The aviation sector, as a whole, can gain from the adoption of RPA tools in areas including airport administration, ticket sales, and aircraft navigation.
The aviation industry is ripe for automation thanks to the never-ending flow of data that could be turned into actionable insight. For instance, a single Boeing 737 voyage from New York to Los Angeles generates 20 terabytes of data every hour (Figure 1).
In this article we explain how RPA can transform the aviation industry by highlighting its top 8 real-life use cases.

What is RPA in the aviation industry?
RPA in the aviation industry is using automation software bots to automate the functioning of different areas, such as airport administration, ticket sales, quality assurance, customer relations, aircraft navigation, air traffic control, and more.
What are the use cases of RPA in the aviation industry?
1. Invoicing
Airlines partner with hundreds of international travel agencies to sell airline tickets. So the list of invoices they receive comes from all over the world and in various formats. Processing all these manually takes time, effort, and is subject to manual errors.
Airlines can leverage RPA in their invoice processing to automate the receival, approval, and logging of the invoices. Moreover, they can program the bot to reformat the data if it comes in an unstructured or atypical way.
Case study:
A Norwegian airport operator had a staff of only 80 people, and had to find a more efficient way to use its scarce human resources than delegate them to process invoices. By leveraging RPA solutions, they were able to fully-automate the processing of more than 100,000 invoices annually, speeding up the process by 90%, equal to having 3 full-time employees.
2. Customer relations
With delayed flights, cramped seats, lost baggages, cold dishes, and unruly fellow passengers, there’s no limit to the number of complaints that airlines receive.
In 2020 alone, US airlines received 102,550 complaints, a 568% increase from 2019. Sorting, categorizing, and addressing all these complaints which vary in format, length, and degree of importance is a time-consuming and repetitive task.
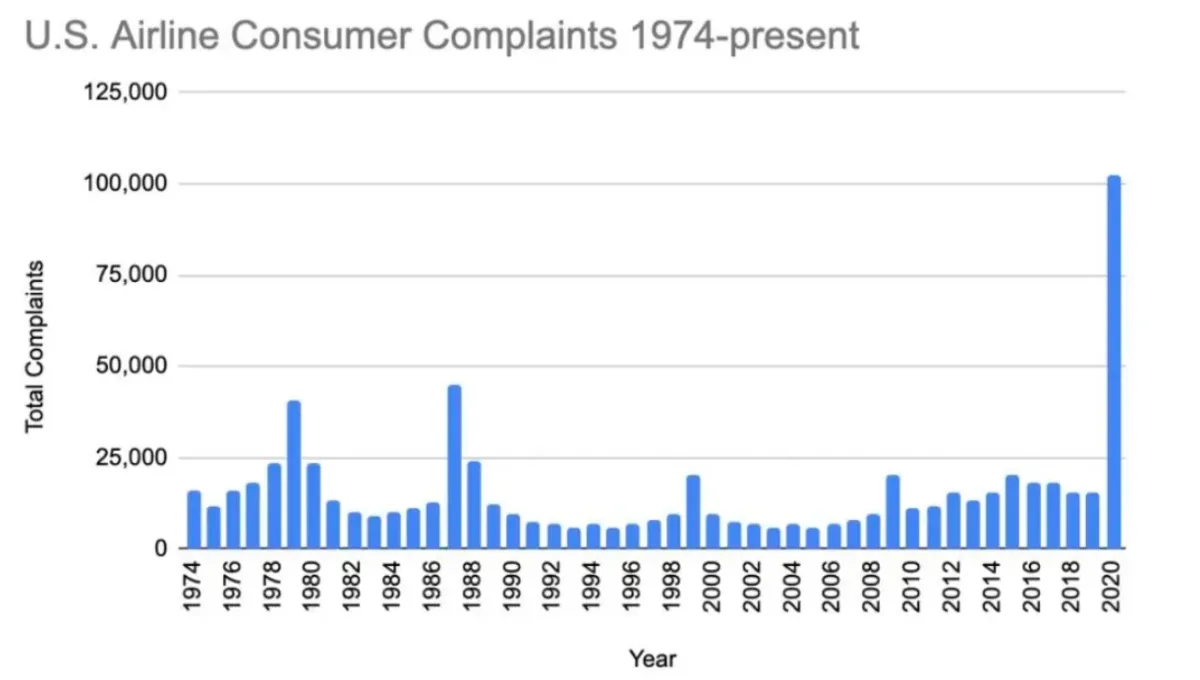
Airlines can leverage NLP, OCR, and RPA to let bots read the complaints, assess the degree of importance, understand the category that they fall into, and automatically send them to the customer relations staff’s email to ERP for them to take action on.
Watch how the German airliner, Lufthansa, uses NLP and AI technology to understand the context of complaints, sort them appropriately, and direct them to the relevant department for resolution:
Case study:
The Norwegian airport operator mentioned above was receiving 6,000 complaints a year, which had to be handled manually. Thanks to RPA, they were able to register the complaint’s data, sort them, create a case for each with a ticket, and refer them to the correct personnel.
The other benefit of automating the handling of customer complaints was that the airport operator saw a reduction in the number of abandoned cases that were previously falling through the cracks because of the staff being overwhelmed.
3. Air traffic control
Poor air traffic control (ATC) not only causes delays and ignites the fury of passengers, but also induces economical costs. The Economist estimates that flight delays and cancellations caused by ATC’s mismanagement had cost the European economy almost $21B in 2017.
What is more surprising amongst all these is that delays caused by ATC – aggravated by 60% due to staff shortage, 25% because of weather conditions, and 14% by workers’ strikes – were approximately twice the delays caused by other factors.
Automating flight schedules by exchanging real-time status data between the aircrafts on the ground and on the sky, ATC, the weather stations, fuelling stations, flight engineers, and other parties through RPA and OLDI (online data interchange) can reduce delays, make schedules more on-time, and reduce the workload of the staff.
Case study:
In 2015, the Heathrow Airport used ML technology enabled with RPA to exchange airplanes’ flight data in real time to automatically calculate the most efficient distance that airplanes have to keep between themselves prior to landing on the runway to:
- First, increase the number of airplanes that can actually land,
- And second, minimize the chance of collisions during unseen circumstances, such as strong headwinds.
4. Aircraft maintenance
Aircraft maintenance, carried out by aircraft engineers, is of the utmost important because it can:
- Ensure the useful life of the aircraft,
- Maintain its performance, in terms of speed, fuel efficiency, and maneuvering,
- Reduce costs by tending to issues before they enlarge,
- By the culmination of previous points, ensure a safe and pleasant travelling experience.
We won’t detail how to automate maintenance checks, as that isn’t the focus of this article. Instead, we’ll discuss how a maintenance checklist and effective communication among engineers ensure all checks are completed on time by the right personnel, minimizing wasted time and resources, such as an engineer repeating a check already done by a colleague.
Case study:
A budget-friendly Spanish airline had to take up the time of 3 engineers daily to create work packages for the maintenance department. Checking a detailed checklist everyday was repetitive, and coupled with the on-hand workload of the engineers, the department was having difficulty keeping up.
By creating a detailed script that connected the aircraft’s information with the maintenance ERP software, the RPA bots were able to exchange data in real-time, create the appropriate checklist, and inform the engineers that concerned them.
5. Informing travelers
On the 27th of July 2022 as this article is being drafted, there have already been 7,085 flight cancellations globally, and it’s not even afternoon yet. It’s the responsibility of the airline agencies or the airports to inform travelers of likely delays or cancellations.
But not only that, there are other on-the-spot changes that can be a nuisance for travelers if they are not informed in advance, such as gate number changes (which can change the amount of time that you need to walk to get there), changes in boarding time, or other factors.
Through API, RPA, and orchestration, the smart applications managing the running of these processes can exchange these information with each other, draft push notifications or emails, and send them to the passengers that these developments concern (see Figure 3).
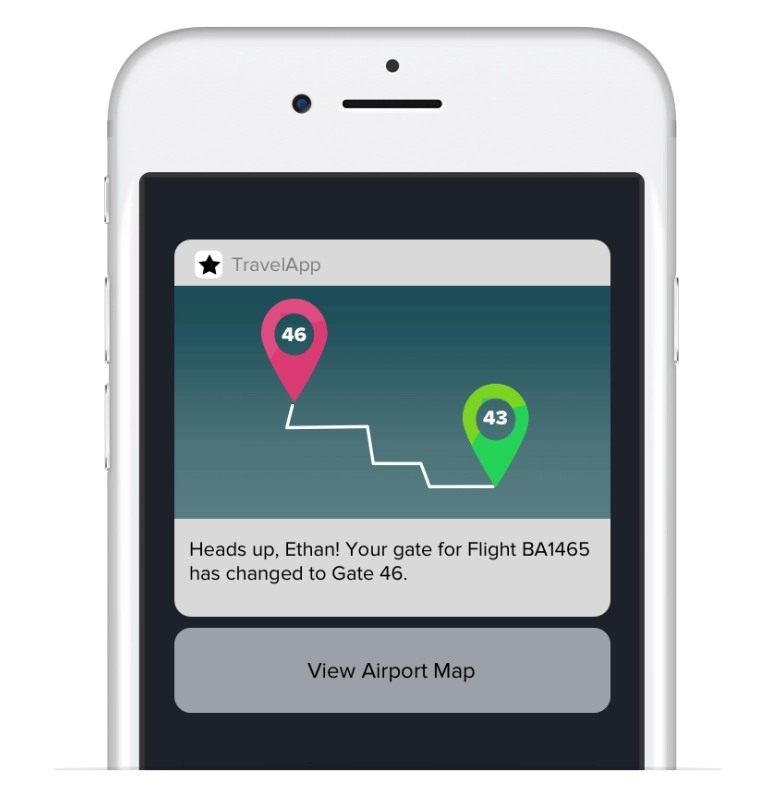
The benefit of automating this task is that RPA robots will ensure that all passengers are updated on the changes to their flight status well in advance. In addition, the software can also include a reason for this change (e.g., “gate number was changed because a vacant jetway could not have been found in time.”) that increases transparency and provides passengers with a sound reason.
6. Cabin crew scheduling
Efficient crew scheduling is a challenge that airline companies have been facing for more than 60 years. That is because airlines should select and assign trips to cabin crew based on their employees’ contracts, union stipulations, safety regulations, the date and time of their last flight, their availability, experience, and more.
Adopting an automated scheduling software that can connect with human resources ERP systems to extract each employee’s contract information, time schedule, and other stipulations to automatically select the most suitable cabin crew pairings for the next flight with RPA will avoid scheduling mishaps and ensure regulatory compliance.
7. Automated check-ins
Automated check-ins via kiosks are perhaps the most tangible automation use case in airports that travelers are familiar with. Even though human staff are still present behind the counters checking-in travelers and giving them their boarding passes, these kiosks are viable alternatives.
Thanks to RPA technology, once the traveler scans their passport’s barcode, the software automatically retrieves their passport number, name, and surname and cross checks it with their flight reservation. After that, the software automatically books them a vacant seat on the flight and prints out their boarding pass, exhibiting all the relevant information on it.
8. Ticket sales
The ticket sales process could be automated by RPA bots so that travelers can enter their information (e.g. name, passport information, email address, etc.) on the website without the need to interact with a live-agent through voice or chat. The solution would then automatically issue an e-ticket and send it to the traveler’s email, with a scannable code.
The benefit of automated ticket sales is that sales representatives can spend their time addressing more important issues (such as refunds). The other benefit is that through electronic data exchange between the sales agents and the airline, no same seat would be sold to multiple travelers mistakenly.
On the other hand, if the sales have not reached a certain, profitable threshold, again the information would be shared with the airline to decide if the flight should be cancelled altogether.
For more on RPA
To learn more about different RPA use cases across various industries, read:
- Top 9 Use Cases of RPA in the Automotive Sector
- 18 Sales Processes to Automate with RPA
- Top 9 Use Cases of RPA in HR
And if you believe your business would benefit from adopting an RPA solution, head over to our RPA hub, where you will find a data-driven list of vendors.
We will help you pick the solution that best meets your specific needs:

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.