Static application security testing (SAST) is often delayed due to time and budget constraints, causing costly refactoring later. Open source SAST tools help:
- budget-conscious teams start early with no cost
- enterprises expand testing without extra spend
Open Source SAST Tools Compared
| SAST Tool | # of stars on GitHub | Supported Languages | Source code | Popular Integrations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semgrep | 9.7 k1 | Java, JavaScript, Go, Python | Community edition is open source | GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Jenkins |
| SonarQube | 8.5 k2 | C#, Java, JavaScript, PHP, Python | Community edition is open source | Azure DevOps, Jenkins, GitHub, GitLab |
| CodeQL | 7.1 k3 | C, C++, C#, Java, JavaScript, Python | Community edition is open source | GitHub Actions, LGTM |
| OWASP Dependency-Check | 5.9 k4 | Java, .NET | Open source | Gradle, Jenkins, Maven |
| PMD | 4.7 k5 | Java, JavaScript, Salesforce.com Apex, Visualforce, PLSQL, Apache Velocity, XML, XSL | Open source | Ant, Maven, Gradle, Jenkins |
| PHPStan | 12.5 k6 | PHP | Open source | Bitbucket, GitHub, GitLab |
| Brakeman | 6.9 k7 | Ruby on Rails | Open source | Jenkins, Travis CI |
| Bandit | 5.9 k8 | Python | Open source | GitLab CI, Jenkins, Travis CI |
| Cppcheck | 5.4 k9 | C, C++ | Open source | Jenkins, Visual Studio |
| Sobelow | 5.4 k10 | Elixir (Phoenix framework) | Open source | |
| SpotBugs FindSecBugs plugin | 3.3 k11 | Java | Open source | Eclipse, Gradle, IntelliJ IDEA, Maven |
| Mobile Security Framework (MobSF) | 16.3 k12 | Android, iOS | Open source | CircleCI, Jenkins, Travis CI, Bugzilla, JIRA, Redmine, Git, Mercurial, SVN |
Inclusion Criteria:
To be listed, a project must:
- Be an open source static analysis tool
- Have ≥1,000 GitHub stars
- Have a commit within the last 2 weeks
Sorting Order:
- Tools supporting multiple languages for web apps (C/C++ counted as one family)
- Language-specific tools for web apps
- Tools for native mobile apps
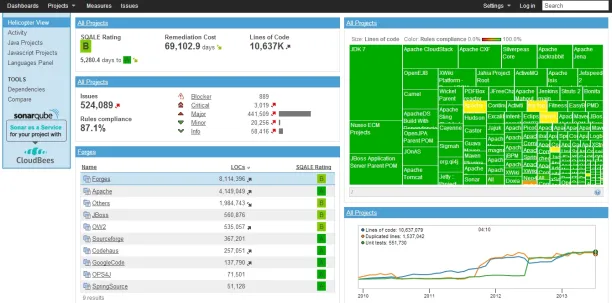
SonarQube
SonarQube offers its free community edition as an open source SAST tool. It is one of the largest SAST tool providers according to metrics like number of employees.
SonarQube is recommended if your team reviewed all SAST tools including commercial ones, chose SonarQube as its solution and decided to start with the free edition. However, if you plan to switch to another SAST tool, starting directly with the latest version of that tool would be a better choice.
OWASP Dependency-Check
OWASP Dependency-Check is not a fully featured SAST tool but leverages software composition analysis (SCA) to identify publicly disclosed vulnerabilities within a project’s dependencies.
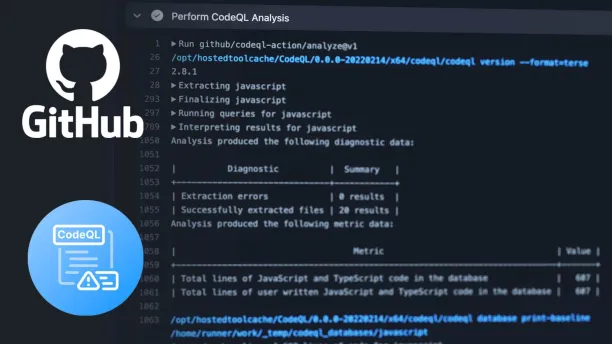
CodeQL
CodeQL, developed by GitHub, is a code analysis engine for discovering security vulnerabilities. Security researchers share queries in its open-source community, keeping its vulnerability detection capabilities up-to-date.
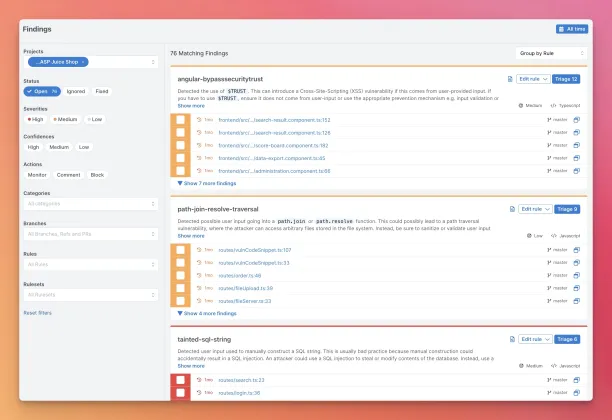
Semgrep
Semgrep is an open source static analysis tool that helps developers find and fix security issues, code quality problems, and enforce code standards. It scans source code using customizable, lightweight rules that resemble the code itself, making it easy to write and understand checks without deep compiler knowledge.
Designed for speed and flexibility, Semgrep supports multiple programming languages and integrates seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines. It’s popular for both security (SAST) and developer workflows, enabling teams to catch issues early in the development process.
PMD
PMD is an open-source static analysis tool that scans Java and other languages for code issues such as bugs, dead code, and style violations. It comes with a wide set of built-in rules and supports custom rule creation. PMD is widely used in Java projects and integrates well with IDEs and build tools like Maven and Gradle.
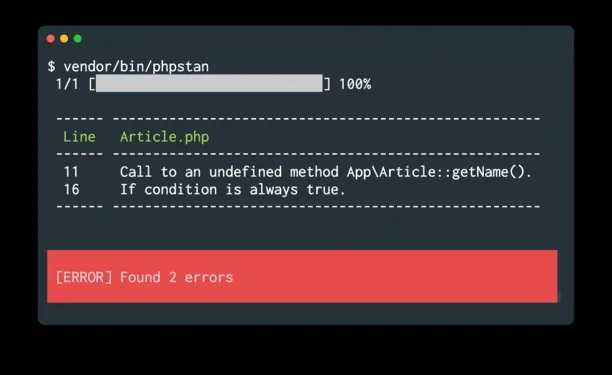
PHPStan
PHPStan is an open-source static analysis tool focused on finding bugs in PHP code without running it. It understands PHP’s type system and catches errors early by analyzing code structure and logic. PHPStan is widely adopted in the PHP community and integrates easily into development workflows.
Brakeman
Brakeman is an open-source static analysis tool specifically designed for Ruby on Rails applications. It scans the codebase to detect security vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and mass assignment. Brakeman runs quickly without needing to load the full app, making it suitable for early-stage security checks.
Bandit
Bandit is an open-source static analysis tool that inspects Python code for common security issues. It analyzes abstract syntax trees (AST) to identify potential vulnerabilities such as hardcoded passwords, use of insecure functions, and more. Bandit is lightweight and easy to integrate into CI pipelines for continuous security checks.
Cppcheck
Cppcheck is an open-source static analysis tool for C and C++ code. It focuses on detecting bugs, undefined behavior, memory leaks, and other issues without requiring code execution. Cppcheck is designed to be highly configurable, supports various coding standards, and integrates well with development environments and build systems.
Open source vs proprietary SAST tools
Though there are numerous open source source code analysis tools, they come with certain limitations:
Programming language coverage limitations
Open source SAST tools typically cover fewer languages than proprietary software. Therefore, as your team switches between different programming languages, they may need to rely on different tools which would need to be configured, maintained and their output needs to be understood by the developers.
Support & maintenance
Enterprise teams may prefer a solution that comes with reliable support and is maintained by an external expert team. This can help improve focus
Updates
Code security landscape is in constant flux. Proprietary SAST tools can invest more in keeping their solutions up to date with the latest security vulnerabilities.
These disadvantages may or may not be worth the cost of a paid solution based on the specific team’s requirements. If you want to be more methodical about whether to choose an open source tool or a proprietary one:
Cost-benefit analysis of SAST tools
For such an analysis, first evaluate both paid and open-source SAST tools and create your shortlist of solutions. For top open-source and paid solutions and measure the following:
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
Total cost of ownership includes more than just the upfront licensing fees. Organizations must also consider implementation costs such as setup, configuration, and integration into existing development workflows, especially the CI/CD pipeline. Hidden costs may arise from the need for additional infrastructure or third-party services required to fully operationalize the tool.
Operational Cost
Ongoing costs include training developers and security teams to effectively use the tool, as well as the time and resources needed for regular maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting. Tools that require heavy customization or generate frequent issues can increase operational burden significantly over time. Additionally, organizations may need to allocate budget for dedicated support plans if the vendor offers tiered support models.
Efficiency Gains
Efficiency is one of the primary motivators for adopting SAST tools, even though it’s difficult to measure directly. Tools that integrate seamlessly into developer workflows and provide actionable, prioritized findings help teams move faster without sacrificing security. Conversely, tools that are slow, noisy (i.e., produce many false positives), or lack remediation guidance can erode developer trust and slow down the overall development lifecycle. Time spent triaging irrelevant issues is time taken away from writing and shipping secure code.
Risk Mitigation
A core benefit of SAST is reducing risk by identifying and eliminating vulnerabilities early in the development lifecycle. A strong SAST tool should consistently detect both common and complex security flaws. If a solution fails to catch critical vulnerabilities that others can detect, this exposes the organization to unnecessary risk. Moreover, preventing a single breach—especially in regulated or customer-facing environments—can avoid millions in costs related to incident response, regulatory fines, and reputational damage. This makes the investment in a more accurate and thorough solution highly defensible.
Compliance
In sectors like finance, healthcare, and government, compliance is non-negotiable. Organizations often need to produce audit trails, risk assessments, or detailed reports to demonstrate adherence to standards such as ISO 27001, HIPAA, or GDPR. SAST tools that offer customizable reporting, role-based access controls, and integrations with GRC systems can play a vital role in achieving and maintaining compliance. In some cases, the ability to meet compliance reporting requirements alone can justify premium pricing tiers.
Choosing the right static application security testing tool
The right tool can be identified in 4 steps:
- Formulate requirements such as programming languages used or planned to be used by your team
- Prepare a shortlist of solutions
- Test solutions to reduce your shortlist to 1-2 candidates
- If the solutions are proprietary, negotiate commercials and implement it in your software lifecycle.
While the right SAST tool is an important choice, static and dynamic analysis need to be considered together. An integrated application security tool supporting both approaches can provide a more comprehensive overview of security issues.
Requirements for source code analysis tools
Requirements include:
- Effectiveness:
- Supported languages such as Python, Ruby on Rails, T SQL, C or Objective C
- Success rate in detecting security vulnerabilities and code quality issues such as code smells. Ideally this should be achieved without heavily relying on hard-to-maintain custom rules.
- False positive rate
- Issue prioritization so critical security issues are resolved earlier.
- Accuracy of remediation suggestions to resolve security issues.
- Ease of use:
- Integrations to IDEs like Visual Studio or Eclipse
- Code review and collaboration features
- Speed & resource consumption
- Scalability
- Other:
- Reporting: Especially in regulated industries, detailed reports including detailed information on security posture are important for compliance.
- Support
How do static code analysis tools work?
Static Application Security Testing (SAST) tools parse source code, analyze potential execution flows, carry out data flow analysis and identify security vulnerabilities without executing the program.
Why should SAST tools be adopted?
Applications with network access are open to attacks. They could be Python applications, Ruby on Rails applications, iOS apps, Windows Mobile apps or a simple Visual Basic script.
Potential security vulnerabilities in these applications enable attackers to carry out attacks such as SQL injection, cross site scripting or take advantage of buffer overflows, security misconfigurations, hard coded secrets or race conditions. These can lead to data leaks and other security issues. Such security and privacy risks need to be minimized in any responsible corporation.
A SAST tool is a type of vulnerability scanner, that enables an efficient software development process as it helps developers to find vulnerabilities and security flaws earlier. This helps prioritize security and adopt secure coding practices without slowing down the software development process. When open source SAST tools are integrated to the IDE, they can provide real time feedback to developers, making security testing part of the development process and reducing code quality issues without disrupting the software lifecycle.
Finally, modern SAST solutions recommend remediation methods for vulnerabilities found, making it easy to improve application security.
A modern DevSecOps pipeline is incomplete without automated testing tools like SAST.
External Links
- 1. "semgrep/semgrep"
- 2. "SonarSource/sonarqube"
- 3. "github/codeql"
- 4. "jeremylong/DependencyCheck"
- 5. "pmd/pmd"
- 6. "phpstan/phpstan"
- 7. "presidentbeef/brakeman"
- 8. "PyCQA/bandit"
- 9. "danmar/cppcheck"
- 10. "nccgroup/sobelow"
- 11. "spotbugs/spotbugs"
- 12. "MobSF/Mobile-Security-Framework-MobSF"

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.