NFTs are digital assets encoded as cryptographic tokens. Although their popularity has waned since 2022, they continue to generate significant global revenue, projected at $608.6 million in 2025—despite a 10% decline from the previous year. 1
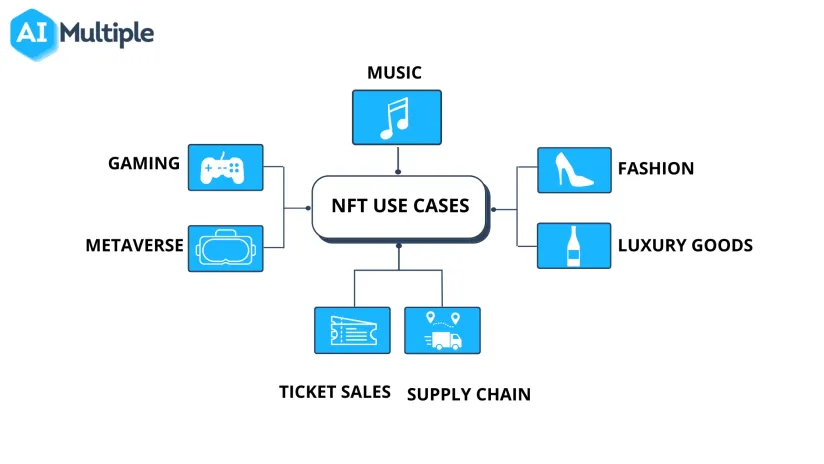
People might think of NFTs as digital images of the Bored Ape Yacht Club, fetching millions of dollars. However, NFTs have grown to be value-adding assets in different industries by providing additional revenue streams and cost-saving mechanisms. We discuss the top 10 use cases of NFTs.
1. Music
Artists can leverage NFTs to:
- Tokenize their songs and albums
- Sell digital merchandise to create additional sources of income (limited digital assets)
- Provide royalties to creators/artists/producers
- Combine them with additional physical benefits to encourage their fans to engage with their songs.
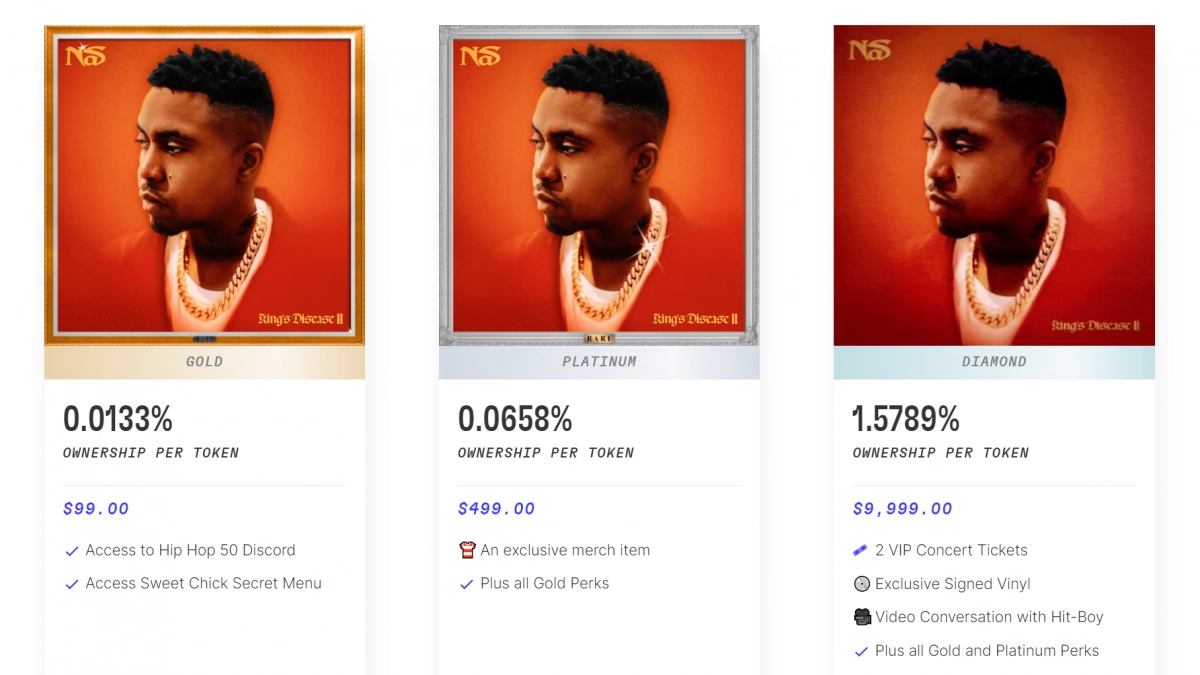
For example, Nas, a prominent American rapper, created2 three tiers of NFTs for two of his songs (Figure 1). These tokens entitle the holders to a percentage of royalty based on the song’s stream volume across streaming platforms, in addition to real-life benefits like merchandise and VIP concert tickets.
For a comprehensive overview of the various categories of NFTs refer to our article on Top 14 Types of NFTs.
2. Fashion
Fashion NFTs can be collected and worn as digital garments during occasions in virtual worlds, such as when visiting a friend, attending a party, or participating in a meeting. Fashion brands have already started experimenting with fashion NFTs. For instance:
- Gucci sold a digital-only bag on Roblox (a metaverse space) for $4,115

- Dolce & Gabbana creatively combined
3. Gaming
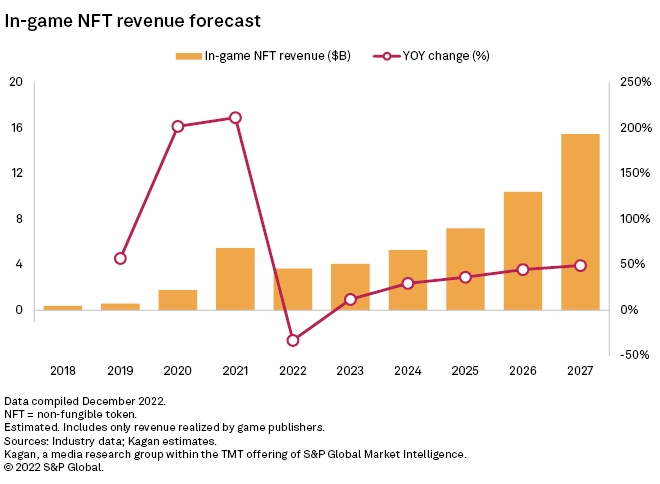
NFT-based play-to-earn games have gained attraction over the last year. For instance, Axie Infinity, the top NFT gaming market leader, now has more than 2M active daily players.3 The NFT gaming market is growing at an exponential rate. If the current trend continues, the revenue generated is expected to reach $15B by 2027, up from the current $4B (Figure 3).4
These NFTs usually concern in-game items such as avatars, skins, and weapons that can be created on the blockchain for game-altering or cosmetic upgrades to the players. In-game NFTs are sold on various platforms, like NFT marketplaces, game-specific marketplaces, and occasionally through the game themselves.
Some traditional gaming companies; however, have largely reacted negatively towards incorporating NFTs into their business model. For example, Steam, the largest PC game store, has banned the use of NFTs and cryptocurrencies, citing instances of fraud and high volatility.5 Or Microsoft Gaming CEO voiced concerns about speculation and exploitation in the NFT market.6
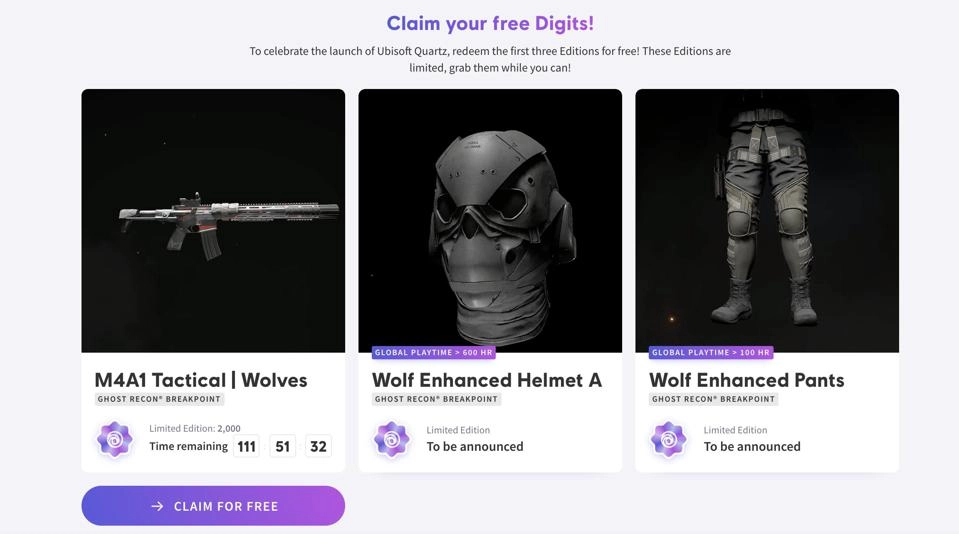
But not every major company has been skeptical of NFTs. Ubisoft, one of the biggest game developers, briefly launched its NFT project Ghost Recon Wildlands, on Tezos. The NFTs represented cosmetic upgrades that gamers could use (Figure 4). The project was short-lived, after making only $400 and being scrapped. However, it indicated the shifting dynamics of established gaming market players in embracing digital tokens.7
4. Luxury goods
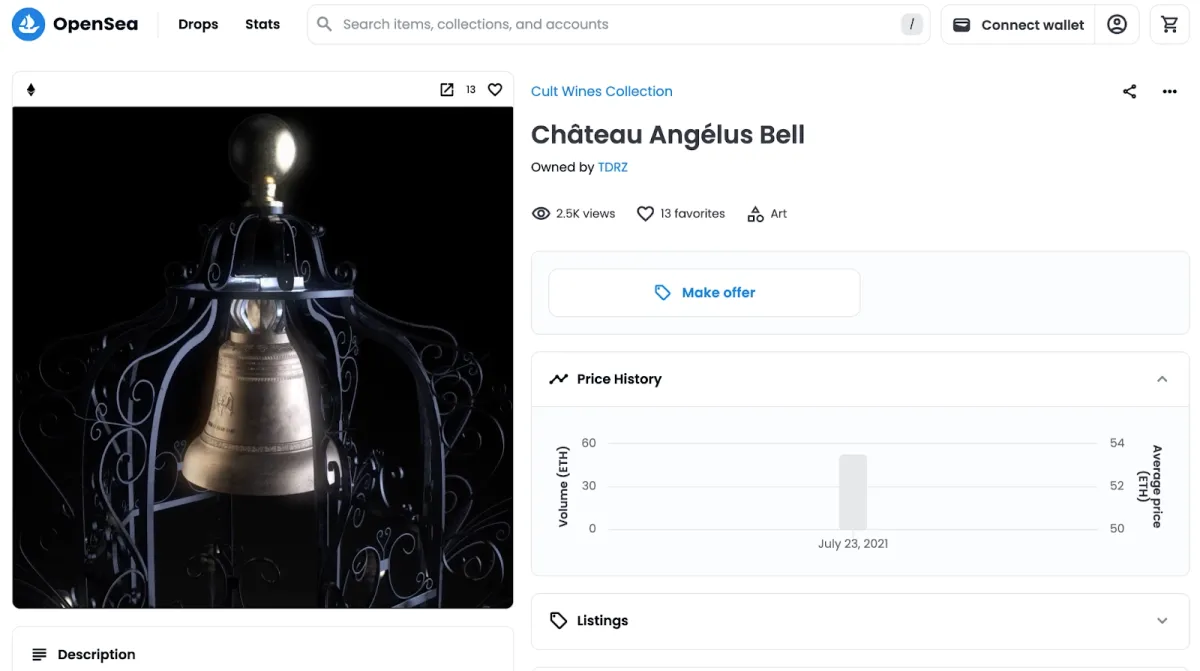
NFTs can act as proof of authenticity for luxury goods by containing all relevant information. For instance, counterfeits are common in the wine industry. Some wineries have started releasing NFTs to store the wines’ data, such as their date of harvest and bottling, grapes’ origin, authenticity certificate, etc. 8 For instance, Château Angélus sold an NFT for $110,000, giving the owner one barrel of wine (equivalent to 30 bottles) and digital artwork (Figure 5).
5. Metaverse
Metaverse is expected to impact almost every industry. Metaverse is a combination of immersive virtual worlds where the user can replicate their “real” life actions and circumstances – like buying a house or wearing clothes – on there (Figure 6).
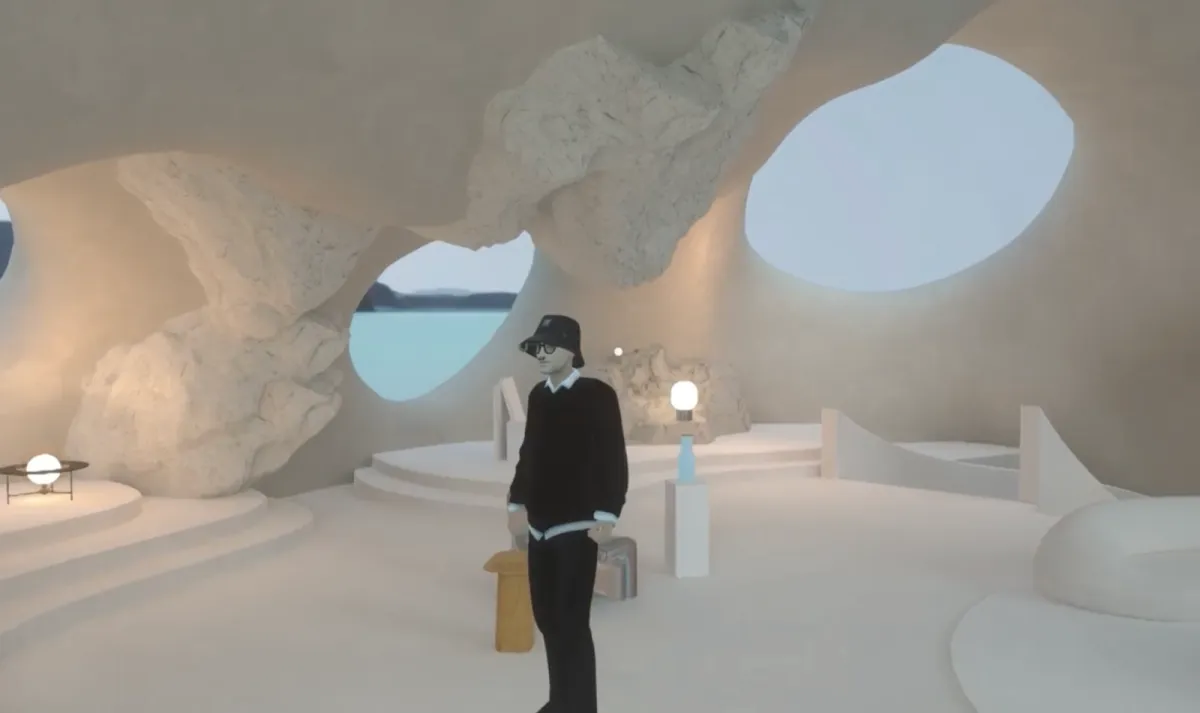

Even though the metaverse is still new, it’s soaring in valuation. Virtual lands are bought and sold through NFTs. When someone buys a virtual land, the NFT representing the ownership of that parcel is transferred to the buyer’s wallet.
The largest metaverse land purchase was made in the Sandbox, one of the virtual worlds, for $4.3 million.9 Large companies from different industries, such as Gucci, PwC, Samsung, and JP Morgan have purchased lands on the metaverse.10 And interestingly, some real estate companies are incentivizing real estate sales in the physical world by promising digital twins on the metaverse. For example, the following is the digital replica of a seven-bedroom house put up for sale in Miami.
6. Supply chain
NFTs can be used to improve supply chain operations by storing metadata of products in the blockchain. In terms of security, blockchain technology in supply chain management prevents data elimination and manipulation.
Logistics-wise, a use case of NFT is supply chain management is end-to-end tracking of goods from origin to destination. For example, Koinearth is a startup that creates enterprise NFTs that enable the tracking of physical goods and documents across the supply chain.
In this method, the user’s device, which is a mobile device connected to the Internet, can scan the NFT’s QR code, forwarding the user to the progressive web decentralized application hosted in the decentralized application (DApp) repository. See the prototype of the DApp.
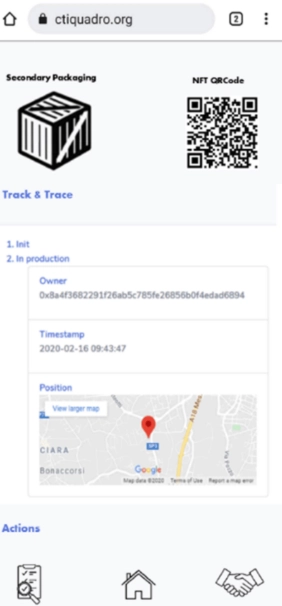
Source: MDPI
7. Ticket sales
Popular event tickets tend to sell out fast. The rise of ticket bots is worsening the situation, as almost 40% of ticketing traffic is coming from ticket bots.11 And once tickets are sold out, they are then resold on secondary markets for profit.
This:
- Robs organizers of additional revenues. While the initial sale still generates income, organizers miss out on potential additional sales from merchandise, food, and beverages that would have been purchased by genuine attendees. This can lead to fraudulent activities. It is estimated that 12% of concert ticket buyers have been scammed (e.g. sold fake tickets).12
- Stops legitimate, interested customers from getting tickets.
NFT transactions on a blockchain will be on a public ledger, making secondary sales trackable and enabling rules-based validations before purchases. For example, eligible purchasers may be required to purchase a specific type of NFT or hold such an NFT.
Therefore, NFTs can improve the ticket industry by:
- Removing the 3rd party ticket seller between the artists and fans.
- Reducing scams due to transparency and authenticity verification provided by NFTs.
- Non-transferable NFTs can prevent ticket reselling.
- Due to the public nature of the blockchain and historical record-keeping, platforms can use smart contracts to establish rules to prevent bots and scammers by checking their transaction history.
- A royalties system can be put in place that pays the artist, producer, or any party a percentage of subsequent sales of the ticket.
8. Asset tokens
NFTs can be used to tokenize physical assets, such as:
Artwork
NFT art examples could be anything from digital art to a song or an album.
- Limited NFT collections examples: Lamborghini has ventured into the blockchain realm with the release of a series of limited edition “World Tour” NFTs.13
- 3D NFTS: JPEG files are the most basic example of 3D NFTS, other examples include animated GIFs, films, music tracks, and, of course, 3D models:
- Digital artwork: An NFT artist can employ 3D to create more visually appealing artwork.
- Digital clothes: Brands, like Nike, Adidas, Gucci, and Louis Vuitton, have developed 3D NFT collections for the metaverse.
Collectibles
NBA player LaMelo has released a set of dynamic NFTs that level up and benefit its holders based on LaMelo’s in-game performance.14

This process involves converting a tangible asset into a digital token on a blockchain, which represents the ownership, provenance, and other information related to the asset.
9. Identity and credentials
NFTs can represent digital identities, certifications, or credentials, which can be easily verified and shared. This can be particularly useful in education, employment, or government services for validating skills, qualifications, or personal information.
10. Financial instruments
Loans
NFTs are being used as collateral for loans, similar to traditional assets like real estate or art. Borrowers can pledge valuable NFTs from collections or digital assets, which are assessed and approved by lenders. Then, the loan amount is then transferred to the borrower’s wallet via smart contracts.
Fundraising
NFTs are increasingly being used for fundraising initiatives. For example, Regenerative Resources Co (RRC) has launched dynamic NFTs tied to short films as a means to raise funds.15
These initiatives leverage the unique and interactive nature of NFTsto engage supporters and generate financial backing for projects. Learn more about NFT loans and lending.
To grasp how smart contracts underpin NFT functionality and transactions, explore our guide on NFTs Use Smart Contracts—But What Exactly Are They?
External Links
- 1. NFT - Worldwide | Statista Market Forecast. Statista
- 2. “Ultra Black” Royal. Retrieved on 20 April, 2023.
- 3. Axie Infinity Live Player Count and Statistics.
- 4. In-game NFTs forecast to grow into $15B market by 2027 | S&P Global .
- 5. eurogamer.net/gabe-newell-explains-why-steam-banned-nfts
- 6. gamesradar.com/xbox-boss-phil-spencer-says-some-nft-games-feel-more-exploitive-than-about-entertainment/
- 7. Ubisoft Quartz’s Ghost Recon NFTs Appear To Have Made Just $400 Total.
- 8. NFT Wine: Just A Fad or A Smart Investment?.
- 9. Ubisoft Quartz’s Ghost Recon NFTs Appear To Have Made Just $400 Total.
- 10. Gucci buys virtual land on The Sandbox, entering the metaverse.
- 11. How Bots Affect Ticketing | Resource Library.
- 12. About 12 percent of people buying concert tickets get scammed . CNBC
- 13. A new chapter for Lamborghini’s NFT journey.
- 14. LaMelo - Sale.
- 15. Announcing: 100 Million Mangroves via Dynamic, Chainlinked NFTs | by Neal Spackman | Medium. Medium

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.