According to McKinsey, only about half of supply chain leaders rate their planning data quality as sufficient or high, underscoring the critical role of accurate master data in enabling visibility, transparency, and practical scenario planning.1 Yet, managers continue to face challenges in sharing data effectively across supply chain partners.
Explore the key barriers in supply chain data sharing and actionable solutions to help managers overcome these challenges and drive supply chain innovation.
What does data sharing mean for supply chains?
Data sharing in the supply chain refers to the process where different entities involved in the supply chain, such as manufacturers, distributors, retailers, and logistics providers, exchange information.
This information can encompass a wide array of data points, such as:
- Inventory levels
- Demand forecasts
- Sales data
- Production plans
- Delivery schedules and more.
Sharing this data can enhance transparency, increase operational efficiency, and improve decision-making across the supply chain.
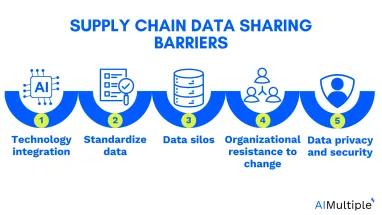
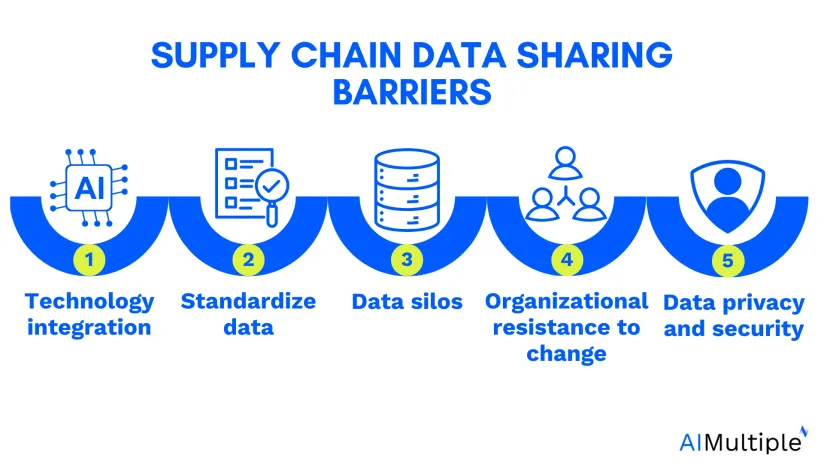
Technical barriers
1. Technology integration
Diverse technological infrastructures may pose significant integration challenges. For instance, a retailer may use one system for inventory management while its supplier uses another, which can complicate real-time data sharing. These misalignments lead to inefficiencies, delayed decision-making, and increased operational costs.
Solutions:
- Leverage low-code or no-code platforms to bridge technological gaps.
- Upgrade legacy infrastructure with interoperable tools that enable real-time data exchange.
2. Data standardization
With multiple entities involved, the data can be presented in various formats and structures, creating problems in assimilation and analysis. The lack of data standardization, in terms of data quality and formats, is a substantial impediment to effective data sharing.
Solutions:
- Adopt industry-wide frameworks, such as electronic data interchange (EDI) or GS1 standards.
- Align on common data quality metrics and reporting standards.
Organizational and cultural barriers
3. Data silos
One significant barrier to sharing data in your supply chain is the existence of data silos. A data silo occurs when data is isolated and hoarded within different departments or organizations, making it inaccessible to others who could potentially benefit from it.
Any organization can develop data silos without a strategic plan for data management. For instance, a manufacturer may not share its production plans with its distributor, leading to overproduction or shortages.
Solutions:
- Implement integrated ERP systems to enable cross-department visibility.
- Set cross-functional KPIs that reward collaborative data sharing.
4. Organizational resistance to change
In supply chain management, an organization’s culture is a significant determinant of how readily data sharing is adopted. If a company’s culture doesn’t endorse openness and collaboration, data-sharing initiatives may be met with resistance.
Employees could view sharing data with other entities in the supply chain as risky, fearing that it might expose vulnerabilities or dilute their unique contribution.
Cultural inertia and fear of transparency within organizations often damage data sharing. Resistance may be caused by concerns about exposing internal processes or perceived risks in collaboration.
Solutions:
- Drive cultural change through leadership support and training.
- Incentivize collaboration and highlight success stories of data-sharing partnerships.
- Promote cross-company workshops to foster trust and alignment.
Legal and regulatory barriers
5. Data privacy and security concerns
Businesses often hesitate to share data due to concerns over data privacy and potential misuse. This becomes even more relevant given the increasingly strict data protection laws and the rising incidents of cyber threats. Another reason is that companies do not wish to disclose their internal operations and share data related to their carbon emissions, labor management practices, sourcing of raw materials, and other relevant information.
Solutions:
- Leverage blockchain for secure, transparent data sharing.
- Implement encryption and multi-layered security protocols.
- Create transparent agreements, such as NDAs, that build trust among partners.
What are supply chain data sharing best practices?
To increase efficiency and foster collaboration, organizations can adopt the following strategies to share data effectively and securely within the supply chain network:
1. Adopt a collaborative mindset
Collaborate with suppliers beyond the tier 2 network. Consider a global company whose various teams (purchasing, logistics, warehouse, and sales) function in silos.
The purchasing team has valuable data about vendor performance and delivery times that the logistics team could use to better plan transportation routes and schedules.
Similarly, the sales team has valuable insights into customer buying patterns and seasonal trends that can help the warehouse team manage inventory efficiently.
Recognizing the potential benefits of collaboration, the SCM team adopts a shared mindset. They implement an integrated SCM system that enables each team to access and utilize data from the others.
The outcome is a cohesive relationship where all teams can make informed decisions based on shared data and information. This results in improved overall supply chain performance with:
- Improved forecasting
- Optimized inventory levels
- More efficient transportation schedules
- Better service to their customers.
2. Ensure data security
Take the case of a logistics and supply chain management company. They handle sensitive data like vendor details, transportation routes, and delivery schedules. To protect this information, the company implements multi-factor authentication for system access and encrypts data both at rest and in transit. They also anonymize the data to safeguard confidentiality further.
Additionally, the company is transparent about its data security practices, sharing updates with its different stakeholders and partners. This transparency helps build trust, ensuring a reputation for secure supply chain operations.
3. Establish clear data-sharing agreements
Consider a group of companies in a supply chain network sharing data for improved operational efficiency. To ensure all members understand their data-sharing roles and responsibilities, they establish a detailed data-sharing agreement.
The agreement outlines what data should be shared, how it should be shared, and who is authorized to access it. It also outlines data usage guidelines, protection measures, and penalties for data misuse. This clear agreement promotes a harmonious and productive relationship among the network members, fostering trust and mutual growth.
FAQ
What is supply chain information sharing?
Supply chain information sharing refers to the collaborative exchange of data among various stakeholders within the supply chain industry, aimed at enhancing supply chain performance, resilience, and efficiency. It involves sharing supply chain data across supply chain networks, including freight logistics optimization, to address supply chain disruptions and build a more resilient supply chain.
By sharing data, supply chain managers can enhance information exchange, reduce costs, and support businesses in achieving a competitive edge. This process leverages technology, such as artificial intelligence and information technology, to enhance accuracy and efficiency in goods movement chains.
Initiatives like the Freight Logistics Optimization Works Flow, supported by public and private sector entities like the White House and companies like Land O Lakes and Georgia Ports Authority, and international conferences like the one in Long Beach, aim to establish foundational freight digital infrastructure and promote open data sharing among different stakeholders.
Accurate information shared across the supply chain, from raw materials to end-to-end logistics, reduces costs and mitigates carbon emissions, contributing to a more sustainable supply chain ecosystem.
Moreover, by participating in pilot programs and adopting digital transformation strategies, companies can unlock additional benefits and realize the actual value of supply chain information sharing, gaining a competitive edge in the global marketplace.
What data can be shared to enhance the supply chain?
Sharing data related to real-time inventory levels, transportation schedules, and demand forecasts can significantly improve the overall supply chain. This information exchange supports better decision-making across supply chain networks, enhances supply chain resilience, and enables more efficient freight logistics optimization.
By sharing accurate data, supply chain stakeholders can mitigate disruptions, reduce costs, and improve the efficiency of goods movement chains. Additionally, access to timely data enables proactive measures to address supply chain issues, ultimately supporting businesses in gaining a competitive advantage and reducing carbon emissions.
External Links
- 1. Supply chain disruption and resilience | McKinsey. McKinsey & Company



Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.