Leveraging AI for IT service management (ITSM) tools supports organizations in terms of:
- operational efficiency,
- proactive maintenance of IT assets,
- scalability,
- improved decision-making, and
- personalization.
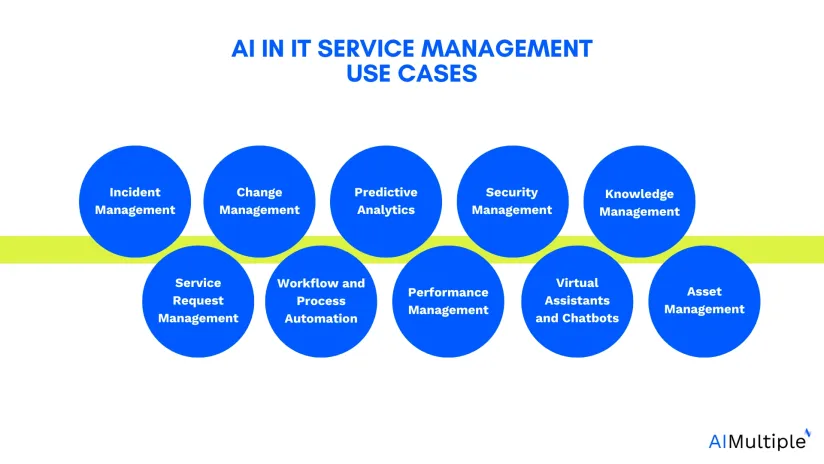
See the top 10 use cases of AI in ITSM, examples, and benefits of leveraging AI in ITSM.
Task management
1. Incident management
Leveraging AI in ITSM plays an important role in incident management through enabling automated ticketing, where AI systems automatically create and categorize tickets based on the content of incoming service requests or incidents.
This process reduces the manual workload on IT staff and ensures that service desk tickets are accurately classified which would lead to quicker resolution times.
Additionally, AI systems utilize machine learning to prioritize incidents based on factors such as severity, impact, and urgency and ensure that critical issues are addressed promptly. This prioritization helps improving service efficiency and minimizing the impact on business operations.
Another application for incident management is AI-powered root cause analysis. By analyzing historical data to identify patterns and predict the root causes of recurring issues, AI in ITSM helps resolve underlying problems more effectively and can reduce the frequency of incidents and enhance system reliability.
Real-life example: BMC HelixGPT
BMC HelixGPT offers real-time insights into root causes by retrieving previous root cause reports to pinpoint connections between past and current incidents, instead of simply correlating incidents.
The tool uses generative and causal AI to identify authentic connections between incidents to deliver clear explanations and solutions for incident and problem management.1
2. Service request management
Service requests are managed through request automation:
AI can automate the handling of routine service requests such as password resets, software installations, and access permissions. By using predefined workflows and intelligent processing, AI systems can manage these requests without human intervention.
For example, when a user submits a request to reset their password, these AI-powered tools can verify the user’s identity through security questions or multi-factor authentication and then proceed to reset the password and notify the user. This reduces the time and effort required by IT staff and provides faster resolution for users.
Automating these routine tasks improves efficiency and also reduces the risk of errors associated with manual processing.
3. Change management
AI brings significant improvements to change management by enhancing the assessment and management of IT changes:
Impact analysis:
Impact analysis with AI evaluates the potential impact of proposed changes on the IT environment. By analyzing historical data and current system configurations, AI can predict potential conflicts and disruptions, helping IT teams to make informed decisions and avoid negative outcomes.
This proactive approach minimizes the risk of downtime and ensures smoother transitions during changes. By providing a detailed impact assessment, AI aids in planning and executing changes more effectively, leading to a more stable and resilient IT infrastructure.
4. Workflow and process automation
Workflow automation:
Workflow automation involves the use of AI to automate routine, repetitive tasks that are typically time-consuming for IT staff.
Process automation:
Process automation takes workflow automation a step further by automating entire processes, from initiation to completion. This can include processes such as software deployment, user onboarding, and system backups. AI tools can manage these processes end-to-end to ensure that each step is executed accurately.
For instance, during the user onboarding process, AI systems can automatically create user accounts, assign appropriate access permissions, and deploy necessary software applications.
Process automation also includes the ability to monitor and optimize processes continuously by analyzing process performance data, identify bottlenecks, and recommend improvements.
Real-life example: SysAid with Ross School of Business
The University of Michigan’s Ross School of Business collaborated with SysAid to support the institution with automated workflows and centralized asset management.
This collaboration led to a 54% reduction in ticket submission time, enhanced collaboration through an extensive knowledge base, and better planning and budgeting through centralized insights. Moving forward, Ross IT plans to extend SysAid’s integration to support more event management activities and build comprehensive employee workflows.2
Real-life example: SysAid with St. George
St. George, the fastest-growing municipality in the US, faced significant IT service management challenges due to rapid expansion and limited resources.
By implementing SysAid, they automated key processes such as patch management, asset tracking, and ticket management, leading to a 90% improvement in software patch success rates and a 20% reduction in Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR).
SysAid’s AI-powered tools, including Copilot’s Chatbot and Emailbot, empowered end-users to resolve issues independently. This transition enabled the IT team to shift from reactive to proactive management, while enhancing productivity.3
Predictive measures and monitoring
5. Predictive analytics
AI models can predict equipment failures before they occur, therefore, can alert IT teams for proactive maintenance. Given that machine learning techniques typically outperform and produce superior results compared to traditional hard computing methods, this predictive approach is crucial.4
By automating workflows, managing schedules, and sending notifications for due tasks, AI-powered ITSM tools aim to extend the lifespan of equipment and ensures uninterrupted IT service management operations.
Utilizing predictive analytics, organizations can forecast future performance and potential failures using historical and real-time data. This process supports decision-making processes and resource allocation for maintenance activities.
Continuous health monitoring of IT infrastructure through AI detects anomalies and provides early warnings to IT teams by enabling them to address potential issues before they escalate.
Real-life example: ServiceNow Predictive Intelligence
ServiceNow Predictive Intelligence leverages historical data to predict outcomes and recommend actions to manage tasks such as categorizing, routing, and prioritizing incidents and requests.
Predictive Intelligence can identify patterns, such as recurring issues or potential bottlenecks, and make suggestions to improve service efficiency.
This feature helps organizations reduce manual work, minimize errors, and improve response times by automating repetitive tasks and predicting issues before they escalate.5
6. Performance management
AI-driven performance management focuses on optimizing IT resources and services by:
Capacity planning, where AI analyzes usage patterns and predicts future resource requirements. This helps organizations in effective capacity planning and resource allocation, ensuring that they can meet future demands without over provisioning.
Performance optimization, where AI tools continuously monitor and optimize the performance of IT services. By analyzing performance metrics in real-time, the AI technology identifies areas for improvement and implements changes to enhance operational efficiency and user satisfaction. This continuous optimization ensures that IT services run smoothly and effectively.
7. Security management
Security management with AI tools focuses on protecting IT systems from threats and ensure compliance via:
Threat detection:
Threat detection includes detecting and responding to security threats in real-time. By analyzing patterns and anomalies, AI can identify potential breaches and take immediate action to mitigate risks. This proactive approach significantly improves the security posture of an organization.
Compliance monitoring:
It includes monitoring IT environments for adherence to policies and regulations. This approach ensures that organizations remain compliant with industry standards and reduces the risk of legal and regulatory issues.
AI-driven compliance monitoring provides continuous oversight, helping organizations maintain a secure and compliant IT infrastructure.
Real-life example: Freshservice with Databricks
Databricks, a leading AI and data analytics company, needed to enhance its IT service operations to reduce downtime and increase scalability.
They chose Freshservice for its no-code capabilities and AI-powered automation. The implementation led to a 23% self-service deflection rate, reducing the workload on IT staff and improving efficiency.
Their collaboration with Freshservice led Databricks to expand its use to eight other departments, including HR and legal, creating a unified hub for employee support.
This transition improved employee experience, supported operations, and reduced IT costs.
Self-service and agent performance
8. Virtual assistants and chatbots
Virtual assistants and chatbots support the ITSM experience by providing personalized and efficient support. AI-powered systems can tailor responses and solutions to individual users based on their roles, preferences, and history and can improve user satisfaction and the effectiveness of IT support.
Sentiment analysis leverages natural language processing (NLP) to allow for the analysis of user feedback to identify areas for improvement in IT services and support. This approach helps organizations to better understand user needs and enhance service quality.
AI-powered chatbots provide 24/7 real-time support, answering common queries and resolving routine issues without human intervention, thus ensuring continuous support availability and reducing wait times.
Additionally, virtual assistants can guide users through troubleshooting steps, offering a more interactive and efficient support experience while reducing the time taken to resolve issues and enhancing overall user satisfaction.
Self-service portals:
Self-service portals leverage AI to analyze user profiles, past interactions, and common issues to offer tailored support. When a user logs in and describes their issue, the AI tools can suggest relevant knowledge base articles, FAQs, or automated solutions that have resolved similar issues in the past.
For instance, if a user frequently requests software installations, the self-service portal can remember this preference and provide quick access to installation procedures or direct links to download the necessary software.
Real-life example: Freshservice Freddy AI
Freshservice‘s Freddy AI supports IT service management processes by integrating three advanced AI features:
Freddy Self-Service provides instant support through AI-powered virtual agents, quickly resolving incidents and service requests.
Freddy Copilot boosts agent productivity by automating responses, offering real-time guidance, and ensuring consistent service delivery.
Freddy Insights delivers proactive insights for decision-making, utilizing AI to gain comprehensive visibility into IT performance and generating actionable recommendations. These capabilities collectively improve efficiency, employee engagement, and overall service quality in IT operations.
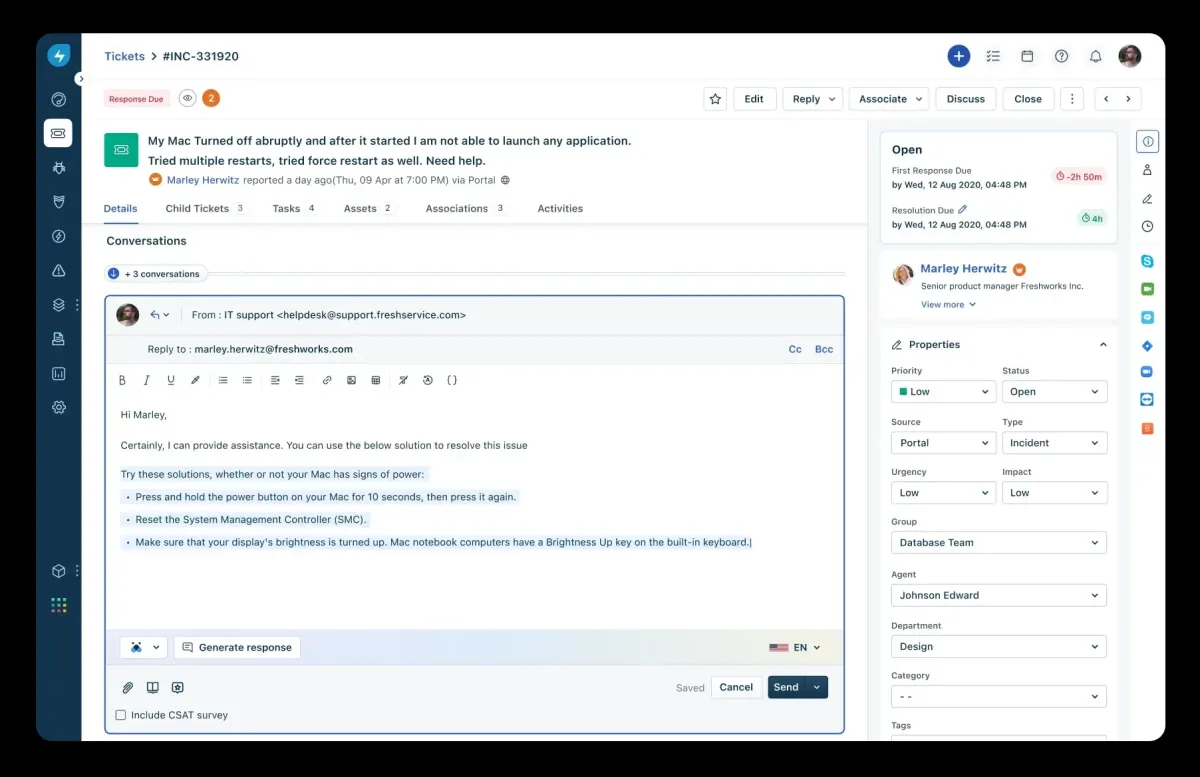
Figure 1: Freshservice Freddy AI copilot dashboard.
Real-life example: Jira Service Management Virtual Agent
Jira Service Management Virtual Agent enhances IT support by automating routine support tasks. This artificial intelligence powered virtual agent integrates with platforms including Slack to provide conversational support, using NLP to understand and respond to user requests, detecting intent, sentiment, and context to deliver personalized interactions.
The virtual agent can handle common issues, answer frequently asked questions, and manage support requests for human agents to focus on more complex tasks. For more complex problems, the virtual agent can create tickets and transition the conversation to a human agent without losing context.
Additionally, the virtual agent leverages Atlassian Intelligence to dynamically generate responses from the existing knowledge base allowing accurate and context-aware answers.
It supports the creation of custom intent flows using templates, and it includes steps including “Ask for information” and “Web request” to gather necessary details and automate actions. The virtual agent’s performance can be monitored and optimized using built-in metrics, ensuring continuous improvement and efficient service delivery.
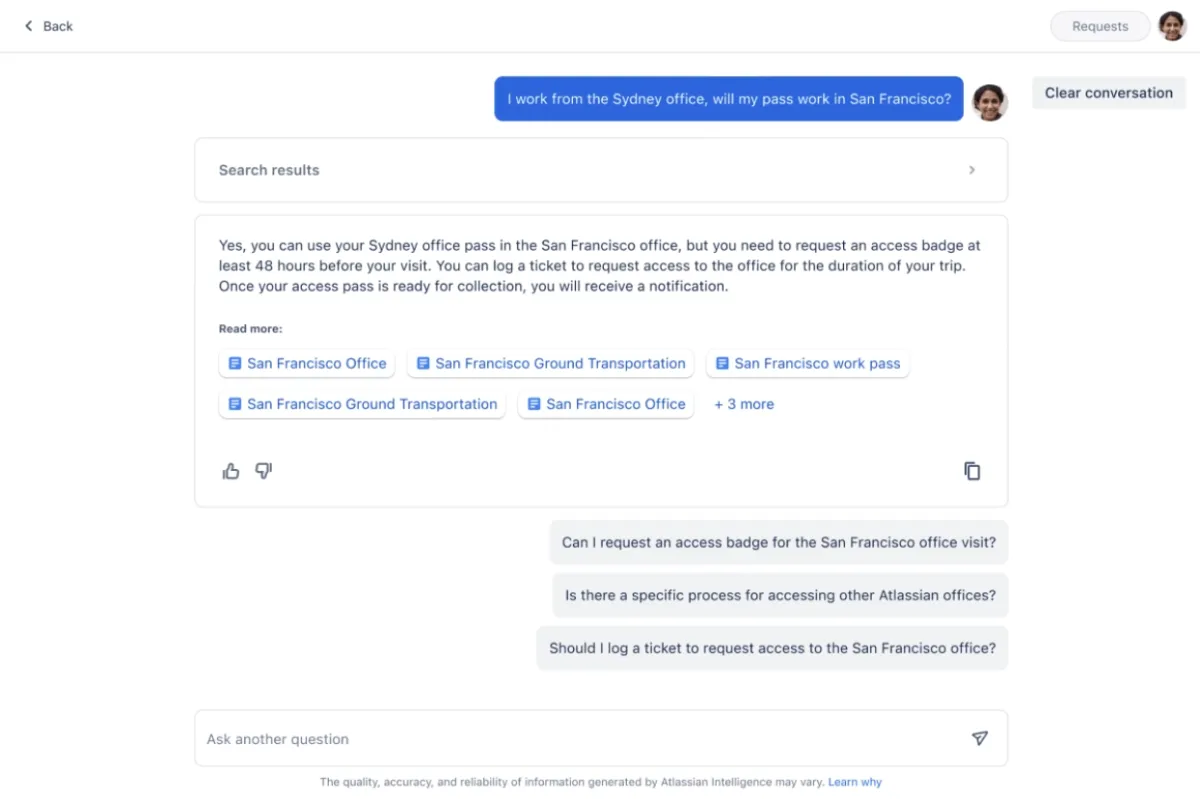
Figure 2: Jira self-service support dashboard.6
9. Knowledge management
Within this domain, AI technologies supports the organization and accessibility of information through:
Content curation:
AI systems can curate and recommend relevant knowledge base articles to both IT staff and end-users based on the context of their queries. This ensures that users receive the required information quickly, and their ability to resolve issues independently increases.
Document analysis:
Document analysis involves analyzing and categorizing large volumes of documentation. This process helps users to find and utilize information while improving the overall efficiency of knowledge management processes.
By organizing documents and creating intuitive categories, AI powered ITSM tools enable easier access to critical information, thereby boosting productivity and reducing the time spent searching for solutions.
Real-life example: Autonomous Knowledge Building with Nebula ITSM
Nebula ITSM automatically gathers data from multiple IT systems, applications, and databases without the need for custom integrations or extensive manual effort.
The system identifies relationships and dependencies within the data to creating a cohesive network of information for the knowledge base.
The system does not require manual curation or intervention from IT staff to maintain or build the knowledge graph. This would result in faster deployment, reduced operational overhead, and the ability to continuously learn and adapt as new data is introduced, without the need for human experts to constantly oversee the process.7
10. Asset management
IT asset management with artificial intelligence focuses on automating and optimizing various aspects of asset lifecycle management.
Automated inventory tracking enables accurate and real-time asset records while reducing manual efforts and improving data accuracy.
AI tools can also predict when assets need maintenance or replacement, thereby optimizes the lifecycle of assets. This predictive approach helps in planning and resource allocation, ensuring that assets are well-maintained and operational.
Additionally, AI tools increase asset security by detecting unauthorized access or unusual activity related to assets and provide an added layer of protection.
AI-driven analytics offer insights into asset utilization, helping organizations make informed decisions and achieve cost savings.
Real-life example: Ivanti Neurons Self-Healing with AI
Self-healing refers to the ability of systems to automatically detect, diagnose, and resolve issues within the IT infrastructure without requiring manual intervention.
The self-healing is enabled through:
- Proactive monitoring: Ivanti Neurons continuously monitors IT assets such as endpoints and servers by using AI to detect anomalies in real-time. It identifies potential issues such as performance degradation, security vulnerabilities, or malfunctions before they escalate.
- Automated diagnostics: When a problem is detected, Ivanti’s AI system automatically runs diagnostics to pinpoint the root cause by analyzing logs, configurations, and patterns.
- Automated remediation: After diagnosing the issue, the system initiates automatic fixes such as patching, restarting services, or running scripts. The process is completed without human intervention to ensure quicker resolutions.
- Endpoint management: Ivanti’s self-healing can be particularly effective for endpoints, monitoring devices and resolving issues such as security vulnerabilities and misconfigurations automatically.8
What are the benefits of leveraging AI in ITSM?
Utilizing AI service management tools offers numerous benefits that can enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and overall effectiveness of IT operations. Here are some key advantages of AI technologies for ITSM:
AI can automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks such as ticket creation, categorization, and routing. This reduces the manual workload on IT staff, allowing them to focus on more complex and strategic tasks.
AI systems can provide consistent responses and actions to minimize human error. This is particularly beneficial in routine tasks such as incident classification, root cause analysis, and solution recommendations.
Chatbots and virtual assistants allow continuous service availability and reduce response times, while improving user satisfaction. These AI tools can scale to handle increasing volumes of requests, which would make them ideal for large and growing organizations
AI systems generate valuable insights from large amounts of data to support IT managers on making informed decisions.
By automating routine tasks and reducing the need for extensive human intervention, artificial intelligence systems can lead to cost savings. These systems optimize resource utilization and reduces the operational costs associated with managing IT services.
External Links
- 1. BMC HelixGPT - BMC Software.
- 2. University of Michigan Case Study - SysAid. SysAid - ITSM Solutions
- 3. St George Case Study - SysAid. SysAid - ITSM Solutions
- 4. Predictive Analytics in IT Service Management (ITSM) - Data Mining and Machine Learning Applications - Wiley Online Library.
- 5. Predictive Intelligence - ServiceNow .
- 6. AI Support: Jira Service Management Virtual Service Agent | Atlassian .
- 7. Nebula ITSM | Accrete. Accrete, Inc
- 8. AI for ITSM | Ivanti.


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.