊 | Regularly calibrate and maintain meters to ensure accurate readings. |
| Data Security 🔐 | Blockchain or distributed ledger technology 🛡️ | Employ strong encryption methods and secure communication protocols for transmitting meter data. |
| System Compatibility 🖥️ | Cloud-based billing solutions 🌐 | Regularly update billing systems to adapt to new technologies and service options. |
| Communication Challenges 📞 | AI-driven chatbots 🤖 | Use clear and transparent communication channels, such as customer portals and notifications. |
| Payment Security 💳 | Blockchain 🛡️ | Employ robust fraud detection mechanisms and secure payment gateways. |
| Customer Education 🎓 | Incentives for secure payment options 💸 | Provide user-friendly guides and tutorials on available payment methods. |
| Proactive Intervention 🚨 | Collaborate with social services 🤝 | Implement AI/ML algorithms to analyze payment patterns and predict potential nonpayment risks. |
| Customer Services 📞 | Proactive communication strategies 📧 | Establish clear communication channels for customers facing financial challenges. |
| Optimize Resources with Automation 🤖 | End-to-end automation solutions 🔄 | Improve overall operational efficiency by streamlining processes and reducing manual efforts. |
| Optimize Field Operations with Mobile Tools 📱 | Mobile data collection tools and IoT devices 📱 | Increase operational efficiency, minimizing disruptions and delays in field data collection. |
Establishing Customer Relationship
1.) Identity Verification Challenges: Verifying customer identity may be challenging, especially for new customers.
- Best practice: Implement advanced authentication methods such as biometrics or multi-factor authentication.
- Recommended Technology: Leverage blockchain technology for secure and immutable identity verification.
2.) Data Privacy Concerns: Ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations when confirming customer existence through third-party data.
- Best practice: Develop robust data protection protocols and comply with relevant privacy regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA).
- Recommended Technology: Use anonymized or tokenized data when confirming customer existence with third-party sources.
Metering issues
3.) Meter Accuracy: Ensuring the accuracy of meter readings, whether mechanical or digital, is crucial for fair billing.
- Best practice: Regularly calibrate and maintain meters to ensure accurate readings.
- Recommended Technology: Implement smart metering with real-time data transmission for more accurate and efficient billing.
- Tip: Avoid human error by automation! Manual meter readings conducted by field workers are prone to human errors due to factors like fatigue, stress, and challenging reading environments. Therefore, Implement automated meter reading technologies, such as smart meters, to reduce reliance on manual readings.
4.) Data Security: Protecting meter data from unauthorized access or tampering.
- Best practice: Employ strong encryption methods and secure communication protocols for transmitting meter data.
- Recommended Technology: Utilize blockchain or distributed ledger technology for secure and tamper-resistant meter data storage. Also, deploy meter data management systems to manage and gain insights without data leaking and other issues.
Billing errors
5.) System compatibility: Ensuring compatibility of billing systems with evolving technologies and personalized service options.
- Best practice: Regularly update billing systems to adapt to new technologies and service options.
- Recommended Technology: Implement cloud-based billing solutions for scalability and easy integration with emerging technologies.
6.) Communication challenges: Addressing potential communication issues with customers regarding billing details or changes.
- Best practice: Use clear and transparent communication channels, such as customer portals and notifications.
- Recommended Technology: Implement AI-driven chatbots for real-time customer assistance and issue resolution.
- Tip: Enhance billing accuracy with advanced analytics! Inaccurate billing may result from manual readings and lead to customer dissatisfaction. Therefore, Integrate advanced analytics, billing rules engines or billing systems to automate and improve accuracy in billing processes.
Payments issues
7.) Payment Security: Mitigating the risk of fraud or unauthorized transactions, especially with diverse payment methods.
- Best practice: Employ robust fraud detection mechanisms and secure payment gateways.
- Recommended Technology: Explore blockchain for secure and transparent payment transactions.
8.) Customer education: Ensuring customers are aware of and comfortable with the available payment methods.
- Best practice: Provide user-friendly guides and tutorials on available payment methods.
- Recommended Technology: Offer incentives for customers to use more secure and efficient payment options.
Collections problems
9.) Proactive Intervention: Identifying and addressing root causes of nonpayment may be complex and require efficient AI/ML methods.
- Best practice: Implement AI/ML algorithms to analyze payment patterns and predict potential nonpayment risks.
- Recommended Technology: Collaborate with social services to identify and address underlying issues contributing to nonpayment.
10.) Customer services: Maintaining clear communication with customers facing financial challenges to avoid service disconnection.
- Best practice: Establish clear communication channels for customers facing financial challenges.
- Recommended Technology: Implement proactive communication strategies, such as personalized assistance programs and early warning notifications. Make sure customer service representatives address customer inquiries promptly and with a commitment to exceeding their expectations, ensuring a positive and efficient interaction.
Overall inefficiency issues
11.) Optimize resources with end-to-end automation: Manual processes are resource-intensive and may lead to delays and inefficiencies.
- Best practice: Improve overall operational efficiency by streamlining processes and reducing manual efforts.
- Recommended Technology: : Invest in end-to-end automation solutions to optimize resource utilization and enhance operational efficiency.
12.) Optimize field operations with mobile data tools: Operational inefficiencies occur when manual processes disrupt field operations.
- Best practice: Increase operational efficiency, minimizing disruptions and delays in field data collection.
- Recommended Technology: Adopt mobile data collection tools and IoT devices to streamline field operations and improve efficiency.
What are meter to cash solutions?
There can be a variety of tools that can help optimize meter to cash process, including:
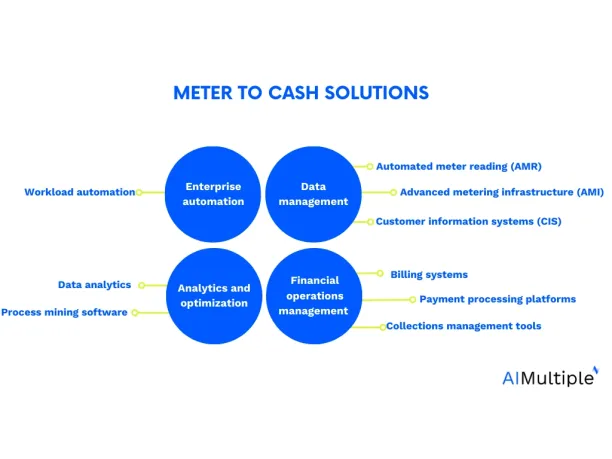
Enterprise automation tools
Such tools can automate end-to-end meter-to-cash process by orchestrating and streamlining each stage of the operational workflow.
1.) Workload automation tools: WLA tools streamline utility workflows by orchestrating tasks such as billing, reporting, and data processing in a unified environment.
Data management
This category focuses on efficient collection, storage, and management of data critical to utility operations. The tools under this category include:
2.) Automated meter reading (AMR):This tool automatically collects consumption data from utility meters.
3.) Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI): This solution enables utilities to interact with smart meters in real time, providing dynamic monitoring and responsive control capabilities.
4.) Customer information systems (CIS): These systems centralize customer account and billing data to improve operational efficiency and accuracy.
Financial operations management
These tools collectively ensure accurate billing, diverse payment methods, and proactive management of overdue payments. Some major examples are:
5.) Billing systems: They calculate charges based on consumption data, generates bills, and facilitate communication with customers.
6.) Payment processing platforms: These tools handle various payment methods, including online payments, credit cards, mobile payments, and others.
7.) Collections management tools: Such tools manage overdue payments, employing predictive analytics and proactive intervention strategies.
Analytics and optimization
These tools leverage data insights for improved decision-making, customer behavior prediction, and process optimization within utility operations, such as:
8.) Data analytics: Data analytics software utilize data for insights, predicts customer behavior, and enhances decision-making, particularly in areas like proactive intervention and personalized services.
9.) Process mining software: This software analyzes, visualizes, and optimizes business processes by tracking and interpreting event logs, enhancing transparency, and streamlining operations. Explore how to deploy process mining for utilities.
Further reading
- Check out our objective meter-to-cash solutions benchmark to find out more on vendors.
- Explore what is SAP meter-to-cash process, what specific tools are offered by SAP and other technologies to deploy.
- Learn how SAP-integrated utility solutions can enhance utility workflows through automation and system connectivity.
- Learn more on workload automation by checking out WLA best practices, SAP workload automation and IT automation software.
External links
- 1. Dobler, M. & Schweinfurth, H. (2022).”International SAP Conference for Utilities Workshop 3: SAP Smart Metering – Deployment Options, New Technologies and Industry Trends.” SAP. Accessed at January 11, 2024.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.