Speech recognition, also known as automatic speech recognition (ASR), enables seamless communication between humans and machines. This technology empowers organizations to transform human speech into written text. Speech recognition technology can revolutionize many business applications, including customer service, healthcare, finance and sales.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explain speech recognition, exploring how it works, the algorithms involved, and its applications in various industries.
If you require training data for your speech recognition system, here is a guide to finding the right speech data collection services.
What is speech recognition?
Speech recognition, also known as automatic speech recognition (ASR), speech-to-text (STT), and computer speech recognition, is a technology that enables a computer to recognize and convert spoken language into text.
Speech recognition technology uses AI and machine learning models to accurately identify and transcribe different accents, dialects, and speech patterns.
What are the features of speech recognition systems?
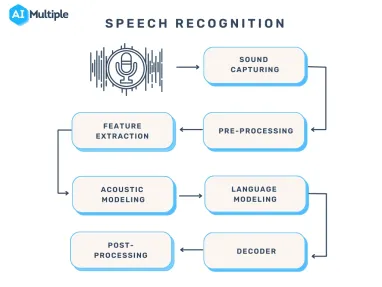
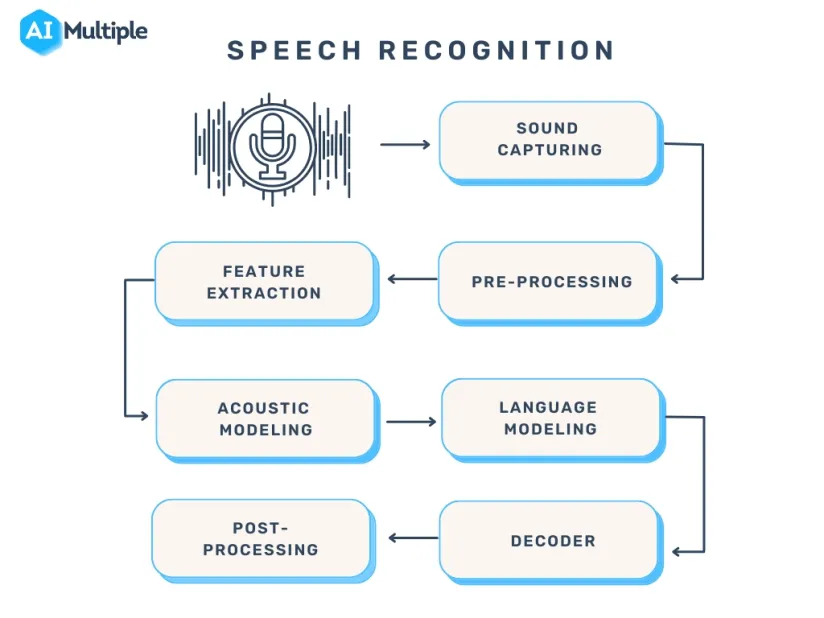
Speech recognition systems have several components that work together to understand and process human speech. Key features of effective speech recognition are:
- Audio preprocessing: After you have obtained the raw audio signal from an input device, you need to preprocess it to improve the quality of the speech input The main goal of audio preprocessing is to capture relevant speech data by removing any unwanted artifacts and reducing noise.
- Feature extraction: This stage converts the preprocessed audio signal into a more informative representation. This makes raw audio data more manageable for machine learning models in speech recognition systems.
- Language model weighting: Language weighting gives more weight to certain words and phrases, such as product references, in audio and voice signals. This makes those keywords more likely to be recognized in a subsequent speech by speech recognition systems.
- Acoustic modeling: It enables speech recognizers to capture and distinguish phonetic units within a speech signal. Acoustic models are trained on large datasets containing speech samples from a diverse set of speakers with different accents, speaking styles, and backgrounds.
- Speaker labeling: It enables speech recognition applications to determine the identities of multiple speakers in an audio recording. It assigns unique labels to each speaker in an audio recording, allowing the identification of which speaker was speaking at any given time.
- Profanity filtering: The process of removing offensive, inappropriate, or explicit words or phrases from audio data.
What are the different speech recognition algorithms?
Speech recognition uses various algorithms and computation techniques to convert spoken language into written language. The following are some of the most commonly used speech recognition methods:
- Hidden Markov Models (HMMs): Hidden Markov model is a statistical Markov model commonly used in traditional speech recognition systems. HMMs capture the relationship between the acoustic features and model the temporal dynamics of speech signals.
- Natural language processing (NLP):NLP is a subfield of artificial intelligence that focuses on the interaction between humans and machines through natural language. Some of the key roles of NLP in speech recognition systems:
- Estimate the probability of word sequences in the recognized text
- Convert colloquial expressions and abbreviations in a spoken language into a standard written form
- Map phonetic units obtained from acoustic models to their corresponding words in the target language.
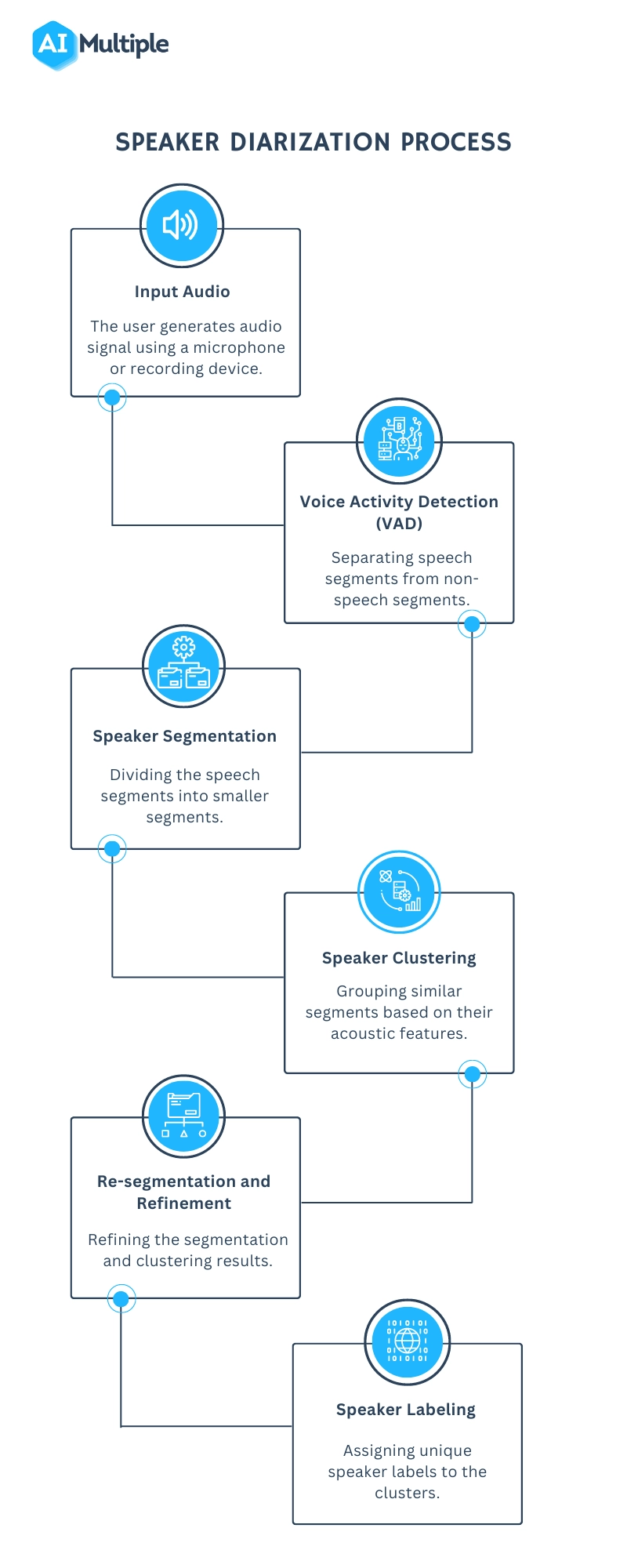
- Speaker Diarization (SD): Speaker diarization, or speaker labeling, is the process of identifying and attributing speech segments to their respective speakers (Figure 1). It allows for speaker-specific voice recognition and the identification of individuals in a conversation.
Figure 1: A flowchart illustrating the speaker diarization process
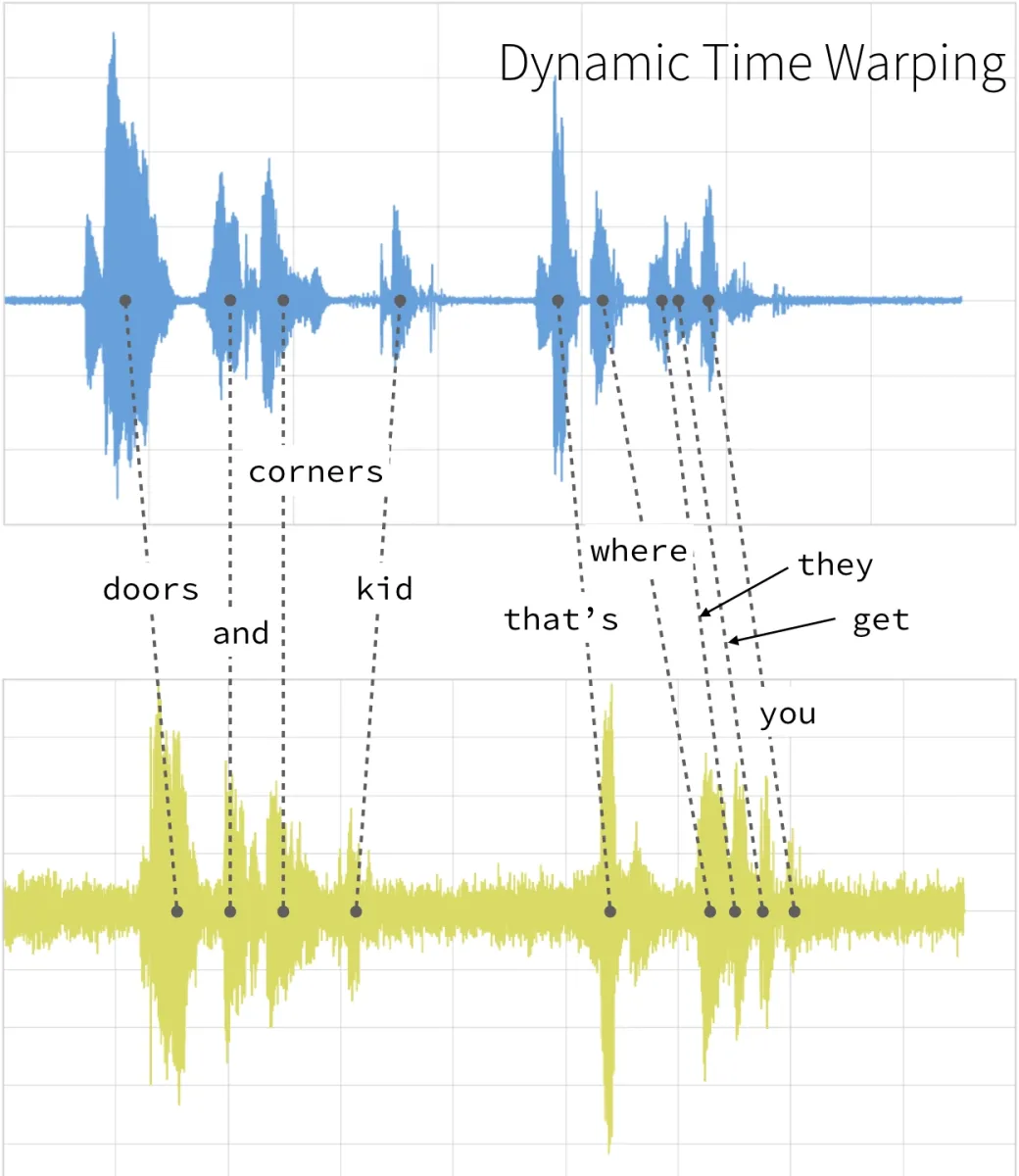
- Dynamic Time Warping (DTW): Speech recognition algorithms use Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) algorithm to find an optimal alignment between two sequences (Figure 2).
Figure 2: A speech recognizer using dynamic time warping to determine the optimal distance between elements
5. Deep neural networks: Neural networks process and transform input data by simulating the non-linear frequency perception of the human auditory system.
6. Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC): It is a training objective introduced by Alex Graves in 2006. CTC is especially useful for sequence labeling tasks and end-to-end speech recognition systems. It allows the neural network to discover the relationship between input frames and align input frames with output labels.
Speech recognition vs voice recognition
Speech recognition is commonly confused with voice recognition, yet, they refer to distinct concepts. Speech recognition converts spoken words into written text, focusing on identifying the words and sentences spoken by a user, regardless of the speaker’s identity.
On the other hand, voice recognition is concerned with recognizing or verifying a speaker’s voice, aiming to determine the identity of an unknown speaker rather than focusing on understanding the content of the speech.
What are the challenges of speech recognition with solutions?
While speech recognition technology offers many benefits, it still faces a number of challenges that need to be addressed. Some of the main limitations of speech recognition include:
Acoustic Challenges:
- Accents and dialects: Accents and dialects differ in pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar, making it difficult for speech recognition applications to recognize speech accurately.
- Assume a speech recognition model has been primarily trained on American English accents. If a speaker with a strong Scottish accent uses the system, they may encounter difficulties due to pronunciation differences. For example, the word “water” is pronounced differently in both accents. If the system is not familiar with this pronunciation, it may struggle to recognize the word “water.”
Solution: Addressing these challenges is crucial to enhancing speech recognition applications’ accuracy. To overcome pronunciation variations, it is essential to expand the training data to include samples from speakers with diverse accents. This approach helps the system recognize and understand a broader range of speech patterns.
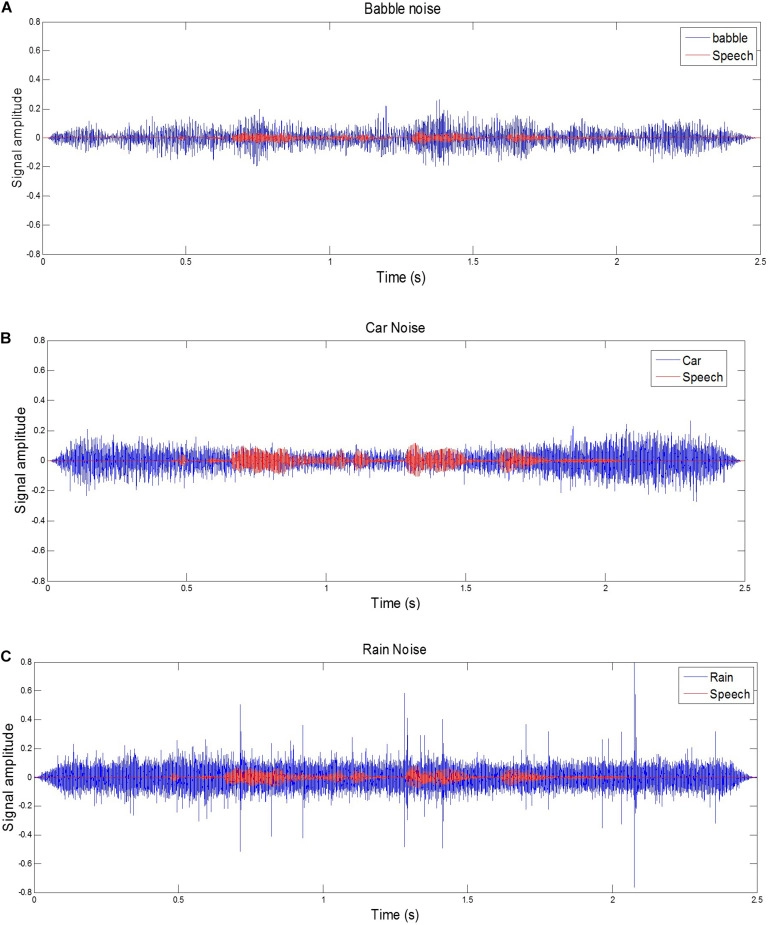
- Background noise: Background noise (e.g., traffic, cross-talk) makes distinguishing speech from background noise difficult for speech recognition applications (Figure 3).
Solution: Pre-processing techniques can be used to reduce background noise in speech recognition, which can help improve the performance of speech recognition models in noisy environments.- For instance, you can use data augmentation techniques to reduce the impact of noise on audio data. Data augmentation helps train speech recognition models with noisy data to improve model accuracy in real-world environments.
Figure 3: Examples of a target sentence (“The clown had a funny face”) in the background noise of babble, car and rain.
Linguistic Challenges:
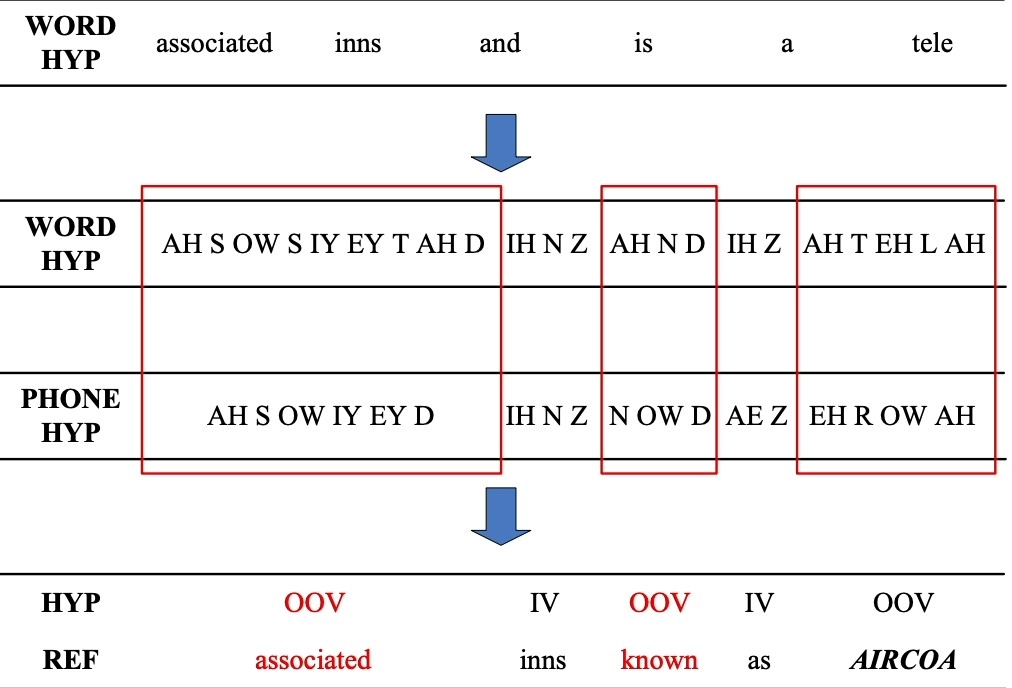
- Out-of-vocabulary words: Since the speech recognizers model has not been trained on OOV words, they may incorrectly recognize them as different or fail to transcribe them when encountering them.
Figure 4: An example of detecting OOV word
Solution: Word Error Rate (WER) is a common metric that is used to measure the accuracy of a speech recognition or machine translation system. The word error rate can be computed as:
Figure 5: Demonstrating how to calculate word error rate (WER)

- Homophones: Homophones are words that are pronounced identically but have different meanings, such as “to,” “too,” and “two”.
Solution: Semantic analysis allows speech recognition programs to select the appropriate homophone based on its intended meaning in a given context. Addressing homophones improves the ability of the speech recognition process to understand and transcribe spoken words accurately.
Technical/System Challenges:
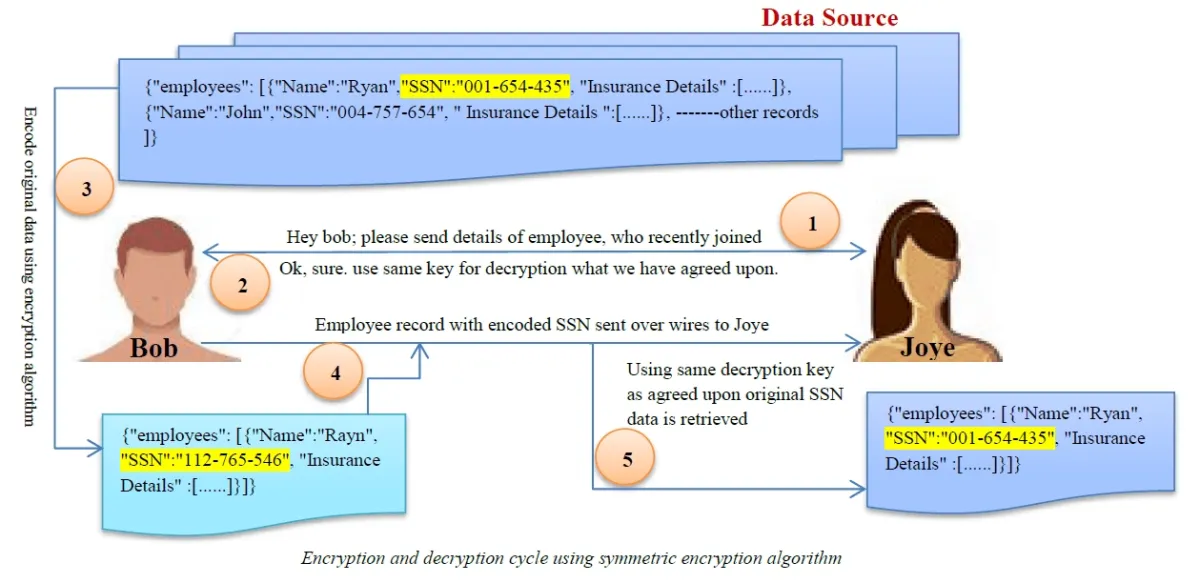
- Data privacy and security: Speech recognition systems involve processing and storing sensitive and personal information, such as financial information. An unauthorized party could use the captured information, leading to privacy breaches.
Solution: You can encrypt sensitive and personal audio information transmitted between the user’s device and the speech recognition software. Another technique for addressing data privacy and security in speech recognition systems is data masking. Data masking algorithms mask and replace sensitive speech data with structurally identical but acoustically different data.
Figure 6: An example of how data masking works
- Limited training data: Limited training data directly impacts the performance of speech recognition software. With insufficient training data, the speech recognition model may struggle to generalize different accents or recognize less common words.
Solution: To improve the quality and quantity of training data, you can expand the existing dataset using data augmentation and synthetic data generation technologies.
13 speech recognition use cases and applications
In this section, we will explain how speech recognition revolutionizes the communication landscape across industries and changes the way businesses interact with machines.
Customer Service and Support
- Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems: Interactive voice response (IVR) is a technology that automates the process of routing callers to the appropriate department. It understands customer queries and routes calls to the relevant departments. This reduces the call volume for contact centers and minimizes wait times. IVR systems address simple customer questions without human intervention by employing pre-recorded messages or text-to-speech technology. Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) allows IVR systems to comprehend and respond to customer inquiries and complaints in real time.
- Customer support automation and chatbots: According to a survey, 78% of consumers interacted with a chatbot in 2022, but 80% of respondents said using chatbots increased their frustration level.
- Sentiment analysis and call monitoring: Speech recognition technology converts spoken content from a call into text. After speech-to-text processing, natural language processing (NLP) techniques analyze the text and assign a sentiment score to the conversation, such as positive, negative, or neutral. By integrating speech recognition with sentiment analysis, organizations can address issues early on and gain valuable insights into customer preferences.
- Multilingual support: Speech recognition software can be trained in various languages to recognize and transcribe the language spoken by a user accurately. By integrating speech recognition technology into chatbots and Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems, organizations can overcome language barriers and reach a global audience (Figure 7). Multilingual chatbots and IVR automatically detect the language spoken by a user and switch to the appropriate language model.
Figure 7: Showing how a multilingual chatbot recognizes words in another language
- Customer authentication with voice biometrics: Voice biometrics use speech recognition technologies to analyze a speaker’s voice and extract features such as accent and speed to verify their identity.
Sales and Marketing:
- Virtual sales assistants: Virtual sales assistants are AI-powered chatbots that assist customers with purchasing and communicate with them through voice interactions. Speech recognition allows virtual sales assistants to understand the intent behind spoken language and tailor their responses based on customer preferences.
- Transcription services: Speech recognition software records audio from sales calls and meetings and then converts the spoken words into written text using speech-to-text algorithms.
Automotive:
- Voice-activated controls: Voice-activated controls allow users to interact with devices and applications using voice commands. Drivers can operate features like climate control, phone calls, or navigation systems.
- Voice-assisted navigation: Voice-assisted navigation provides real-time voice-guided directions by utilizing the driver’s voice input for the destination. Drivers can request real-time traffic updates or search for nearby points of interest using voice commands without physical controls.
Healthcare:
- Medical transcription:Medical transcription, also known as MT, is the process of converting voice-recorded medical reports into a written text document. The following are the main steps in the medical transcription process:
- Recording the physician’s dictation
- Transcribing the audio recording into written text using speech recognition technology. Advanced speech recognition systems may also include speaker diarization. It identifies and segments different speakers in an audio recording.
- Editing the transcribed text for better accuracy and correcting errors as needed
- Formatting the document in accordance with legal and medical requirements.
- Virtual medical assistants: Virtual medical assistants (VMAs) use speech recognition, natural language processing, and machine learning algorithms to communicate with patients through voice or text. Speech recognition software allows VMAs to respond to voice commands, retrieve information from electronic health records (EHRs) and automate the medical transcription process.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR) integration: Healthcare professionals can use voice commands to navigate the EHR system, access patient data, and enter data into specific fields.
Technology:
- Virtual agents: Virtual agents utilize natural language processing (NLP) and speech recognition technologies to understand spoken language and convert it into text. Speech recognition enables virtual agents to process spoken language in real-time and respond promptly and accurately to user voice commands.
Further reading
External Links
- 1. Understanding Dynamic Time Warping | Databricks Blog.
- 2. The Influence of the Type of Background Noise on Perceptual Learning of Speech in Noise - PMC .
- 3. Word error rate - Wikipedia. Contributors to Wikimedia projects

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.