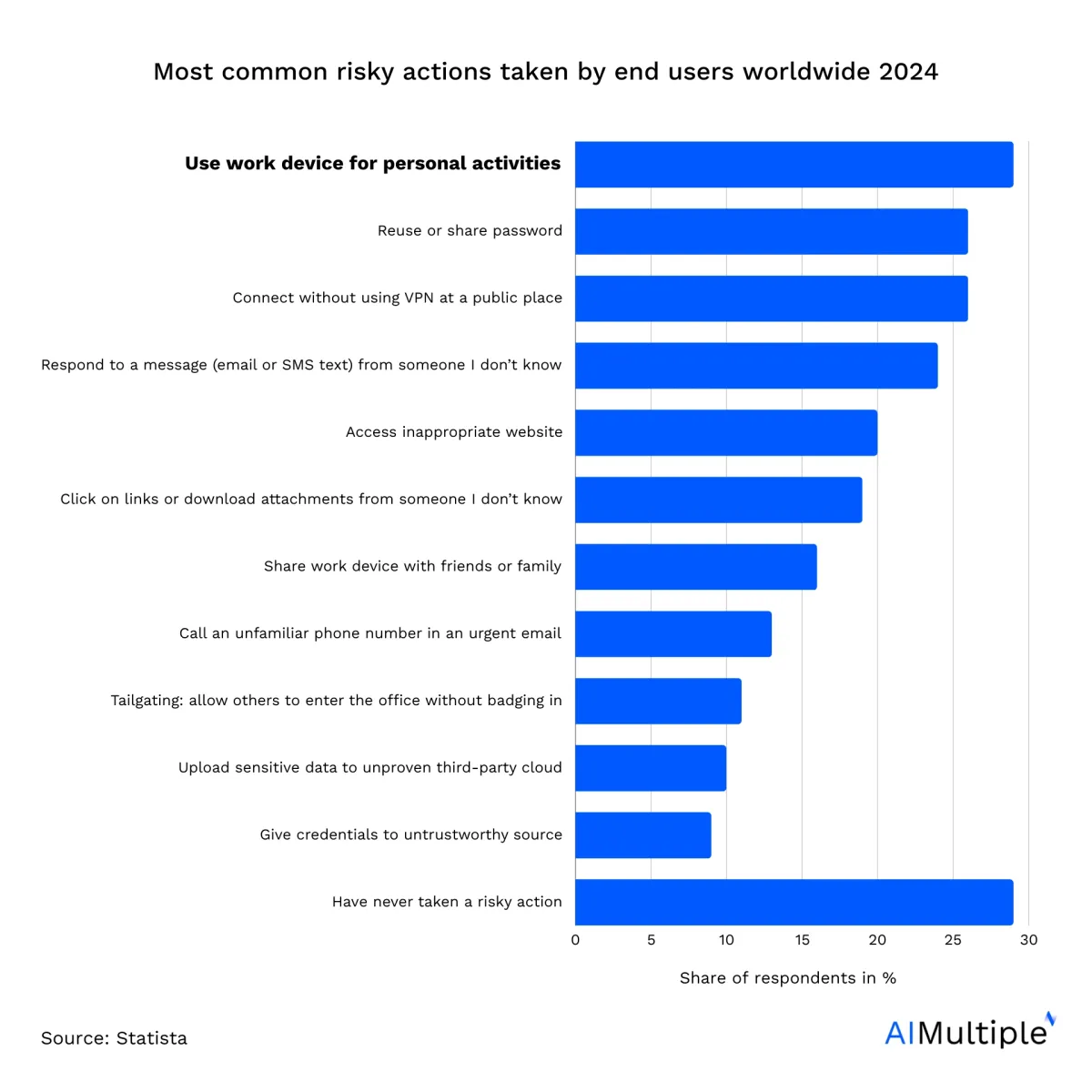
As remote work and mobile device usage continue to increase, protecting sensitive data on mobile platforms has become a top priority for organizations. Mobile devices often present vulnerabilities for DLP software due to their portability, access to cloud systems, and various apps (Figure 1). This article discusses the top 10 mobile DLP best practices alongside real-world case studies to showcase effective implementation.
This article provides the top best practices and case studies to help organizations implement effective mobile DLP through their DLP solutions.
To find the right DLP solution for your business, consider endpoint DLP software.
Figure 1. Most common risky end-user behavior worldwide1
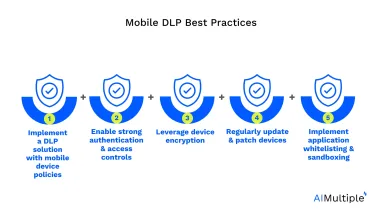
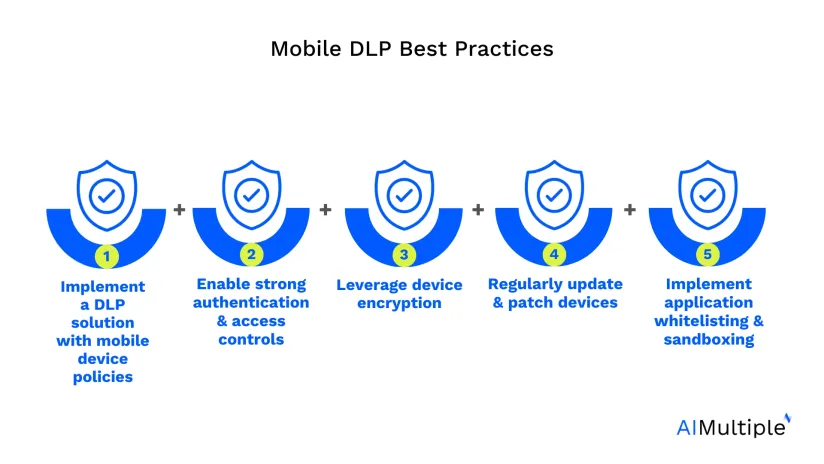
Best practices with case studies
1. Enforce Device Encryption and Secure Access Controls
Best Practice: To enhance security, it is crucial to encrypt mobile devices to ensure data remains unreadable in the event of theft. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) alongside strong password policies provides an additional layer of protection when accessing corporate applications and data.
Additionally, integrating mobile device management (MDM) solutions helps enforce encryption and access rules across all devices.
Case Study: Sentara Healthcare
Sentara Healthcare integrated Duo Security’s solution to combine two-factor authentication with MDM, enhancing the security of patient data. This approach not only fortified data protection but also reduced operational costs associated with managing and deploying MDM solutions.
Case Study: Spectrum of Hope
This U.S. behavioral health provider deployed Endpoint Protector’s DLP solution with MDM integration. The system enforced AES-256 encryption and biometric multi-factor authentication (MFA) on staff tablets accessing electronic health records. During a 2024 phishing attack targeting over 200 devices, no patient data was exfiltrated. The solution also automatically quarantined devices exhibiting suspicious activity. 2
2. Implement Application-Based DLP Controls
Best Practice: To safeguard sensitive information, it is essential to limit or monitor its transfer through mobile apps such as email, file-sharing, or collaboration tools. Implementing data loss prevention (DLP) rules can further restrict the unauthorized sharing of sensitive data across unmanaged apps.
3. Monitor and Secure Data Transfers on Mobile Networks
Best Practice: To protect data in transit, particularly over public Wi-Fi and unsecured networks, it is important to implement robust monitoring mechanisms. Deploying virtual private networks (VPNs) ensures secure data transfer between mobile devices and corporate servers, thereby protecting sensitive information. Real-time monitoring of outbound traffic can help identify and mitigate potential data leaks, enhancing overall security.
Case Study: FTI Consulting
After field consultants reported 37% of staff used public Wi-Fi for client work, FTI rolled out CrowdStrike Falcon Data Protection with:
- Always-on VPN for mobile devices
- Deep packet inspection for cloud uploads
- Real-time alerts for data transfers exceeding 500MB
The system blocked 12,000+ high-risk transfer attempts in 2024, reducing mobile-related breaches and ensuring ISO 27001 compliance. 3
Best Practice: Establishing a Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policy with strict guidelines on acceptable use and security measures is crucial for managing personal devices in the workplace. To maintain security without compromising user privacy, ensure that data loss prevention (DLP) tools can discreetly monitor personal devices. Case Study: Samsung BYOD leaks fell, while employee satisfaction increased due to privacy-respecting monitoring. 4
Best Practice: Integrating AI and machine learning tools into mobile device security allows for the identification of anomalous behaviors, such as unauthorized downloads or suspicious file transfers. By leveraging predictive analytics, organizations can proactively identify and mitigate insider threats, as well as prevent accidental data leaks. Automating responses, such as blocking compromised devices or alerting administrators in real-time, enhances the speed and efficiency of threat management. Best Practice: Mobile DLP solutions must prioritize encryption to protect sensitive data stored on devices and transferred between apps or networks. Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) protocols, such as 128-bit or 256-bit encryption, are effective in mitigating data leaks. Case Study: ScienceSoft Users could securely decrypt files for viewing or editing, safeguarding data even when accessed remotely. The company’s focus on encryption highlighted its ability to prevent unauthorized data access across platforms while maintaining usability. 5
Best Practice: By assigning specific permissions to roles rather than individuals, organizations can simplify access management, minimize unauthorized access, and reduce the risk of data breaches. RBAC enhances security by adhering to the principle of least privilege, granting users access only to the information required for their role. Best Practice: Mobile endpoints, such as smartphones and tablets, are among the top threat vectors for data loss. Endpoint DLP solutions that monitor and block unauthorized transfers of sensitive data can significantly reduce breaches. Case Study: Aspire Pharmaceuticals Aspire Pharmaceuticals adopted CoSoSys’ Endpoint Protector to enforce granular control over data transfers via USB and other removable media. The solution provided real-time monitoring and quick response to policy changes, enhancing data security. 6
Best Practice: Organizations must continually audit mobile DLP strategies to adapt to emerging threats. This includes reviewing BYOD policies, updating security software, and conducting employee training on secure mobile practices. Case Study: Microsoft Intune Regular audits revealed areas for improvement, prompting updates to their mobile security framework. This ensured secure handling of patient data while enabling healthcare workers to access systems from their devices. Best Practice: Cloud-based DLP tools enable seamless integration between mobile environments and organizational networks. These solutions help monitor sensitive data transfers and enforce security policies across mobile and cloud ecosystems. Case Study: German Multinational Investment Bank Infosys assisted a German multinational investment bank in building a centralized DLP platform using Google Cloud Platform (GCP). The integration allowed for uniform data protection across cloud and mobile environments, enhancing the organization’s security posture. 7
Mobile DLP (Data Loss Prevention) is a strategy that protects sensitive data on mobile devices by implementing robust security policies and technologies. It integrates with mobile device management (MDM) to monitor and control data access, preventing data leakage and ensuring compliance with security standards. Mobile DLP solutions, such as DLP software, classify and encrypt data, define granular access controls, and provide monitoring to secure data in a mobile environment. This approach helps organizations protect critical business information, manage devices, and maintain data security across networks, ultimately safeguarding sensitive information from data loss and unauthorized access. Endpoint DLP (Data Loss Prevention) supports a variety of devices to ensure comprehensive data security across an organization’s infrastructure. This includes desktop computers, laptops, and mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Endpoint DLP solutions are compatible with multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and various mobile OS platforms. These solutions provide data classification, encryption, and monitoring capabilities to protect sensitive data, prevent data leakage, and ensure compliance with security policies across all supported devices. If you need further help in finding a vendor or have any questions, feel free to contact us:4. Establish Policies for BYOD (Bring Your Own Device)
Facing 59% BYOD adoption among engineers, Samsung deployed endpoint protection with Bluetooth/USB restrictions. The solution:
5. Use AI-Driven Mobile DLP for Threat Detection
6. Enforce Strong Encryption for Mobile Devices
ScienceSoft worked with a Swedish IT company to develop an AES-based mobile encryption solution compatible with iOS, Android, and Windows Phone. Using Xamarin and Bouncy Castle cryptography, the solution ensured robust protection of files stored on mobile devices.7. Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is an effective strategy for mobile DLP, ensuring that access to sensitive data is granted based on an individual’s job responsibilities.8. Implement Endpoint Security Solutions
9. Regularly Audit and Update Mobile Security Policies
A large healthcare organization implemented Microsoft Intune to enforce mobile device and data loss prevention (DLP) policies. Intune allowed IT teams to implement conditional access rules, encrypt sensitive healthcare data, and monitor devices for compliance.10. Integrate Cloud-Based DLP with Mobile Solutions
FAQs
What is mobile DLP?
Which devices support endpoint DLP?
Further reading
External resources
- 1. Risky actions taken by end users worldwide 2024| Statista. Statista
- 2. Endpoint Protector case studies, Spectrum of Hope.
- 3. FTI Consulting | Endpoint Protector.
- 4. Endpoint Protector case studies, Samsung-SDS.
- 5. AES Encryption Mobile App Development - Case Study.
- 6. Endpoint Protector, Aspire-Pharmaceuticals Case Study.
- 7. Unified Platform Using GCP for Data Loss Prevention | Infosys.


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.