We previously explained open source & commercial SIEM tools, including how to select the best solution. In this article, we listed the most common SIEM use cases and real-life examples:
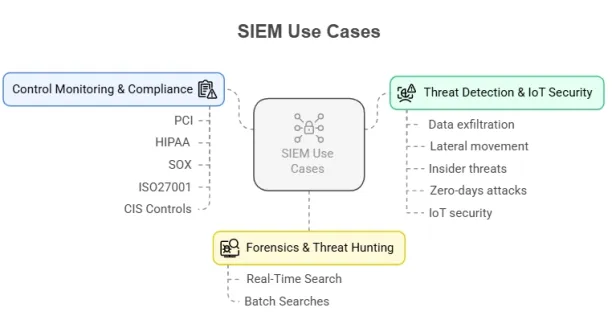
What is SIEM?
At its core, SIEM has two key functions:
- Security information management (SIM) collects, stores, and correlates historical security-related data.
- Security event management (SEM) is a real-time monitoring system that generates alerts based on security incidents.
This way SIEM solutions integrate and analyze data from various sources, helping organizations identify and address potential security threats and vulnerabilities that can disrupt business operations.
1. Detecting and preventing data exfiltration
Data exfiltration is the unauthorized transfer or extraction of data from a computer, network, or storage system to a location outside the organization’s control, often by a malicious actor. Data exfiltration can be performed manually or automated using malware.
How SIEMs detect and prevent data exfiltration:
Figure 1:
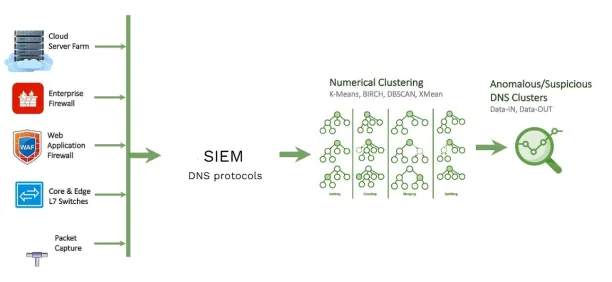
Source: Medium1
- Detect compromised credentials: Use correlation engines to identify unusual user behavior, such as accessing sensitive data at unusual times, triggering alerts for IT managers.
- Monitor command and control communication: Correlate network traffic with threat intelligence to identify malware communicating with external servers, signaling a compromised account.
- Analyze data exfiltration: Detect compromised credentials, SIEMs identify abnormal activities, such as USB usage, personal email, cloud storage access, or high data traffic, that may indicate data exfiltration.
- Detect encryptions: Detect unusual data encryption on user systems, which could signal a ransomware attack.
- Prevention: Automatically trigger containment measures such as isolating compromised devices, blocking malicious IPs.
Real-life example2
Sector: Banking (Bank of Wolcott)
Challenges:
- Bank of Wolcott faced challenges managing the massive volume of data created, modified, moved, or deleted daily.
- The bank needed a reliable solution to monitor changes in files and folders, ensuring file integrity and preventing data theft and misuse.
Solutions and outcome:
- The bank adopted ManageEngine DataSecurity Plus. The solution helped by tracking critical file modifications and movements across file servers and sending alerts based on predefined criteria.
- The bank detected and responded to data exfiltration attempts through USBs, email, printers, and other channels.
2. Detecting lateral movement
Lateral movement refers to any activity that allows adversaries to gradually move deeper into a system in search of high-value assets. SIEM tools can detect lateral movement activities using predefined correlations and threat intelligence integrations.
How SIEMs detect lateral movements:
Figure 2: SIEM detecting abnormal user behavior
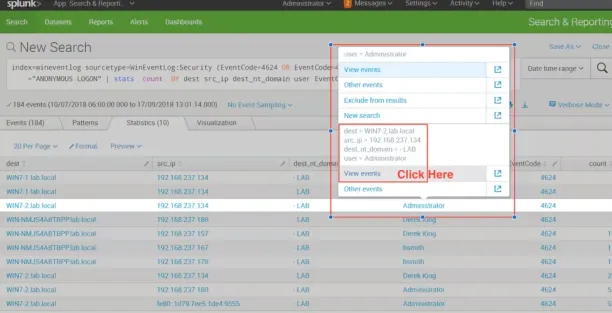
Source: Splunk3
- User behavior correlation: Detect abnormal user behavior by correlating data, such as access to unusual systems or data at odd times, triggering alerts for IT admins. See: UEBA use cases.
- Behavioral analysis: Based on their activities, users are categorized as attackers, victims, or suspicious through multiple correlation processes.
- Malware communication detection: Integrate network traffic with cyber threat intelligence tools to identify malware communicating with control servers.
- Security event analysis: SIEMs also collect data from security systems, endpoints, and intrusion detection systems to identify lateral movement.
Real-life example4
Sector: Multiple sectors (VMWare customers)
Figure 3: An example of one of the intrusions included in this dataset.
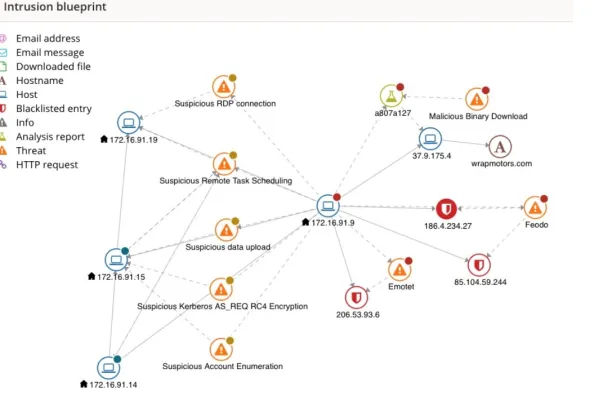
Source: VMWare5
Challenges:
- Difficulty in identifying attacks inside the network
- Insufficient visibility across endpoints
Solutions and outcome: VMware’s NSX SIEM solution addressed lateral movement for NSX customers by leveraging:
- Monitoring endpoints for abnormal activities, such as:
- Unusual privilege escalation attempts.
- Suspicious file or process activity across multiple machines.
- Anomalous network connections that don’t fit the typical user or system behavior
- Enabling real-time monitoring of endpoint activities.
- Isolating compromised endpoints.
3. Detecting insider threats
Insider threats are security risks from authorized users, such as employees, subcontractors, and business partners, who intentionally or mistakenly exploit their legitimate privileges or have their accounts hijacked by cybercriminals.
How SIEMs detect insider threats:
Figure 4:
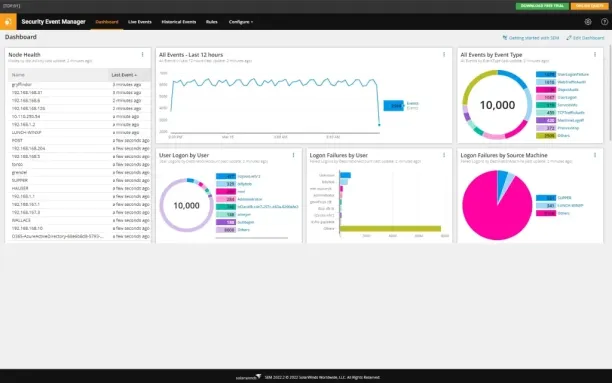
Source: SolarWinds6
SIEMs detect insider threats by collecting and correlating data from various sources across the network, like user activity logs, system logs, and network logs. Here are methods of SIEM detecting insider threats:
- Real-time monitoring and correlation: SIEMs monitor activities in real-time, correlating data from multiple sources (e.g., user login behavior, file access patterns, and network traffic).
- Correlation with external threat intelligence: SIEM pull data with external threat intelligence feeds (e.g., IP reputation, known bad actors) to identify any correlation with external attacks.
- Compromised user credentials detection: SIEMs apply correlation rules to identify compromised credentials, including usernames, passwords, security questions, and other sensitive details used to verify a user’s identity and gain access to accounts and systems.
- Behavioral anomaly detection: SIEMs with UEBA use machine learning algorithms to identify deviations from normal user behavior (e.g., accessing data at unusual hours or from unfamiliar locations).
Real-life example7
Sector: Technology, Fintech, Financial, Manufacturing (CrowdStrike customers)
Challenges:
- 150+ companies targeted by famous “chollima insider threats”.
- 50% of cases reviewed included data theft.
Solutions and outcome: Targeted companies combined telemetry and human analysis to uncover insider threats and implemented CrowdStrike Falcon SIEM & endpoint security software. CrowdStrike Falcon provided:
- Real-time monitoring of endpoints and user activity.
- Automatically assess potential insider threats based on known indicators and real-time data.
- Querying capabilities for insider threat hunting for human analysts.
4. Detecting zero-days attacks
A zero-day is a vulnerability or security hole in a computer system unknown to its owners, developers, or anyone capable of mitigating it. SIEMs can detect zero-day attacks in several ways.
How SIEMs detect zero-days attacks:
Figure 5:
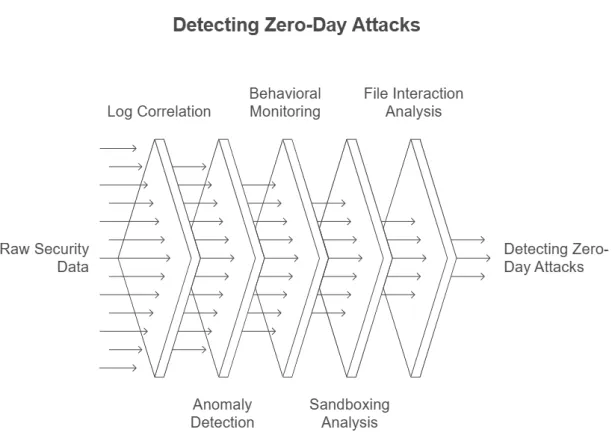
- Cross-system log correlation: Aggregate data from various sources (e.g., firewalls, endpoints, intrusion prevention systems, and DNS logs) to detect access attempts.
- Anomaly detection: SIEMs include built-in machine learning models to analyze large volumes of data from past interactions and known exploits. These models help detect subtle patterns that are indicative of zero-day exploits by flagging anomalies.
- Behavioral detection: Detect zero-day exploits by monitoring unusual behaviors in system interactions, rather than relying solely on known malware signatures.
- Sandboxing: Some SIEMs integrate with sandboxing technologies to analyze suspicious files in a safe, isolated environment. The SIEM can monitor the file’s behavior, looking for malicious actions such as changes to the registry, attempts to exploit vulnerabilities.
- File interaction analysis: Analyze how files interact with the system to detect zero-day exploits based on abnormal file behaviors or system changes.
5. Maintaining IoT security
Organizations rely on connected devices to run essential operations, such as networked medical equipment, industrial machinery, sensors, and power grid infrastructure. However, these Internet of Things (IoT) devices were not originally built with strong security features, leaving them vulnerable to various threats. Once deployed, these vulnerabilities are often difficult to remedy.
How SIEMs maintain IoT security:
Figure 6:
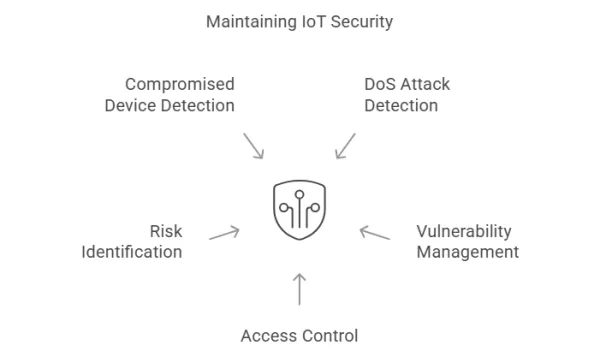
- Denial of Service (DoS) attacks: Detect unusual traffic patterns from IoT devices and DoS attacks.
- IoT vulnerability management: Identify outdated operating systems, unpatched security holes, and insecure communication protocols on IoT devices.
- Access control: Monitor access to IoT devices, track their connection sources, and send alerts if connections are made from unknown locations.
- Devices at risk: Identify vulnerable IoT devices.
- Compromised devices: Identify unusual or suspicious activity from IoT devices and alert the security teams when a device is compromised.
6. Centralized log management
Security professionals or automated security solutions, such as SIEMs, historical log data, and real-time alerts from various security solutions and IT systems, such as email servers and authentication systems.
How SIEMs provide centralized log management:
Figure 7:
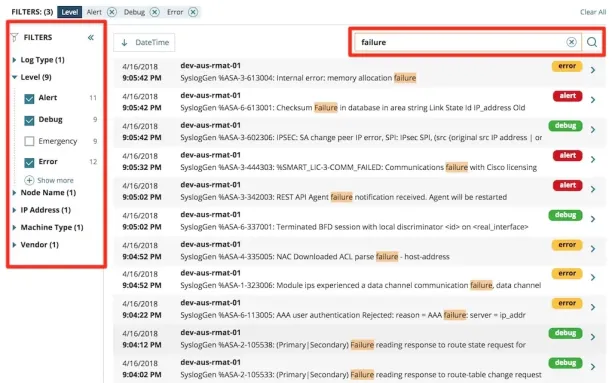
Source: SolarWinds8
- Data collection from multiple sources: Collect log data from various security solutions, IT systems, and devices, including email servers, authentication systems, firewalls, network devices, and endpoint protection tools.
- Centralized storage and aggregation: Aggregate data from intrusion detection systems (IDS) or network monitoring tools, providing insights into potential network intrusions alongside other security logs.
- Log analysis and correlation: Use machine learning, and statistical models to detect patterns in log data for more accurate threat detection and identifying complex attack patterns (e.g., unauthorized access) that might go unnoticed in isolated logs.
Real-life example9
Sector: Banking, Pakistan (Askari Bank)
Challenges:
- Government regulators issued new guidelines, including the Cyber Security Policy 2021, urging banks to enhance security measures.
- Askari Bank had minimal security capabilities and lacked a dedicated security team.
- The bank’s governance structure for security was limited, leaving it vulnerable to cyber threats.
Solutions and outcome:
- Askari Bank implemented IBM Security QRadar SIEM solution to strengthen threat detection.
- The QRadar SIEM system consolidated logs from multiple sources into a single repository for centralized monitoring. QRadar used to filter out false positives.
- The solution was integrated into the bank’s Security Operations Center (SOC) for more effective monitoring and response.
The following outcomes have been achieved:
- The bank’s SOC significantly reduced the number of daily security incidents from approximately 700 to fewer than 20.
- The average time to remediate security incidents dropped from 30 to 5 minutes.
7. Forensics & threat hunting
Forensics and threat hunting are critical components of a proactive security strategy, helping organizations identify, investigate, and mitigate threats before they cause damage. SIEMs can be used in forensics (e.g. log forensics) and threat hunting cases since these tools provide real-time visibility into the security events for investigation.
- Real-time search: SIEM systems enable live querying on logs, traffic, and event data, allowing security teams to identify potential risks as they emerge before they escalate into full-fledged attacks.
- Batch searches: SIEM systems allow processing large volumes of historical data to uncover long-term trends or patterns that may reveal hidden threats.
How SIEMs help forensics & threat hunting:
Figure 8:
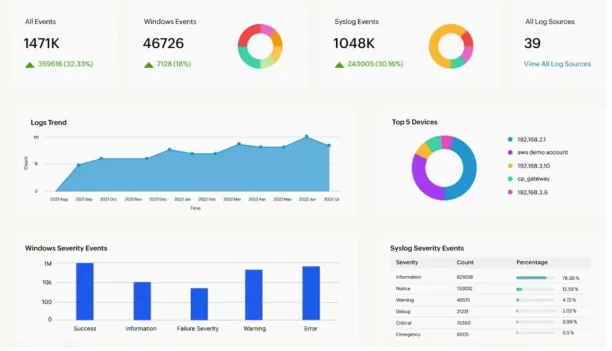
Source: MCSI Library10
- Proactive threat detection: SIEM platforms help security teams actively search for threats, rather than only reacting to alerts, by allowing in-depth analysis and investigation of potential risks.
- Incident investigation: With advanced log aggregation, correlation, and querying, SIEM tools provide a unified view that supports thorough forensic analysis, making it easier to understand the full scope of an attack.
- Incident response: Automated actions based on forensic analysis and threat hunting efforts help security teams respond to incidents more quickly.
- Post-incident learning: By documenting and analyzing past incidents, SIEMs help improve detection capabilities and strengthen defenses against future attacks.
8. Control monitoring & compliance
SIEM solutions assist with compliance monitoring and ensuring adherence to standards such as PCI, HIPAA, SOX, ISO 26001, CIS controls. SIEMs detect unauthorized network connections and correlate them with change management, searching for dangerous protocols and services, and monitoring how traffic flows across the DMZ.
How SIEMs help compliance monitoring:
Figure 9:
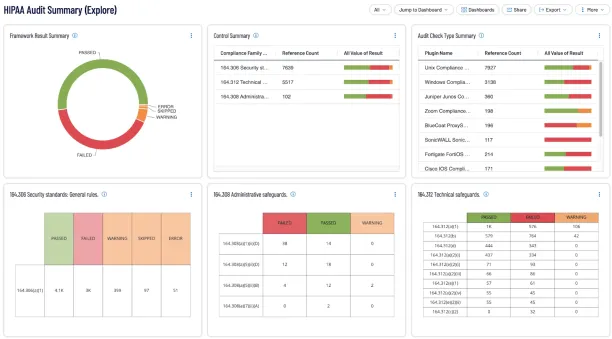
Source: Tenable.io11
- Logging: SIEMs aggregate logs from various sources (network devices, servers, endpoints, firewalls, etc.), ensuring that all activities are recorded.
- Retention of logs: Compliance standards often require a specific duration for log retention (e.g., 1 year, 5 years). SIEM solutions enable businesses to store logs in a compliant manner.
- Monitoring system changes: Changes to system settings, such as user privilege escalations or modifications to system files, trigger alerts. Additionally, monitors antivirus logs, unsecured ports and services, and correlates with threat intelligence.
- Detailed audit trails: SIEMs provide a history of all security events, access logs, and activities. Searches for dev/test or default credentials, duplicates, and others on production systems.
- Predefined compliance templates: SIEM solutions often offer built-in templates and predefined rules.
- Automated reporting: SIEM systems collect logs, including specific logging requirements, audit them in a format suitable for reporting, and generate compliance reports.
Real-life example12
Challenge:
- RCO Engineering had limited visibility into IT events and security incidents.
- IT team had to sift through Windows Event Viewer manually logs to identify the root cause of security incidents.
Solution and outcome:
- Implemented ManageEngine Log360 for unified log management and network security.
- Log360 helped the company monitor, audit, and control with its dashboard, predefined reports, and customizable alerts.
- Enhanced network control and security posture, ensuring better compliance.
The guiding principles for setting effective SIEM use cases
Creating a SIEM use case is only the first step. Continuously reviewing and improving these use cases ensures they remain effective and aligned with current security needs. By following the guiding principles outlined below, you can greatly improve the performance and relevance of your SIEM use cases.
| 🛠️ Guiding principle | 🔍 Implication | ✅ Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| Building a use case can be expensive. | Only build and manage necessary use cases. | Avoid scope creep—prioritize based on ROI. |
| Use cases have different granularity levels. | Multiple granularity levels will be needed. | Structure for both fine-grained and coarse use cases. |
| Sending data to the SIEM tool can be expensive. | Send and manage only necessary data. | Avoid sending all data “just in case.” Ensure required access. |
| Computing analytics in the SIEM tool can be expensive. | Use complex analytics only if needed. | Start with simple analytics before advancing. |
| The right stakeholders need to be involved early. | SIEM engineers shouldn’t work alone. | Involve business leaders, HR, and privacy officers. |
| Workflows affected by SIEM should be addressed. | SIEM insights need actionable workflows. | Build processes to act on SIEM alerts. |
| SIEM generates real-time alerts 24/7. | Alerts are useful only if action-ready 24/7. | Ensure incident and case management processes exist. |
Source13
External Links
- 1. Using Machine Learning for DNS Exfiltration / Tunnel Detection | by Syed Suleman Qutb | Medium. Medium
- 2. Customer case study: Data Security Plus keeps Bank of Wolcott safe as the bank caters to its community - Date Security Plus .
- 3. Detecting Lateral Movement with Splunk: How To Spot the Signs | Splunk.
- 4. Lateral Movement in the Real World: A Quantitative Analysis - VMware Security Blog - VMware.
- 5. Lateral Movement in the Real World: A Quantitative Analysis - VMware Security Blog - VMware.
- 6. Insider Threat Detection & Management Tool | SolarWinds.
- 7. Defend Against Insider Threats case study. Accessed: March 2025
- 8. Enterprise Server Log Management System - Server Log Monitoring | SolarWinds.
- 9. Case Studies - IBM QRadar SIEM.
- 10. SIEM Dashboards: Invaluable Data Sources for Incident Investigations — MCSI Library.
- 11. HIPAA Audit Summary (Explore) - Tenable.io Dashboard | Tenable®.
- 12. Wyndham Hotels Reduces Risk Score with the Rapid7 Platform - Rapid7.
- 13. How to Build Security Use Cases for Your SIEM.


Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.