As more sectors explore virtualization, digital twin solutions are gaining mainstream traction. According to Deloitte study, the global market for digital twins is expected to grow with 38% CAGR to reach $16 billion by 2023, and the proliferation of IoT technology accelerating this growth. 1
Digital twin applications
Supply Chain
Digital twins are also widely used in the supply chain/logistics industry. Some applications include:
Predicting the performance of packaging materials
product packaging can be virtualized and then tested for errors before being packaged. Digital twins help logistics companies determine material feasibility.
Enhancing shipment protection
Logistics companies can analyze how different packaging conditions can affect product delivery with the help of digital twins.
Optimizing warehouse design and operational performance
Digital twins enable logistics companies to test warehouse layouts so companies can choose the most efficient warehouse design to maximize operational performance.
Creating a logistics network
A digital twin of a road network carries information about the traffic situation, road layout, and construction. With that knowledge, logistics companies can design the distribution routes and inventory storage locations.
Construction
Construction companies use digital twins to monitor real-time building performance and optimize energy efficiency. Data collected from digital twin can be used for planning and designing future buildings.
Healthcare
It’s been reported that 66% of healthcare executives expect increasing investment in digital twins over the next three years.2 Digital twins can help healthcare providers virtualize healthcare experience to optimize patient care, cost, and performance.
Top use cases of digital twin of healthcare include:
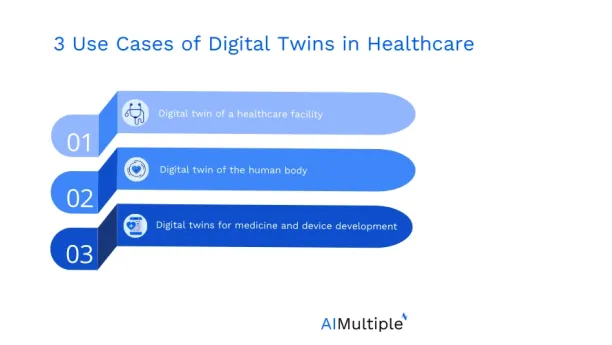
Digital twin of a healthcare facility
Digital twin technology can be used to generate a virtual twin of a hospital to review operational strategies, capacities, staffing, and care models to identify areas of improvement, predict future challenges, and optimize organizational strategies. Therefore, digital twins of hospitals can be used for generating facility replicas, and in turn this enables:
- Resource optimization: Leveraging historical and real-time data of hospital operations and surrounding environment (e.g. COVID-19 cases, car crashes, etc.) to create digital twins enables hospital management to detect bed shortages, optimize staff schedules, and help operate rooms. Such information increases the efficiency of resources and optimized the hospital’s and staff’s performance, while decreasing costs.
- For example, a review study has shown that utilizing digital twins to manage the smooth coordination of several processes enabled a hospital to reduce the time in treatment of stroke patients by. 3
- Risk management: Digital twins provide a safe environment to test the changes in system performance (staff numbers, operation room vacancies, device maintenance, etc.) which enables implementing data-driven strategic decisions in a complex and sensitive environment.
Digital twin of the human body
Digital twins are also applied for modeling organs and single cells or an individual’s genetic makeup, physiological characteristics, and lifestyle habits to create personalized medicine and treatment plans. These replicas of the human body’s internal systems improve medical care and patient treatment by:
- Personalized diagnosis:
- Digital twins allow collection and usage of vital data (e.g. blood pressure, oxygen levels, etc.) at the individual level which helps individuals to track persistent conditions and, consequently, their priorities and interactions with doctors by providing basic information. Thus, such personalized data serve as the basis of clinical trials and research data at labs.
- By focusing on each individual separately, doctors do not derive treatments from large samples. Rather, they rely on customized simulations to track the reactions of each patient to different treatments, which increases the accuracy of the overall treatment plan. Despite the interest and increasing amount of efforts for personalized medicine, there are no digital twins applications for actual patients. One of the centers specialized on personalized medicine is Linköping University in Sweden who mapped mice RNA into a digital twin to predict the effects of medication.
- Treatment Planning: With advanced modeling of the human body, doctors discover the pathology before the disorders are evident, experiment with treatments, and improve preparation for surgeries.

Digital twins for medicine and device development
Digital twin in healthcare can improve the design, development, testing, and monitoring of new drugs and medical devices. For example:
- Drugs: Digital twins of drugs and chemical substances enable scientists to modify or redesign drugs considering particle size and composition characteristics to improve delivery efficiency.
- Devices: A digital twins of a medical device enables developers to test the characteristics or uses of a device, make alterations in design or materials, and test the success or failure of the modifications in a virtual environment before manufacturing. This significantly reduces the costs of failures, and enhances the performance and safety of the final product.

Manufacturing
Digital twins are most widely used in the manufacturing industry. Manufacturing relies on high-cost equipment that generates a high volume of data which facilitates creating digital twins. This is why digital twins technology has become one of the essential production planning tools.
Digital twin applications in manufacturing are as follows:
Product development
Digital twins can help engineers test the feasibility of upcoming products before launching. According to the test results, engineers start producing or shift their focus to creating a feasible product.
Design customization
With digital twins, businesses can design various permutations of the product so that they can offer personalized products and services to their customers.
Shop floor performance improvement
A digital twin can be used to monitor and analyze end-products and help engineers see which products are defected or has lower performance than intended.
Predictive maintenance
Manufacturers leverage digital twins to predict potential downtimes of machines so that businesses minimize non-value adding maintenance activities and improve the overall efficiency of machines since technicians take action before a failure happens.
However, using digital twins for predictive maintenance tasks is not scalable as it is a machine-specific virtual replica and requires expensive data science talent to build and maintain twins.
For more info on digital twin applications in manufacturing, feel free to check our article about manufacturing AI where we explain each AI application.
In aerospace and automotive manufacturing, there are further applications of digital twins:
Aerospace
Before digital twins, physical twins were used in aerospace engineering. An example is Apollo 13 program in the 1970s where NASA scientists on earth were able to simulate the condition of the ship and find answers when critical issues arose. Later in 2002, the digital twin concept is introduced by John Vickers from NASA.
Today the importance of digital twins in the aerospace industry is acknowledged by experts that 75% of air force executives have cast the vote of confidence in favor of the digital twin, according to Business Wire’s survey report.4 In the automotive sector, digital twins streamline testing and support condition-based maintenance.
For more on digital twin applications in manufacturing, feel free to watch the video of Dr. Norbert Gaus who is head of R&D in Automation and Digitalization at Siemens. He is explaining how digital twins help streamline the production process in the real world and providing examples:
Retail
Customer modeling & simulations
Retailers can create digital twins of customer personas to improve the customer experience they deliver. For example, retailers can provide ideal fashion clothing products to customers based on their digital twin models.
Today, businesses use digital twins in numerous ways from product development to operational performance improvement. Market forecasts suggest digital twin technologies will reach $73.5 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of over 60%. 1 As IoT devices proliferate, creating real-time digital replicas of assets and operations has become easier.
What is a digital twin?
A digital twin replicates real-world systems or objects in a digital environment for monitoring or simulation. One core use of digital twins is enabling affordable, scalable simulations in complex environments.
The digital twin technology uses IoT sensors, log files and other relevant information to collect real world data for accurate modeling of real-world assets. These models are then combined with AI-powered analytics tools in a virtual setting.
3 Types of digital twins
There are three main types of digital twins:
- Product Twins: Digital twin prototype of a physical object enables run-in scenarios to predict potential issues and optimize product quality.
- Process Twins: Process digital twins, also known as a digital twin of an organization (DTO), can help design, plan and improve processes to obtain best outcome.
- System Twins: Virtual replicas of systems obtain information generated by systems to manage and optimize them.
Why are digital twins important now?
Digital twins can improve enterprises’ data-driven decision-making processes since they rely on real-time and historical data to simulate, diagnose and predict. Companies apply digital twin technology to monitor asset conditions and adapt systems for optimal performance.
According to a survey, organizations implementing IoT already use digital twins (13%) or plan to use it within a year (62%).5 Digital twins are helpful for growing smart city, urban space and autonomous things (AUT).
In a review study, researchers collected academic publications that contain digital twin as a keyword for 5 years period.4 Among these academic articles, top digital twin use cases were found for urban spaces and smart cities.
How does a digital twin work?
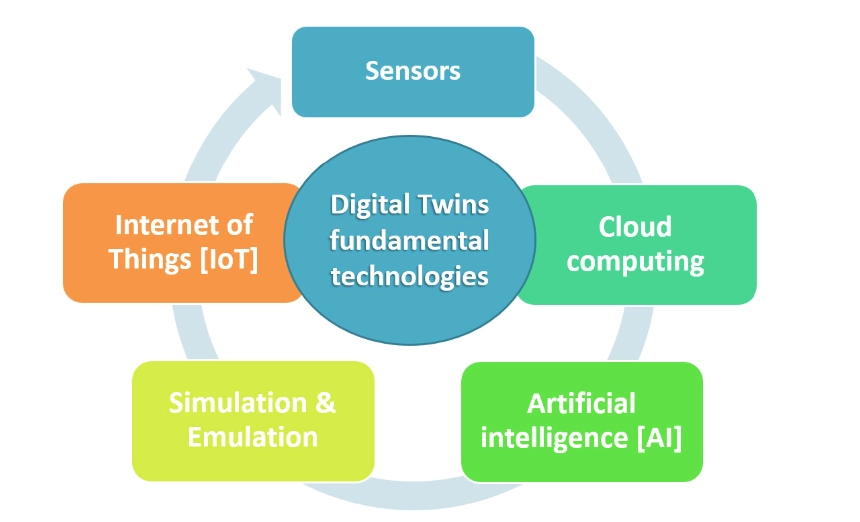
These digital assets can be created even before an asset is built physically. Regardless of when it is created, the process of creating a virtual twin has basic steps:
- Research the physical object or system that will be mimicked
- Integrate sensors into physical assets or monitor log files and other sources to collect sensor data
- All this collected information along is integrated into the virtual model with AI algorithms
- By applying analytics into these models, data scientists and engineers get relevant insights regarding the physical asset.
These basic steps required to create digital twin simulations include major technologies which are the components of fourth industrial revolution (See Figure 1).
What are the benefits of digital twins?
A rising trend involves using digital twins to mirror entire organizations and simulate business outcomes:
- Lower maintenance costs via predictive maintenance: Digital twins enable businesses to understand potential sources of failure so that businesses minimize non-value adding maintenance activities
- Improved productivity: Gartner predicts that industrial companies could see a 10 percent improvement in effectiveness via digital twins. This is due to reduced downtime due to predictive maintenance and improved performance via optimization.
- Faster production times: IDC claims that businesses who invest in digital twin technology will see a 30 percent improvement in cycle times of critical processes including production lines.
The a digital twin of an organization (DTO) expands the traditional scope by replicating enterprise-wide systems. Benefits in this area include:
- Improved business outcomes: Digital twins enable businesses to be more resilient to shocks thanks to virtual representations and this can translate into more enduring customer relationships and profitability.
- Improved customer satisfaction: A digital twin allows users to gain a deeper understanding about their services, potential disruptions and customers’ needs. As a result, businesses can deliver better, more consistent services that eventually enhance the customer experience.
What is the relation between AI and digital twins?
Artificial intelligence and digital twins have a mutualist relation where both contribute to each other.
Digital twin environments serve as training grounds for AI, offering diverse, simulation-based datasets. Artificial intelligence can also benefit from digital twins since digital twins can virtually create an environment for machine learning test scenarios. Depending on the utility score of virtual environment data scientists and engineers can deploy artificial intelligence solutions.
When paired with AI, digital twins become predictive tools that optimize asset performance and maintenance. AI and machine learning algorithms enable businesses both to build some digital twins and also to process a large amount of data collected from digital twins.
For example, by leveraging AI capabilities with digital twins, engineers can accelerate the design processes by quickly evaluating many possible design alternatives.
What are the leading digital twin tools?
This is a list of digital twin providers, excluding digital twin of an organization vendors.
- Akselos
- Ansys Twin Builder
- Autodesk Digital Twin
- Bosch IoT Suite
- CONTACT Elements for IoT
- Flutura Decision Science
- IoTIFY
- Oracle IoT Production Monitoring Cloud
- Predix
- ScaleOut Digital Twin Builder
- Seebo
- ThingWorx Operator Advisor.
Conclusion
Digital twins have been helpful to mirror, monitor, and optimize real-world systems virtually. From smart factories and cities to healthcare and energy, these use cases show how digital twins can drive data-driven decisions and improve performance.
Their success, however, relies on accurate models, real-time data integration, and the right mix of AI technologies. As digital twin adoption grows, their value will hinge on clear objectives, robust design, and integration into broader digital strategies.
External Links
- 1. Budman, Mathew; Garia, Nikita; Khan, Abrar (2018). “Signals for Strategists Expecting Digital Twins.” Deloitte. Revisited January, 2023.
- 2. Healthcare Consulting Services & Solutions | Accenture.
- 3. A year later: MUSC, Siemens Healthineers partnership shows progress | MUSC | Charleston, SC. © Medical University of South Carolina
- 4. “Future role of digital twins in the aerospace industry“Challenge. Retrieved at April 29, 2025.[/efn-note]
With digital twins, engineers can use predictive analytics to foresee any future problem involving the airframes, engine, or other components to ensure the safety of the people onboard.
Automotive
Developing new cars mostly takes place in a virtual setting. Digital Twins are used in the automobile industry to create the virtual model of a connected vehicle. Automotive companies use the technology to design the ideal automotive product even before production starts. They simulate and analyze the production phase and the problems that might occur once the vehicle hits the roads.
Self-driving car development
Though digital twin practices can be used in the traditional automotive manufacturing industry, digital twins are handy for autonomous vehicle companies. Self-driving cars contain numerous sensors that collect data regarding the vehicle itself and the environment of the car.
Due to the liability questions, creating a digital twin of an autonomous vehicle and testing it can help identify and minimize unexpected damage and injuries.4 “Self-driving car liability.” Wikipedia.Retrieved at April 29, 2025.
- 5. How Digital Twins are Entering Mainstream Use | Gartner.

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.