In a research, IT teams reported spending 70% of their time on repetitive tasks and time-consuming activities.1 IT automation is a broad automation type like robotic process automation (RPA) or intelligent automation that aims to overcome this challenge by automating manual processes and IT operations. By doing so, IT automation software can enable:
- Speed up production of information system
- Reduce human intervention and operational costs
- Increase customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. However, 88% of IT decision-makers and business leaders reported that they experience at least one challenge while scaling automation.2 Such challenges can be prevented if the leaders know how to apply IT automation software in complex tasks and workflows.
Therefore, this article explains IT automation use cases under three categories:
- General
- Industry-specific
- Business function-specific
General applications
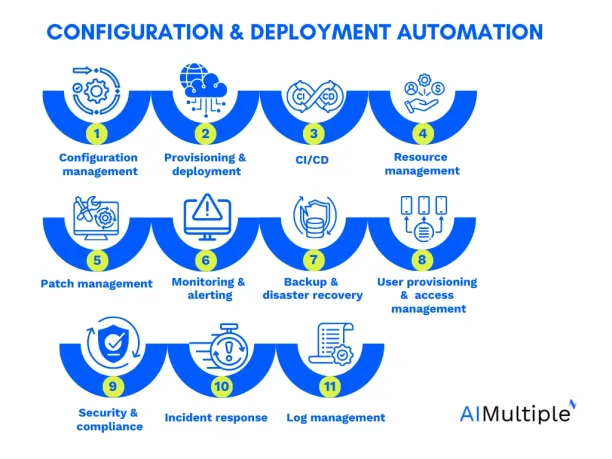
Configuration and deployment automation
Configuration and deployment automation refers to automating the configuring and deploying of software applications, systems, or infrastructure. It involves activities such as:
- Configuration management: It involves setting up and configuring systems, applications, and services.
- Provisioning and deployment: It refers to the deployment of infrastructure, servers, and applications.
- Continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD): It is the build, testing, and deployment process for software development.
- Resource management: includes the provisioning, management, and optimization of physical and virtual resources in these environments:
- Data center resource management
- Cloud server management
- On-premise resource management
- Patch management: It includes the installation of software patches and updates across systems and applications.
- Monitoring and alerting: It requires monitoring system performance, generating alerts, and taking corrective actions.
- Backup and disaster recovery: It refers to the backup, replication, and recovery of critical data and systems.
- User provisioning and access management: It is the creation, modification, and deletion of user accounts and access permissions.
- Security and compliance: It contains security controls, vulnerability scanning, compliance audits, and threat response.
- Incident response: Automating the detection, investigation, and remediation of security incidents and breaches.
- Log management: Automating the collection, analysis, and archiving of system logs for troubleshooting and compliance.
Data management automation
181 zettabytes of data are expected to be generated by 2025, which requires effective data management strategies. Data management automation optimizes management strategies to improve efficiency, accuracy, and reliability in an organization by automating data-related tasks and activities, such as:
- Data integration and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load): With these activities, IT teams extract data from different systems and databases to transform and load data.
- Data backup and restore: It refers to the backup and restoration of data across different storage systems.
- Data cleansing and transformation: IT teams are expected to clean and transform data to improve data quality and consistency in analysis.
Network and Infrastructure Automation
Network and infrastructure automation allows organizations to manage and control networking and infrastructure components automatically. The way automation applies to these tasks and activities involve:
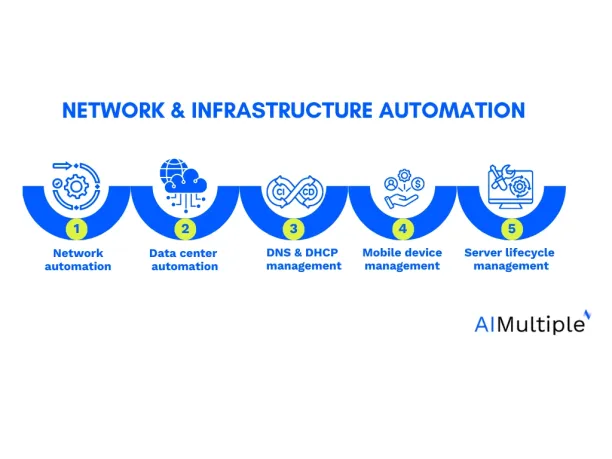
- Network automation: It includes automating repetitive tasks like network configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting tasks.
- Data center automation: Data centers are servers, storage, and networking that can be automatically managed and provided by IT automation tools. Check out some of these data center automation tools.
- DNS and DHCP management: IT automation can help with the management and configuration of DNS (Domain Name System) and DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) services.
- Mobile device management: IT teams can automate mobile device management and security including applications and data. Review our comprehensive list of MDM software.
- Server lifecycle management: It is the automation of servers management throughout their lifecycle, from provisioning to decommissioning.
Process and Workflow Automation
According to McKinsey, 66% of businesses automated processes and workflows at least in one business function. 3 Process automation helps automating individual tasks and activities within a business process, while workflow automation automates the entire process or end-to-end process workflow.
IT automation integrates systems and applications, orchestrates the information and action flow, and replaces routine tasks, approvals, and workflows to improve efficiency and reduce manual effort. Some of the examples include:
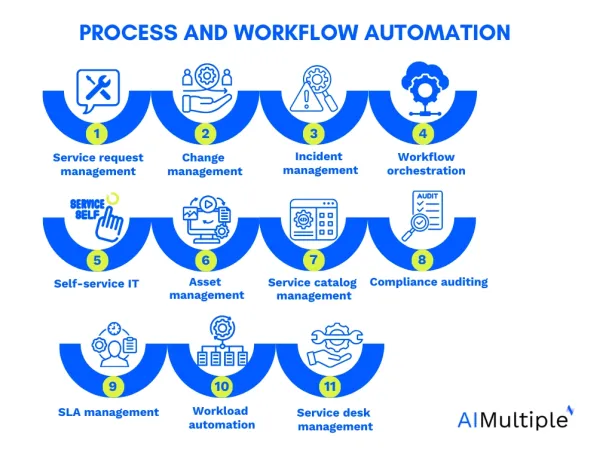
- Service request management: IT teams can handle and fulfill user service requests automatically.
- Change management: Automated change management allows changing approvals to IT systems and infrastructure.
- Incident management: IT automation can track, escalate and resolve IT incidents with minimal human intervention. It can also automate the escalation and notification processes for critical incidents. Compare top incident management tools.
- Workflow orchestration: It automates the coordination and sequencing of complex workflows involving multiple systems and processes.
- Self-service IT: End-users can manage IT resources without manual intervention.
- Asset management: IT teams can automatically track and manage IT assets throughout their lifecycle.
- Service catalog management: It refers to the creation, management, and delivery of IT service catalogs.
- Compliance auditing: Automating the assessment and reporting of compliance with regulatory and industry standards.
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) management: Automating the monitoring and reporting of SLA compliance for IT services.
- Workload automation: Workload automation tools are a type of IT automation tools that can automate the scheduling and execution of batch jobs, complex tasks and processes.
- Service desk automation: It is another type of use case that can automate common service desk tasks, such as ticket routing, categorization, and resolution.
Performance measurement automation
IT automation can help monitor, analyze, and optimize the performance of systems, apps, and infrastructures. Some examples are:
- Capacity planning: It automates resource usage analysis and forecasting to optimize capacity requirements.
- Performance monitoring and optimization: IT teams can leverage automation tools to monitor and tune system performance to ensure optimal operation.
Other IT automation examples
Some IT automation techniques do not fall under specific categories. These tools may utilize software bots and machine learning technologies to automate an organization’s diverse business processes, functions, or activities.
Here are some examples of miscellaneous automation:
- DevOps automation: It refers to automated process of collaboration and integration between development and operations teams for faster software delivery.
- Configuration compliance: Automating the enforcement and validation of system configurations against established standards.
Quality assurance and testing automation
Quality assurance and testing automation refers to the use of automated tools and processes to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of software testing and quality assurance activities. It involves automating tasks within the testing and quality assurance lifecycle, such as:
- Test data generation: IT automation can automate the generation of test data sets to ensure sufficient and representative test coverage.
- Test environment setup: In the testing cycle, test environment setup takes 17% of the time. IT automation can reduce this time by assisting with setting up and configuring test environments, including deploying required software and infrastructure.
- Test result analysis: It refers to the automated analysis of test results, including the identification of failures, defects, and performance issues. Also, it can automate the generation of test reports and documentation to provide comprehensive test coverage and traceability.
- Test script maintenance: It is the automated maintenance and version control of test scripts to ensure accuracy and consistency, which counts for 12% of time if done manually.
- Test execution scheduling: IT automation enables the scheduling and coordination of test executions across different platforms and environments.
- Test coverage analysis: IT automation tools can analyze test coverage to identify gaps and ensure adequate testing of software functionality.
- Test automation: In a research, manual testing is identified as the most time-consuming activity in the testing cycle by 35%. IT automation can tackle this challenge by automatically executing software tests to validate functionality and performance.
Note that all the research and data are extracted from QA automated testing statistics.
Industry-specific use cases
IT automation software can be deployed in different industries to reduce human error, manual processes, and operational costs. There are numerous different automation-related terms to describe automation technologies and these could be referred to as health tech or HR tech in different settings. However, they will involve automating tasks of IT processes.
These industries include:
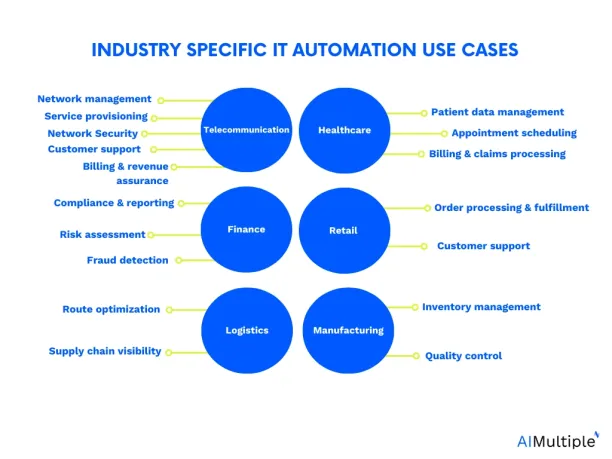
Healthcare
According to McKinsey’s report, 43% of healthcare tasks can be automated to reduce processing costs and human error. 4 The ways IT automation can help the healthcare industry include:
- Patient Data Management: IT automation allows healthcare organizations to update and synchronize patient records across different systems and departments.
- Appointment Scheduling: Automated systems can handle appointment booking, reminders, and rescheduling, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
- Billing and Claims Processing: IT automation can streamline billing and claims processes by minimizing manual data entry and ensuring accurate and timely transactions.
Finance
Finance automation can save ~70% of finance operations costs by lowering mistakes and human intervention. IT automation in finance can streamline following activities:
44. Fraud Detection: IT automation can help detect suspicious activities and patterns in real-time, enabling financial institutions to prevent fraud and enhance security.
45. Compliance and Reporting: It refers to automating regulatory compliance processes, such as generating reports and ensuring data accuracy, can save time and reduce the risk of errors in financial services.
46. Risk Assessment: Finance teams can automatically analyze large volumes of financial data and identify potential risks, such as credit risks or market trends.
Manufacturing
64% of manufacturing-related activities can leverage AI powered automation technologies, such as intelligent automation, robotic process automation, or IT automation tools.5 The ways IT automation can transform manufacturing involve:
47. Inventory management: Manufacturing firms can automate inventory tracking, ordering, and restocking processes to optimize stock levels, reduce costs, and prevent stock-outs.
48. Quality Control: Manufacturing companies play automated systems for real-time monitoring, data collection, and analysis to ensure product quality and identify defects early in the manufacturing process.
Retail and E-commerce
Retailers can lower IT inefficiencies and data inaccuracy by increasing automation use. The way an automated system can help retail and e-commerce platforms include:
49. Order Processing and Fulfillment: It automates order processing, inventory updates, and fulfillment workflows to accelerate order handling and reduce errors.
50. Customer Support: IT automation solutions can handle common customer inquiries, provide support, and improve response times.
Logistics / supply chain
IT automation types like workload automation and data warehouse automation software can help logistics firms with:
51. Route Optimization: IT automation tools can automate the process of selecting optimal routes based on real-time data, such as traffic conditions, to improve efficiency and reduce delivery times.
52. Supply chain visibility: Logistics firms can use IT automation to track and monitor shipments, provide real-time customer updates, and enhance overall supply chain visibility.
Telecommunication
Telecom companies can benefit from IT automation in several ways. Here are a few examples:
53. Network management: Automation can assist in managing and monitoring telecom networks, improving efficiency, and reducing manual errors. It can involve provisioning, configuration management, and network troubleshooting. Automated network management systems can identify and resolve network issues in real-time, leading to faster problem resolution and improved network performance.
54. Service provisioning: Automating service provisioning in telecom can streamline processes such as order management, new service activation, and provisioning resources like phone lines, broadband connections, or cloud services. Reducing manual intervention can accelerate service delivery, improve customer satisfaction, and minimize errors.
55. Customer support: Automation can enhance customer support services in the telecom industry by automatically handling basic customer inquiries, troubleshooting, and checking ticket status. Such automated ticketing systems can categorize and route customer issues to the appropriate support teams, ensuring faster response times and efficient issue resolution.
56. Billing and revenue assurance: IT automation can improve telecom companies’ billing accuracy and revenue assurance processes. Automated systems can gather customer data to generate accurate invoices and reconcile billing information with service provisioning and usage data. This helps reduce billing errors, identify revenue leakage, and improve financial processes.
57. Network Security: Automated systems can continuously monitor network traffic, detect anomalies, and trigger security alerts. Additionally, automated patch management and vulnerability scanning can help ensure that network infrastructure and systems are up-to-date and protected against potential security threats.
Business functions-specific
The major business functions that can leverage IT automation include:
HR
HRIT automation can significantly streamline and enhance HR processes such as employee onboarding process, recruitment process, and performance management. According to Mckinsey, 56% of HR tasks can be automated to decrease processing costs and time.6 Here are some ways it can be used:
58. Creating user Accounts: IT automation can create and provide new user account for a new employee, including:
59. Equipment and Software Setup: Automated workflows can assist and set up the necessary equipment for a higher employee experience, such as:
60. Onboarding workflows: IT automation can facilitate the creation and execution of standardized onboarding workflows, with onboarding tasks like digital forms completion (e.g., tax forms, emergency contacts), training module assignments, and task reminders for HR teams. Automated notifications can be sent to new employees to ensure a smooth employee onboarding process.
61. Self-Service Portals: Self-service portals or intranet platforms with automation capabilities can allow new employees to access essential information, resources, and training materials at their convenience. Automated workflows within this portal may guide employees through the process, provide relevant documentation, and facilitate communication with HR and IT departments.
62. IT Policy Compliance: Automation can help ensure that new employees are aware of and compliant with IT policies and security measures.
63. Recruitment process: By leveraging IT automation in recruitment processes, HR teams can automatically scan job boards, career websites, and social media platforms to source candidates, screen resumes based on predetermined rules to shortlist candidates, manage applicant information to track applicants and schedule interviews.
Sales
With IT automation, sales and marketing teams can:
- Increase customer retention
- Lead to higher an uplift by 10% 7
- Improve customer experience by 43% 8
- Handle customer onboarding process with minimal human intervention by automating.
64. Lead generation and management: IT automation can assist in lead generation by automating the collection and organization of prospect data. It can automatically capture leads from various sources such as websites, social media, and email campaigns. Automation can also help in lead scoring and lead nurturing, ensuring that sales teams focus their efforts on the most promising leads.
65. Customer relationship management (CRM): Automation can be used to simplify CRM tasks. It can automate data entry, update customer information, and provide real-time insights on customer interactions. By automating routine CRM tasks, sales representatives can spend more time on building relationships and closing deals.
66. Sales process and workflow automation: IT automation can streamline the sales process, other processes, and workflows, such as the procurement process or purchase orders process, by automating repetitive tasks such as sending follow-up emails, generating quotes, and managing contracts. Automated workflow can improve customer experience and reduce human errors.
67. Reporting and analytics: IT automation tools can collect and consolidate real-time and historical data from various sources, providing actionable insights into sales performance. As a result, a sales team can make data-driven decisions to enhance their customer retention rate.
Further reading
Explore more on IT automation types by checking out:
Assess different vendors for each IT automation type by checking out our comprehensive and data-driven lists:
- IT Automation software
- Workload automation tools
- Batch scheduling software
- Data warehouse automation tools
- Service orchestration and automation platforms
- Enterprise job scheduler
If you have more questions, we can always help:
External links
- 1. Flip the ratio: Taking IT from bottleneck to battle ready | McKinsey. McKinsey & Company
- 2. “The State of Process Automation.” Camunda. 2020. Revisited June 15, 2023.
- 3. The imperatives for success with automation technologies | McKinsey. McKinsey & Company
- 4. Making healthcare more affordable through scalable automation | McKinsey. McKinsey & Company
- 5. Human + machine: A new era of automation in manufacturing | McKinsey. McKinsey & Company
- 6. Human resources in the age of automation.
- 7. Sales automation: The key to boosting revenue and reducing costs | McKinsey. McKinsey & Company
- 8. Marketing automation main benefits 2022| Statista. Statista

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.