Network security audit tools provide real-time insights into a network’s security by scanning tools across the environment and alerting administrators to emerging threats, vulnerabilities, or new patches.
Given the broad scope of their functions, these tools vary significantly. Some focus on simplifying patch management, while others can be categorized as:
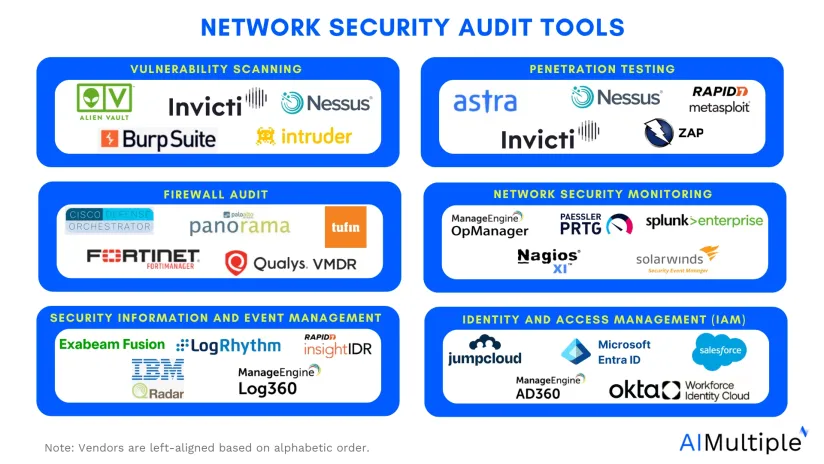
- Vulnerability scanners
- Penetration testing tools
- Firewall audit tools
- Network security monitoring tools
- Security information and event management (SIEM) tools
- Identity and access management (IAM) tools
Compare top 30 network security audit tools
| Name | Category | # of employees | Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| AlienVault USM (from AT&T Cybersecurity) | Vulnerability scanning, Penetration testing | 174,166 | 4.4 based on 112 reviews |
| Intruder | Vulnerability scanning, Penetration testing | 67 | 4.6 based on 153 reviews |
| Burp Suite | Vulnerability scanning, Penetration testing | 214 | 4.7 based on 124 reviews |
| Nessus | Vulnerability scanning, Penetration testing | 2,202 | 4.6 based on 360 reviews |
| Astra Pentest | Vulnerability scanning, Penetration testing | 2 | 4.6 based on 97 reviews |
| Invicti | Vulnerability scanning, Penetration testing | 314 | 4.6 based on 203 reviews |
| Owasp ZAP (Zed Attack Proxy) | Vulnerability scanning, Penetration testing | N/A | 4.7 based on 25 reviews |
| Metasploit | Vulnerability scanning, Penetration testing | 3100 | 4.5 based on 157 reviews |
| Cisco Defense Orchestrator | Firewall audit | 100,466 | 4.7 based on 16 reviews |
| FortiManager | Firewall audit | 14,138 | 4.5 based on 86 reviews |
| Palo Alto Networks Panorama | Firewall audit | 16,348 | 4.5 based on 60 reviews |
| Qualys VMDR | Firewall audit | 2,783 | 4.2 based on 167 reviews |
| Tufin Orchestration Suite | Firewall audit | 458 | 3.8 based on 100 reviews |
| ManageEngine OpManager | Network security monitoring | 387 | 4.4 based on 204 reviews |
| Nagios XI | Network security monitoring | 68 | 4.4 based on 94 reviews |
| Paessler PRTG | Network security monitoring | 381 | 4.4 based on 336 reviews |
| SolarWinds Event Manager (SEM) | Network security monitoring | 2,626 | 3.3 based on 926 reviews |
| Splunk Enterprise | Network security monitoring | 9,229 | 4.5 based on 926 reviews |
| Exabeam Security Intelligence Platform | Security information and event management (SIEM) | 905 | 4.8 based on 13 reviews |
| IBM QRadar Network Security (XGS) | Security information and event management (SIEM) | 4.0 based on 1 reviews | |
| ManageEngine Log360 | Security information and event management (SIEM) | 387 | 4.5 based on 22 reviews |
| LogRhythm | Security information and event management (SIEM) | 279 | 4.2 based on 141 reviews |
| InsightIDR | Security information and event management (SIEM) | 3,076 | 4.4 based on 75 reviews |
| JumpCloud | Identity and access management (IAM) | 789 | 4.4 based on 1,923 reviews |
| ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus | Identity and access management (IAM) | 387 | 4.6 based on 62 reviews |
| Microsoft Entra ID | Identity and access management (IAM) | 228,000 | 4.5 based on 1,555 reviews |
| Okta Workforce Identity | Identity and access management (IAM) | 5,908 | 4.8 based on 4 reviews |
| Salesforce Platform: Identity | Identity and access management (IAM) | 7 | 4.4 based on 1,438 reviews |
Insights come from Capterra 1 , Gartner 2 , G23 , and PeerSpot4 .
Vulnerability scanners
These tools scan these assets for vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit. They create a detailed inventory of all assets, such as desktops, laptops, servers, firewalls, printers, and software components like applications, containers, and virtual machines.
There are three key things vulnerability scanners provide security teams with:
- Known weaknesses: Vulnerability scanners identify weaknesses based on previously exploited threats.
- Risk level: The scanners assess how dangerous each weakness could be.
- Actionable recommendations: Vulnerability scanners can suggest patching a specific software version or reconfiguring a firewall.
Examples of vulnerability scanners:
These tools can also be used as penetration testers.
- AlienVault USM (from AT&T Cybersecurity): A vulnerability scanning solution as part of a unified security management platform, combining asset discovery, intrusion detection, and threat intelligence.
- Intruder: A cloud-based vulnerability scanning platform for real-time discovery and prioritization of attack surface issues.
- Invicti: Specializes in web application security by providing detailed vulnerability scanning for web apps, with automated testing and in-depth remediation guidance.
- Burp Suite: A web application security testing tool that combines vulnerability scanning, manual testing, and automated scanning.
- Nessus: A popular vulnerability scanner with extensive coverage for IT assets, including servers, devices, and applications. It also offers penetration testing features.
Read more: Top open source vulnerability scanning tools.
Penetration testing tools
Penetration testing is a cybersecurity technique used by organizations to identify, test, and remediate vulnerabilities and weaknesses in their security controls. Some common examples include:
- Port scanners: Identify open ports to detect running systems and applications, helping testers find potential attack vectors.
- Vulnerability scanners: Search for known vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in servers, OS, and apps, guiding testers to exploitable weaknesses.
- Network sniffers: Monitor network traffic to analyze communication, protocols, and encryption, revealing potential vulnerabilities.
- Web proxy: Intercepts and modifies web traffic to detect hidden vulnerabilities like XSS and CSRF.
- Password crackers: Test password strength by cracking hashes, identifying weak passwords that could be exploited for privilege escalation.
Examples of penetration testing tools:
- Kali Linux (open source): Kali Linux is an operating system maintained by Offensive Security. It provides tools (some of which are covered separately below) for cybersecurity tasks like penetration testing and security audits:
- Armitage: Graphical network attack management tool
- Nmap: Port scanner
- Metasploit: Penetration testing framework with thousands of exploits
- John the Ripper: Password cracker
- Wireshark: Packet analyzer
- OWASP ZAP: Web application security scanner
- Burp Suite: Web application security testing suite
- Burp Suite (free and paid): Burp Suite by Portswigger is a suite of tools designed for testing web application security. It includes Burp Proxy, a popular web proxy used for man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks, enabling penetration testers to intercept and analyze traffic between the web server and browser.
- Wireshark (open source): Wireshark is a network protocol analyzer used to capture and inspect network traffic. It allows penetration testers and security analysts to examine the packets traveling through a network in real time and analyze them for vulnerabilities.
- Hashcat (open source): Hashcat is a password-cracking tool known for its ability to crack complex password hashes.
- Nmap (open source): Nmap is a network scanning tool used to discover devices and services on a network. It is widely used for network inventory, monitoring host uptime, and detecting security vulnerabilities.
- Invicti (commercial): Invicti is a tool that provides automated vulnerability assessment for web applications. It helps penetration testers find and fix vulnerabilities in websites, including dynamic web applications and HTML5 sites.
Firewall audit tools
An automated firewall audit tool automatically examines firewalls and their rule sets, eliminating the need for manual review and human involvement. It audits all aspects of network traffic control, such as access control lists (ACLs).
Additionally, it monitors firewall rule modifications in real-time and conducts audits based on a scheduled timeline.
Examples of firewall audit tools
- Tufin Orchestration Suite: For change management tracking
- FireMon: For proactive firewall policy tuning
- ManageEngine Firewall analyzer: For analyzing firewall logs
- Vanta: For simplifying security compliance
- Panorama: For consolidated policy visualization
- Fortinet FortiManager: For large-scale network management
- Skybox: For identifying policy violations
Network security monitoring tools
Network security monitoring involves examining network traffic and IT infrastructure to identify potential security threats. These indicators can offer valuable insights into an organization’s cybersecurity status.
For example, these tools can scrape metrics from network devices like firewalls, routers, and switches via exporters (e.g., SNMP exporters). These metrics can provide insights into network performance, traffic anomalies, and potential security issues such as unusual spikes in traffic or unusual patterns that may indicate an attack.
Examples of network security monitoring tools
These tools are primarily used for network monitoring and historical performance data collection. While they are not a dedicated security tool, they can complement a SIEM by monitoring infrastructure and providing valuable data for security analysis and performance tracking.
- Paessler PRTG: For Windows performance monitoring
- AKIPS: For high-performance, scalable monitoring
- Zabbix: Open-source, enterprise-level monitoring
- Prometheus: For real-time monitoring and alerting
- LiveAction LiveNX: Network visualization & analytics
Read more: Free network monitoring tools.
Security information and event management (SIEM) tools
SIEM tools serve as a central control system for an organization’s security infrastructure. These software solutions gather, analyze, and correlate data from various sources within the IT environment, including network devices, servers, and security systems.
Examples of SIEM tools
- Splunk Enterprise Security: SIEM with network/application monitoring. Limited behavioral analytics, no built-in SOAR/UEBA, requires customization.
- Microsoft Sentinel: SIEM & SOAR for Microsoft environments. Extensive playbooks but require coding knowledge. Limited non-Microsoft compatibility.
- IBM QRadar SIEM: Modular design for threat identification. Supports 300+ log sources but slow search, complex pricing, and offshored support.
- Exabeam Fusion: Primarily a UEBA solution with SOAR and log management. Efficient investigative management but may need custom parsing for integrations.
- Sumologic: Great search syntax, fast query results, and powerful data transformation. Excellent for log analysis with quick visualizations.
- Datadog: Log ingest with good integration into APM and metrics. Lacks strong plotting capabilities and requires field marshaling for better searchability.
Examples of free open-source SIEM tools
Core SIEM tools: These solutions offer key SIEM functionalities, including built-in log correlation, alerting, data visualization, compliance reporting, and more.
- Wazuh (free for on-prem version): Open-source SIEM solution that provides security log analysis, vulnerability detection, and regulatory compliance with alerting and notification capabilities.
- Graylog (freemium): Centralized log collection with basic alerting and dashboard features; offers additional functionalities like anomaly detection.
- OSSEC (freemium): Host Intrusion Detection System (HIDS) for log collection and analysis; lacks some SIEM components like log management and correlation.
- SecurityOnion (free): SIEM and IDS solution integrating tools like Snort and Suricata for comprehensive security monitoring, including network and host-based intrusion detection.
- AlienVault OSSIM (free): Open-source SIEM offering event collection, processing, and correlation, but lacks features like reporting and real-time alerting in its free version.
Logging Repository & Analytics tools that can be used as SIEM: These tools are designed for collecting and processing logs but do not include essential SIEM features such as built-in log correlation.
- Logging Repository & Analytics tools (no SIEM features): Tools like Fluentd, OpenSearch, and the ELK stack focus on log collection and processing but lack core SIEM capabilities like log correlation.
- The ELK Stack (freemium): Log aggregation, processing, and visualization tool, but lacks built-in correlation and alerting features for a complete SIEM solution.
- Fluentd (freemium): A log collector and forwarder that integrates with other platforms but lacks SIEM features like event correlation and alerting.
- OpenSearch (freemium): An open-source alternative to Elasticsearch for log storage and analysis, requiring custom SIEM features like detections.
- Apache Metron (freemium): A platform for managing security telemetry, offering SIEM features like alerting and data collection, but requires deployment and configuration.
Identity and access management (IAM) tools
IAM tools focus on access security by centralizing and enforcing secure access management for applications and APIs. They use identity attributes and contextual data to authorize authenticated users, ensuring they have access only to the relevant apps, resources, and APIs.
Examples of IAM tools:
- ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus: Suitable for mid-size and large companies with remote workforces. Focuses on self-service password management, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and single sign-on (SSO).
- LastPass: Ideal for companies looking for a free multi-factor authentication (MFA) solution.
- Cisco Duo: Best for companies needing seamless API integrations with third-party security platforms.
- Microsoft Entra ID: A cloud-based IAM solution focusing on authentication and access management. Best for mid-market companies.
- Symantec: Best suited for large enterprises and organizations needing strong integration with existing security and compliance frameworks, focusing on securing access to resources.
- RSA SecurID: Best for enterprises seeking granular access controls. Offers risk-based authentication
- IBM Verify: Suitable for companies with large-scale cloud access management needs.
- Okta Workforce Identity: Best for companies looking for multiple authentication factors. Offers adaptive risk-based MFA, access controls, and user lifecycle management.
For guidance on choosing the right tool or service, check out our data-driven sources: network security policy management (NSPM) tools and incident response tools.
Further reading
- Top 10 Microsegmentation Tools
- Intrusion Prevention: How does it work? & 3 Methods
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Network Segmentation: 6 Benefits & 8 Best Practices
- 80+ Network Security Statistics
- Network Security Policy Management Solutions (NSPM)
- Cybersecurity Risk Management
AIMultiple can assist your organization in finding the right vendor.


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.