Open-source vulnerability scanning tools offer potent features without a price tag, making them accessible to a wide range of users, from individual developers to large enterprises. Follow the links below to see our rationale for each selected tool:
- OWASP ZAP– Web application security testing
- Nmap – Network discovery and security auditing
- Nikto– Web server vulnerability scanning
- OpenVAS– Network vulnerability scanning
- Wapiti – Web application vulnerabilities
- Tenable Nessus Essentials– Personal and small-scale vulnerability scanning
- Burp Suite Community Edition– Manual web application security testing
AIMultiple researched and selected the top 7 open-source vulnerability scanning tools based on our research, the tools’ effectiveness, popularity, community endorsement and reliability.
Open source vulnerability scanning tools compared
| Software | Stars on GitHub | License | Limitations of Free Edition | Issue Tracker Integration | Operating Systems* | Deployment Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OWASP ZAP (Zed Attack Proxy) | 12k | Open Source | Not applicable | Jira, Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions | Windows, Unix/Linux, and Macintosh | On-prem |
| Nmap | 9.4k | Open Source | Not applicable | Not shared | Windows, macOS, Linux, BSD | On-prem |
| Nikto | 8k | Open Source | Not applicable | Not shared | Windows, macOS, Linux | On-prem |
| OpenVAS | 3k | Open Source | Not applicable | Not shared | Linux | On-prem |
| Wapiti | 1k | Open Source | Not applicable | Not shared | Windows, MacOS, Linux | On-prem |
| Tenable Nessus Essentials | Not available | Proprietary | Limited to 16 IPs, fewer features than paid version | Jira, ServiceNow, various SIEM and ticketing systems | Windows, macOS, Linux | On-prem, Cloud |
| Burp Suite Community Edition | Not available | Proprietary | Limited features, no automation, slower scanning | Not shared | Windows, macOS, Linux | On-prem |
*OS where solution can be deployed Enterprises and mid-market companies may also want to consider the complete set of vulnerability scanning tools which include proprietary software.
Sorting: According to the number of stars on GitHub.
Selection Criteria
- Open source projects: 1000+ stars on GitHub
- Proprietary software: Must be a free-to-use package provided by a vulnerability scanning or DAST software provider
Read more: Open source network security software.
Top Software Analyzed
1. OWASP ZAP (Zed Attack Proxy)
OWASP ZAP is an open-source vulnerability scanner widely used to identify vulnerabilities in web applications. It offers automated scanners for quick assessments and a variety of manual testing tools for in-depth analysis. Key features include an intercepting proxy that allows users to view and modify HTTP/S traffic, spiders to discover the application’s structure, and various utilities for fuzzing and scanning WebSocket connections.
Its extensibility through add-ons and graphical user interface (GUI) makes it accessible to beginners, while its comprehensive feature set caters to advanced users. Despite its strengths, ZAP has a steeper learning curve for its more advanced features.
2. Nmap (Network Mapper)
Nmap is a versatile open-source tool that is suitible for network discovery and security auditing. It offers a wide range of scanning options, including port scanning, OS detection, service version detection, and more. The Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE) further extends its capabilities, allowing for complex and customizable scanning tasks using scripts.
Nmap is supported on multiple operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and macOS, and is backed by extensive documentation and a strong user community. While it is primarily command-line based, which may pose a challenge to those unfamiliar with command-line interfaces, GUI front-ends like Zenmap are available. Nmap’s ability to provide detailed information about networked devices makes it ideal for security auditing and network mapping.
3. Nikto
Nikto is an open-source web server scanner that performs comprehensive tests against web servers for multiple items, including over 6,700 potentially dangerous files and programs. It checks for outdated versions of servers, identifying server misconfigurations and security issues.
Nikto is straightforward to use with a simple command-line interface, making it accessible for quick scans. However, its focus on known issues means it might miss more complex vulnerabilities, and it can generate a high number of false positives, requiring manual verification. Nikto is best suited for web server administrators who need a quick, thorough check of their server’s security posture and can handle its simplicity and potential for false positives.
4. OpenVAS (Open Vulnerability Assessment System)
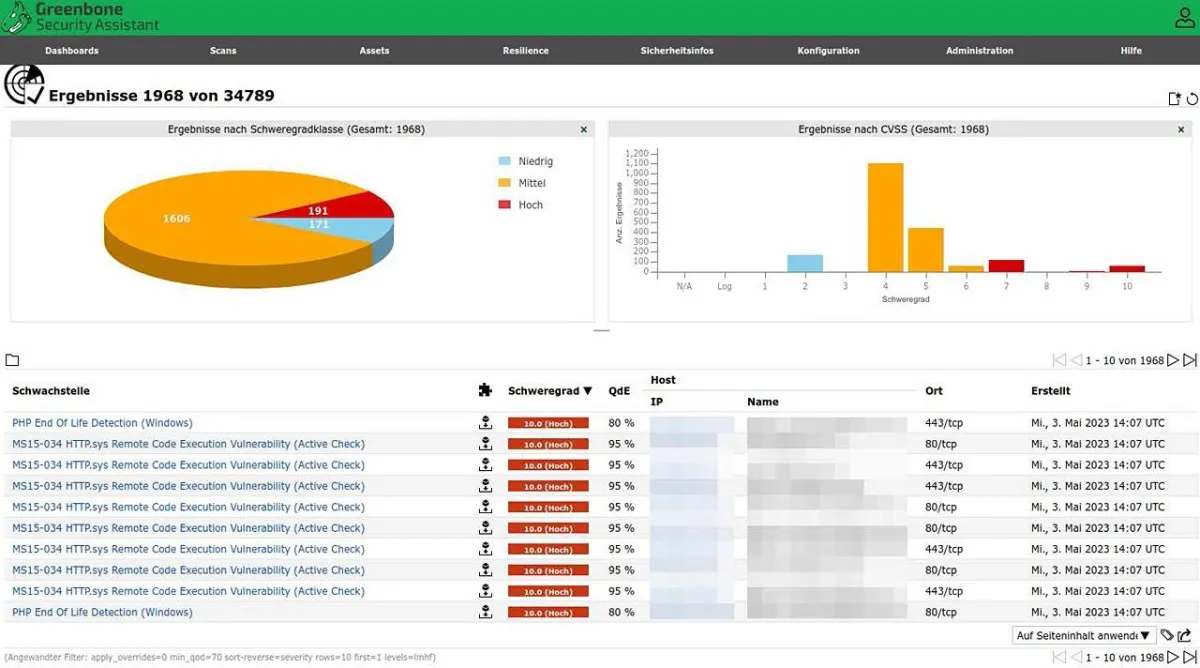
OpenVAS is an open-source framework for network vulnerability scanning. It is known for its extensive vulnerability database, which is regularly updated to include the latest threat information. OpenVAS provides detailed reports that include the vulnerabilities’ severity and remediation recommendations. It can be integrated with various other security tools, making it a versatile choice for security professionals.
OpenVAS enables scanning large networks due to its scalability and thorough scanning capabilities. However, its setup can be complex, especially for beginners. OpenVAS is best suited for organizations needing detailed and comprehensive network vulnerability management.
5. Wapiti
Wapiti is an open-source web application vulnerability scanner used to detect security vulnerabilities within web applications. It analyzes the structure of web applications and attempts to identify potential weaknesses that attackers could exploit. Wapiti performs various types of tests, including SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), remote file inclusion, and other common vulnerabilities.
The highly configurable tool allows users to customize the scanning process based on their specific requirements. Wapiti generates detailed reports outlining the discovered vulnerabilities, including their severity levels and recommendations for remediation. Its versatility, ease of use, and active development community make Wapiti a valuable asset for organizations seeking to enhance the security of their web applications.
6. Tenable Nessus Essentials
Tenable Nessus Essentials is a free version of the well-known Nessus vulnerability scanner designed for personal, non-commercial use. It allows users to scan up to 16 IP addresses, making it suitable for small networks or individual use. Nessus Essentials provides comprehensive scanning capabilities, identifying a wide range of vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and compliance issues.
Its user-friendly interface makes it easy to set up and use, even for those with limited security expertise. The web vulnerability scanner is regularly updated to ensure its vulnerability database is current. However, its free version is limited to a small number of IP addresses and lacks some of the advanced features found in the commercial version, such as extensive reporting and integration capabilities. It is best suited for personal use or small-scale security assessments.
7. Burp Suite Community Edition
Burp Suite Community Edition is a free, limited version of the widely used Burp Suite Professional. It is ideal for manual web application security testing and offers essential tools such as an intercepting proxy, spidering to discover application structure and basic scanning for common vulnerabilities.
The Community Edition is favored by security enthusiasts and professionals for its reliability and effectiveness in manual testing scenarios. It provides detailed insight into the HTTP/S traffic, allowing testers to manipulate requests and responses to uncover security issues.
However, the community edition lacks the automation and advanced features of the Professional Edition, such as advanced scanning capabilities and the ability to save work. This makes it less suitable for extensive or long-term projects but good for learning and conducting manual web security tests. Burp Suite can also be considered as part of pentesting tools.
FAQ: Open Source Vulnerability Scanning Tools
What are open-source vulnerability scanning tools?
Open-source vulnerability scanning tools are software applications that help identify security vulnerabilities in software, networks, and systems. They are freely available, allowing anyone to inspect, modify, and enhance their source code.
Why should I use open-source vulnerability scanning tools?
Open-source tools offer several advantages, including cost-effectiveness, transparency, and community support. They are often updated frequently by a community of developers and can be customized to fit specific needs.
How do these tools compare to commercial vulnerability scanners?
Open-source vulnerability scanners can be as effective as commercial ones but may require more technical expertise to set up and use. Commercial scanners often come with dedicated support and user-friendly interfaces.
How do I choose the right vulnerability scanning tool for my needs?
Choosing the right tool depends on your specific requirements, such as:
The type of environment (network, web application, etc.)
Ease of use
Community support
Public vulnerability databases
Customization capabilities.
Evaluating the features and capabilities of each tool against your needs will help you make an informed decision.
Can I integrate open-source vulnerability scanning tools with other security tools?
Yes, many open-source vulnerability scanning tools offer integration capabilities with other security tools and systems, such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) solutions, DevOps pipelines, and issue-tracking systems. This helps streamline security operations and enhance overall protection.
Where can I find more resources and support for using these tools?
You can find more resources and support in each tool’s official documentation and community forums. Additionally, many open-source projects have dedicated mailing lists, chat channels, and user groups where you can seek help and share knowledge.


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.