Choosing the right IT Asset Management (ITAM) software can be challenging, especially with a number of providers with various pricing. We evaluated more than 10 solutions and selected below providers for businesses to compare different IT asset management pricing plans:
| IT Asset Management Pricing | Best for | |
|---|---|---|
1. | A comprehensive solution encompassing both ITSM and ITAM | |
2. | SMEs looking for a full-featured solution | |
3. | A free plan for businesses to try out ITAM features | |
4. | Unlimited number of users | |
IT asset management starter package
| Vendor | Starting price/month | Basic plan includes |
|---|---|---|
| Freshservice | $15 | Core ITSM features. Basic drag-and-drop workflow automation. Lacks asset management features. |
| AssetSonar | $70 | Hardware management with barcode, QR code, and RFID scanning. Advanced access control, customizable roles, and employee offboarding workflows. Agentless device discovery for agents and network devices. Integrates with Jira and Zendesk for ITSM. |
| Atomicwork | $8* | Single company-wide workspace. Service requests and approval management. No-code workflow builder for automation. Password login for easy access. Limited access to Atom AI. |
| Lansweeper | $200 | IT, cloud, and OT discovery for network-wide device visibility. Up to 3 federation installations for unified asset, software, and user data. Up to 3 asset scopes for controlled data visibility. Starter support desk. SSO and success manager not included. |
| Timly | $205 | Unlimited users and profiles. Digital stocktaking for mobile device management. Support via email, phone, live chat, and Timly Q&A help center. Optional IT discovery, GPS tracking, and SSO. Add-ons like smart inventory, asset deployment planning, and performance tracking not included. |
*Only an annual plan is offered. However, we displayed the monthly equivalent for ease of comparison.
Sorting in the above table: Sponsors are listed at the top with their links. The rest of the table is sorted alphabetically.
Check out IT service management pricing for more vendors with various pricing options.
IT asset management pricing key components
| Vendor | Free plan | Free trial | Pricing based on | Deployment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freshservice | ❌ | 14-day | Number of assets | SaaS |
| AssetSonar | ❌ | 15-day | Number of devices & seats & admins | SaaS |
| Atomicwork | ❌ | ❌ | Number of employees & agents & features | SaaS |
| Lansweeper | ✅ | 14-day | Number of assets | On-prem & Cloud |
| Timly | ❌ | 10-day | Availability of add-ons | SaaS |
Sorting in the above table: Sponsors are listed at the top with their links. The rest of the table is sorted alphabetically.
Pricing comparison of IT asset management software
Freshservice
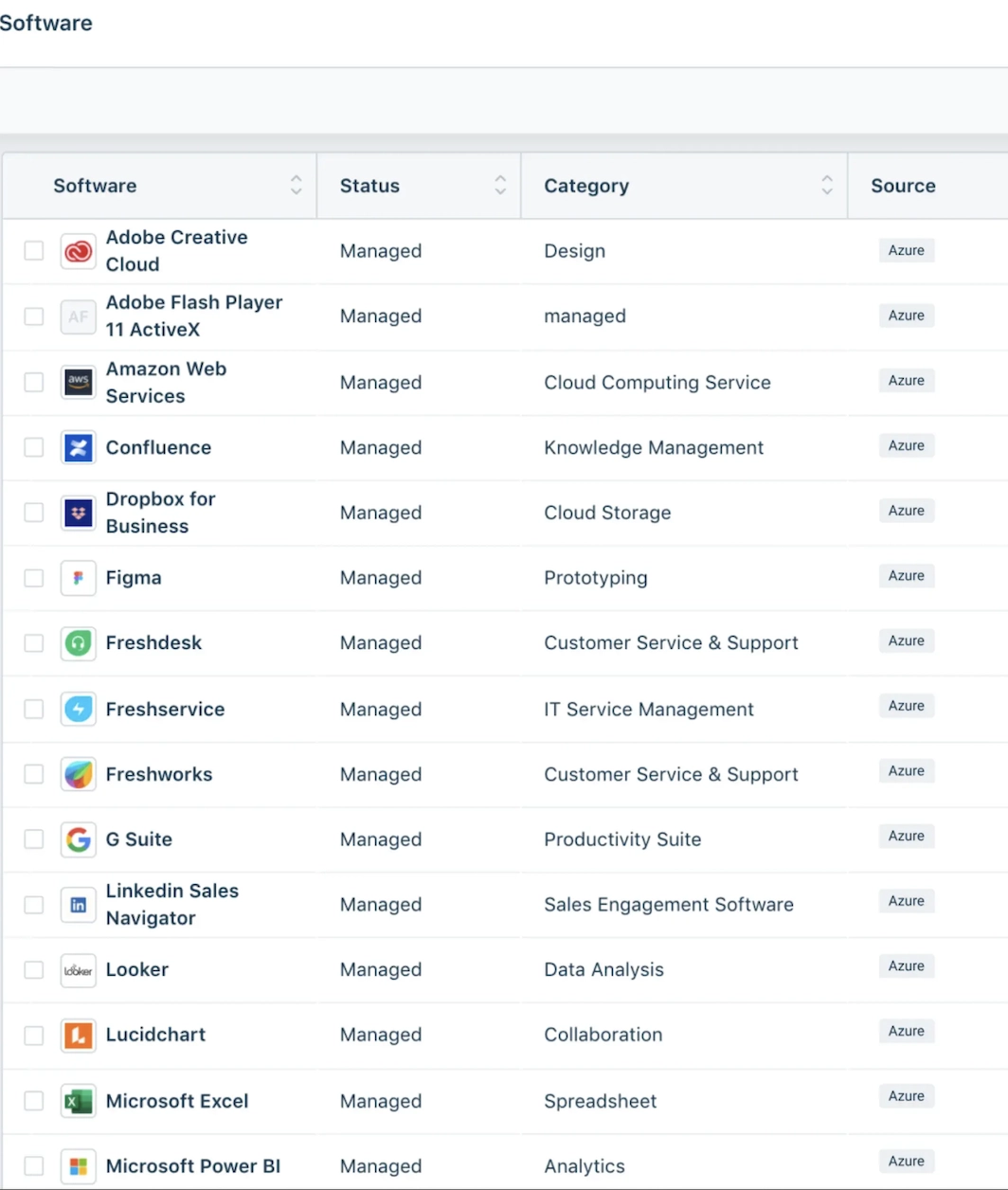
Figure 1: Freshservice software asset management dashboard.
Freshservice starter plan costs $19/agent/month and it includes:
Core ITSM features such as incident management, knowledge base, self-service portal, and SLA management.
Basic workflow automation with a drag-and-drop interface.
Basic analytics to assess service desk performance.
Does not include asset management features.
Growth plan costs $49/agent/month and it includes:
Asset management for up to 100 assets.
Multiple SLAs with policies for ticket management by department or group.
Purchase order management for complete expense management from purchase to fulfillment.
Pro plan costs $95/agent/month and it includes:
Critical issue alert management with automated resolutions.
Advanced analytics with custom, scheduled reports, and filters.
Workload management for better task allocation and team insights.
Enterprise plan costs $119/agent/month and it includes:
Audit logs for tracking changes in the Admin section.
ServiceBot with a virtual agent for Microsoft Teams and Slack, featuring on-demand self-service.
AssetSonar
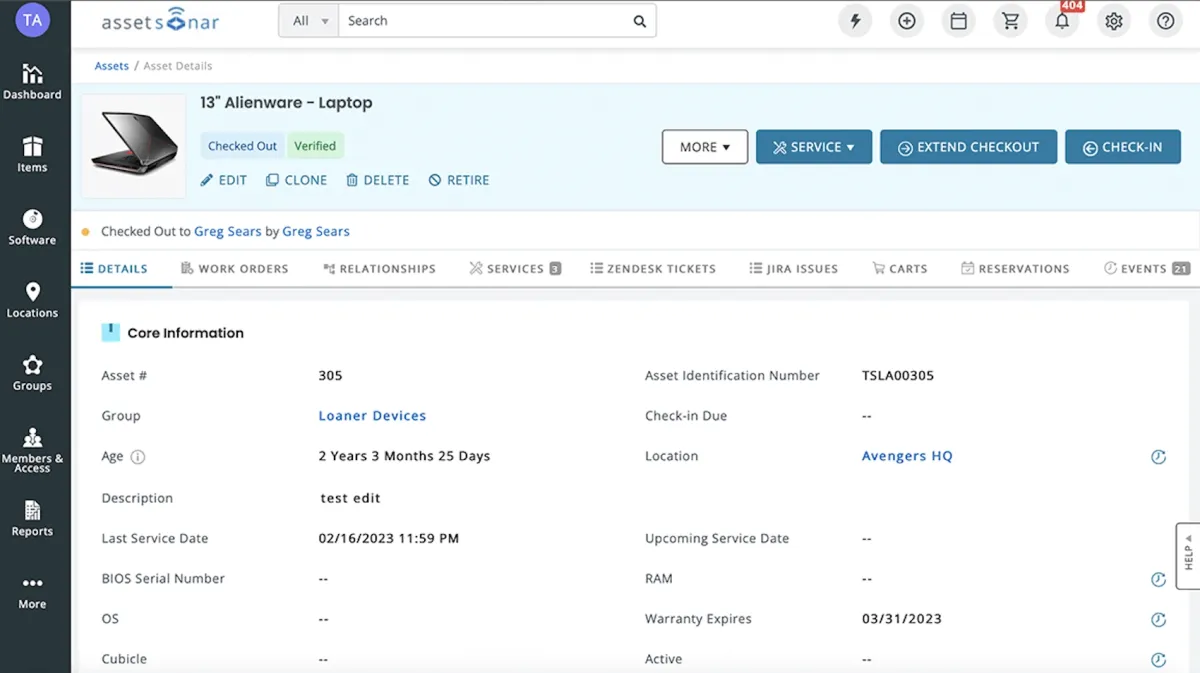
Figure 2: AssetSonar hardware asset management dashboard.1
AssetSonar’s pricing is calculated based on the number of assets/devices, registered software license seats and admins.
For example, a plan with for 100 devices, 500 registered software license seats and 1 admin costs 70$ per month. As the device and admin number and registered software license seats goes up, the price also increases. Each device costs $0.25.
Regardless of the number of devices, registered software license seats and admins, AssetSonar includes:
Barcode, QR code, and RFID scanning for hardware management.
Advanced access control and customizable role-based permissions and employee off-boarding workflows.
Management of both installed and cloud software licenses.
Device discovery for agents and network devices using agentless methods.
ITSM with integrations for Jira and Zendesk help desk, as well as a service catalog available on Zendesk.
Asset visibility through integrations with endpoint managers such as Google Endpoint Manager, Kandji, SCCM, Jamf, and Microsoft Intune.
Management of contracts, work orders and purchases.
Mobile app available on iOS and Android platforms.
Atomicwork
Figure 3: Atomicwork IT asset lifecycle and workflow automation.2
Atomicwork’s Professional plan for companies with 500-1.000 employees costs $90 per year and it includes:
Single workspace for the entire company.
Service requests and approval management.
No-code workflow builder for process automation.
Login with a password for easy access.
Email support available during business hours.
Limited access to Atom AI which is a conversational AI assistant that automates end-to-end resolutions for common issues and simplifies the request process via Slack and Microsoft Teams. Atom AI also personalizes responses based on the employee’s role, location, and permissions.
Business plan for companies with 1.000-5.000 employees with a custom pricing includes:
Dedicated workspaces tailored for each team.
Enterprise-level single sign-on (SSO).
IT service management (ITSM) features.
Triggers and actions for external applications.
Phone support available during business hours.
Unlimited access to Atom AI.
Enterprise plan for companies with more than 5.000 employees with a custom pricing includes:
Unlimited access to APIs and comprehensive audit logging and monitoring.
Personalized AI branding and training.
Customizable roles and data governance.
Dedicated expert support.
Lansweeper
Figure 4: Lansweeper asset management analytics diagram.3
Lansweeper includes a forever free plan for small networks with less than 100 assets, unlimited users and community support.
Lansweeper Starter plan costs $200 per month and includes:
2.000 assets,
IT, cloud and operational technology (OT) discovery to provide visibility to all devices and systems on the network.
Lansweeper cloud access to manage the asset inventory from anywhere.
Up to 3 federation installations. This means that data related to assets, software, and users from different Lansweeper installations can be consolidated and viewed in a single, unified interface.
Up to 3 asset scopes to manage who can see which data for the entire application.
Starter support desk.
Single sign on (SSO) and success manager are not included.
Lansweeper Pro plan for larger organizations with higher security, customization, and support needs costs $400 per month and includes:
Up to 5 federation installations.
Starter and pro apps to integrate Lansweeper with other tools via certified plug-and-play integrations.
Up to 10 asset scopes.
Pro support for support desk.
Lansweeper Enterprise plan with a custom pricing plan includes:
From 10,000 assets and can be increased based on the business needs.
Lansweeper Concierge add-on for easier set-up and adoption.
Unlimited asset scopes.
Enterprise level customer support.
Timly
Timly Essential plan costs $205 and includes:
Access permissions management
Unlimited users and profiles.
Digital Stocktaking to manage mobile devices.
Email, phone, live chat and Timly Q&A help center.
IT Discovery, GPS location tracking and single sign-on (SSO) are optional.
Add ons including smart inventory, asset deployment planning, extended audit log, tracking of performance & usage data are not included.
Timly Professional plan costs $550 and includes:
Ticketing system, digital signature at check-out, consumables and inventory items, and basic GPS location tracking.
Access to REST API interface.
Timly Enterprise plan with a custom pricing includes:
Custom user roles.
SSO, smart inventory, extended audit log, and IT discovery.
Multi-client availability to leverage Timly in different organizational units.
Implementation and training customized to special needs of customers.
What is the average cost of IT asset management software?
Average starter plan costs between $8-200/month.
Which factors affect pricing?
ITAM pricing is shaped by various factors related to managing assets and their lifecycle within an organization. Here are the some of the key considerations that affect pricing:
Number of users and devices
ITAM pricing often depends on the number of users and assets (e.g., hardware, software, and network devices) being managed.
Larger organizations with more assets and multiple users will typically see higher costs, as the system needs to accommodate increased asset lifecycles and complex configurations.
Features and customization
Advanced asset management software with higher costs offers features such as service management, configuration management databases (CMDB), and integration with IT infrastructure monitoring tools. This helps organizations track and manage asset lifecycles, contract renewals, compliance, and audits.
Cloud vs. on-premise deployment
Pricing can vary based on whether the asset management tool is cloud-based or on-premise. Cloud solutions may include subscription costs that are influenced by data storage needs and the number of users.
Hosting services within specific regions or ensuring data security to minimize risks such as GDPR compliance can also impact pricing.
Support and services
Comprehensive customer support, implementation assistance, and training can increase the cost of an asset management tool.
Higher-tier pricing usually includes premium support, which is beneficial for managing a strong foundation of IT infrastructure, handling complex contracts, and addressing security risks.
Add-ons and integrations
Additional features like automation for managing purchase orders, impact analysis, and compliance tracking often involve extra cost.
Integrating the tool with other components of the IT infrastructure, such as Microsoft systems or third-party services, can also influence ITAM pricing.
Scalability and enterprise requirements
Organizations that need to maintain extensive IT infrastructure and optimize asset management lifecycles typically require custom pricing based on their scale and specific requirements.
Enterprise-level ITAM systems often require scalability to handle a comprehensive range of assets and users across multiple locations. These systems provide the ability to manage and track assets across their entire lifecycle while minimizing risks and maximizing utilization.






Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.