According to IBM’s “Cost of a Data Breach Report,” the average financial impact of a data breach has surged to an alarming $4.45 million per incident.1 With the growing reliance on digital platforms and accelerated digital transformation, penetration testing has become an indispensable tool for businesses seeking to fortify their cybersecurity defenses.
Penetration testing, or pentesting, involves simulating cyber attacks on computer systems, networks, or web applications to identify and address security vulnerabilities. We delve into the key use cases of penetration testing, highlighting its significance in a modern business environment and giving real-life use cases as examples.
1. Identifying Security Vulnerabilities
Penetration testing is employed to detect vulnerabilities in a business’s digital infrastructure. By simulating real-world cyber attacks, penetration testing goes beyond theoretical assessments to uncover practical weaknesses that malicious actors could exploit.
This process involves ethical hackers using the same techniques as potential attackers but in a controlled and safe manner, allowing them to identify and document vulnerabilities that automated tools might miss.
Penetration testing is a key component of proactive cybersecurity, but it works best when paired with complementary tools and practices. For example, teams often follow up on findings with vulnerability scanning tools and DAST tools to ensure broad and continuous coverage of known issues.
Case Study
Target suffered a massive data breach due to a vulnerability in its payment system, resulting in the compromised personal and financial information of over 70 million customers. 2
While a pre-attack vulnerability scan had identified this weakness, the issue was not immediately remediated, leading to the breach. This case underlines the importance of identifying vulnerabilities through penetration testing and prioritizing their immediate rectification.
2. Testing Security Measures and Enhancing Awareness
Regular pentesting assesses the effectiveness of existing security measures. It ensures that firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security protocols function correctly and provides insights into areas needing enhancement.
Through penetration testing businesses can identify vulnerabilities in their systems and assess the resilience of their security protocols. For example, if a penetration test successfully breaches a network, it indicates a need to strengthen the network’s defenses. This process goes beyond theoretical analysis, offering concrete evidence of security performance.
Penetration testing also helps validate the efficacy of employee security training and awareness programs. For instance, pen tests can reveal flaws in security policies, configurations, and even employee susceptibility to social engineering tactics like phishing. By doing so, organizations can gauge how well employees adhere to security policies and procedures in the face of a simulated attack.
3. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Figure 1: The rising cost of Compliance
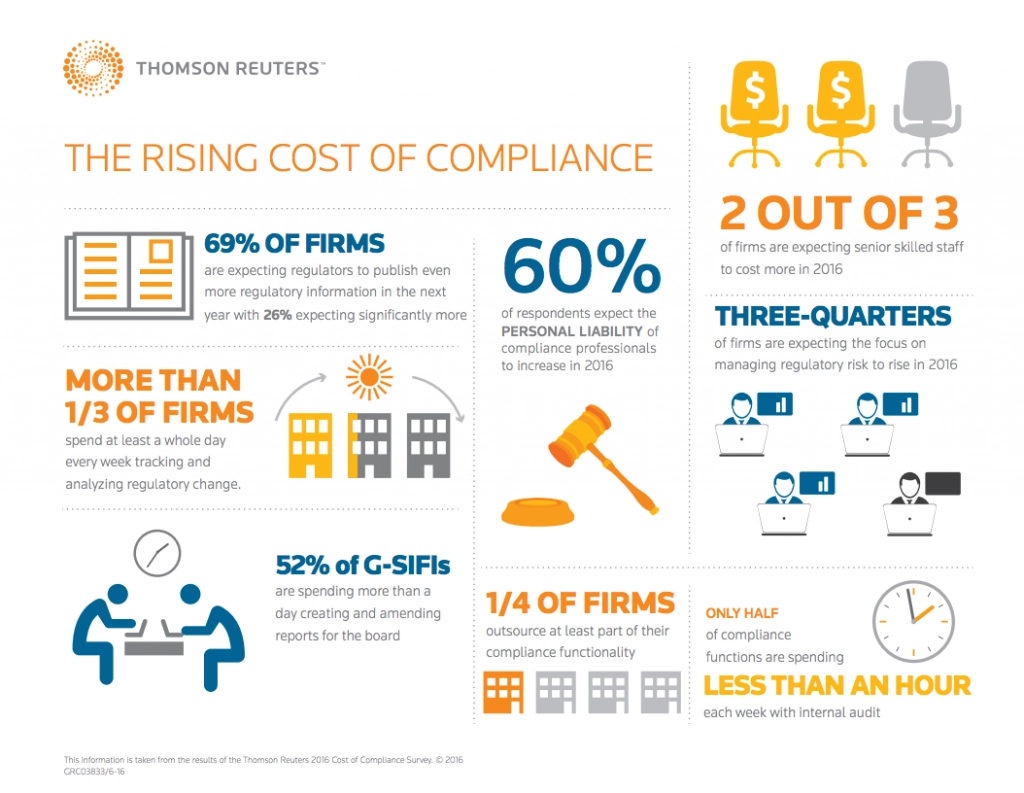
Source: Reuters3
The average total data breach cost in smaller companies (500 employees or less) increased from $2.92 million in 2022 to $3.31 million in 2022.4 , and for large firms, compliance costs can be $10,000 per employee. 5 The cost of compliance is growing, and firms are putting in significant effort to overcome challenges related to compliance see Figure 1.
Penetration testing is crucial in helping organizations comply with regulatory and compliance requirements. Many industries and data protection laws require regular security assessments to protect sensitive data. For instance, standards like the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) mandate regular penetration testing for entities handling credit card transactions. Similarly, healthcare organizations under HIPAA, financial institutions under GLBA, and companies subject to GDPR must adhere to stringent data security measures, often validated through penetration testing.
Pentesting tools help organizations demonstrate due diligence in identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities, a key aspect of compliance. They provide detailed documentation of assessments, including discovery, exploitation, and remediation, which is crucial for audits and regulatory reviews. Additionally, penetration testing uncovers security gaps beyond compliance checklists, ensuring stronger regulatory adherence.
Case Study
A U.S. government lab faced challenges in protecting its massive database of sensitive information and sought to improve its interpretation of vulnerability scanner results. By implementing regular penetration testing, they were able to better prioritize risks and demonstrate due diligence in compliance audits.
This approach highlights the complementary nature of penetration testing to other vulnerability management practices. This integration helped rapidly weed out false positives and effectively prioritize the most crucial security threats, thus reducing the time and manual effort needed to manage IT security risks. 6
4. Business Continuity Planning
Penetration testing significantly contributes to Business Continuity Planning (BCP) robustness. For example, if a penetration test reveals that specific cyber attacks could disrupt critical business services, the organization can prioritize protecting these services in its BCP. This includes preparing for scenarios like data breaches, system outages, or other disruptions caused by cybersecurity incidents.
Case Study
A real-life example of how penetration testing aids in Business Continuity Planning can be seen in the 2021 ransomware attack on Ireland’s healthcare system. The attack led to widespread operational disruptions, affecting outpatient services, hospitals, employee payment systems, and COVID-19-related services.
The attack’s impact, including significant recovery costs and the implementation of new security protocols, underscores the importance of proactive measures like penetration testing in identifying and mitigating such threats before they manifest into major disruptions. This case demonstrates the integral role of penetration testing in preparing and safeguarding an organization’s continuity plan against cyber threats. 7
5. Assessing Third-Party Risks
Penetration testing is a vital tool for assessing third-party risks, especially for organizations who increasingly rely on external vendors for services and data processing. When an organization integrates third-party services into its infrastructure, it also inherits the cybersecurity risks associated with those services.
Pentesting tools can be used to evaluate the security posture of these third-party systems, ensuring that they meet the organization’s security standards and do not introduce vulnerabilities into the broader network. By conducting penetration tests on third-party services and applications, organizations can gain access to potential security gaps that could be exploited by cyber attackers. This is particularly important for vendors who have access to sensitive data or critical systems.
The test results provide valuable insights into the security practices of these vendors, enabling organizations to make informed decisions about continuing or altering their partnerships. Additionally, it helps in ensuring compliance with various regulatory requirements, as the responsibility of protecting sensitive data extends to third-party handlers.
If third-party services are part of the infrastructure, it’s important to evaluate their risks as well. That’s where extended assessments like open source SAST tools or partner-focused audits become relevant.
Case Study
SolarWinds, a software provider, was compromised in a supply chain attack, affecting numerous government agencies and private companies. At the beginning of 2020, cyber attackers covertly infiltrated the systems of Texas-based SolarWinds, inserting malicious code into the company’s software. Starting from March 2020, SolarWinds unknowingly distributed software updates to its clients, which contained the compromised code. This scenario emphasizes the importance of conducting security assessments not only on your own systems but also on third-party systems or software you rely on. 8
6. Automation
Penetration testing and automated tools are crucial for cybersecurity and IT automation. Pen tests uncover recurring vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to develop scripts or tools for continuous monitoring and mitigation. Automated testing enhances efficiency, streamlining vulnerability management and ensuring consistent threat detection and response, reducing manual effort while improving security posture.
Furthermore, the insights gained from penetration testing can inform and refine automated security solutions. Organizations can tailor their automated security tools, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) systems, by understanding the nature and complexity of identified vulnerabilities to be more effective. This tailoring is crucial because it ensures that automated systems are well-equipped to detect and respond to sophisticated and evolving cyber threats.
7. Secure Product Development
During the development process, penetration testing helps identify security vulnerabilities that might not be evident during regular testing phases. By simulating real-world attack scenarios, penetration testers can uncover weaknesses such as injection flaws, broken authentication, or insecure configuration. Early detection of these issues allows developers to address them before the product is released, significantly reducing the risk of security breaches post-launch.
In API-driven environments, it’s common to also run API security testing to identify vulnerabilities at the interface level—especially when endpoints are exposed externally.
Popularity of Penetration Testing
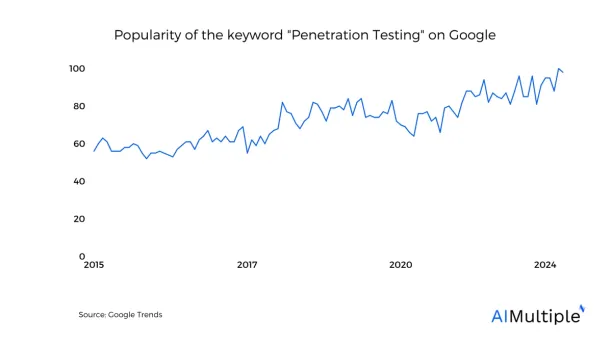
Penetration testing has gained steady prevalence over the years as you can see in the data above.
Penetration Testing FAQ
What is Penetration Testing?
Penetration Testing, commonly referred to as pen testing, is a simulated cyber attack against your computer system, network, or web application to check for exploitable vulnerabilities. It’s akin to a controlled experiment to identify security weaknesses. It can also identify spam attacks.
Why is Penetration Testing Important for Businesses?
Penetration Testing is crucial for businesses to identify and fix security vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by hackers. It helps safeguard sensitive data, ensure compliance with regulatory standards, verify wifi network security, and maintain customer trust.
How Often Should a Business Conduct Penetration Testing?
The frequency of penetration testing can vary depending on several factors, such as changes in network infrastructure, introduction of new applications, compliance requirements, or major upgrades. Typically, it’s recommended to conduct pen testing annually or bi-annually.
What Are the Different Types of Penetration Tests?
Common types of penetration tests include network services testing, web application testing, client-side testing, wireless security testing, and social engineering tests. Each type focuses on different aspects of your organization’s security.
Can Penetration Testing Disrupt Business Operations?
While pen testing is designed to be non-disruptive, certain tests may pose risks to operational stability. It’s important to plan the testing carefully and possibly conduct it during non-peak hours to minimize potential disruptions.
What Should a Business Do After a Penetration Test?
After a penetration test, businesses should review the report provided by the testers, prioritize the vulnerabilities found, and implement the recommended security measures. Ongoing monitoring and additional testing after fixes are also essential.
Is Penetration Testing the Same as Vulnerability Scanning?
No, they are different. Vulnerability scanning is an automated process to identify potential vulnerabilities, while penetration testing involves a more in-depth, manual process of exploiting vulnerabilities to understand their impact.
Who Should Perform Penetration Testing?
Penetration Testing should be performed by skilled and experienced security professionals, often from a third-party organization, to ensure an unbiased and comprehensive assessment.
Are There Any Legal Considerations with Penetration Testing?
Yes, legal considerations include obtaining explicit permission to perform the tests, ensuring data privacy, and adhering to legal and regulatory standards. Always consult with legal advisors before initiating a pen test.
How Does Penetration Testing Improve Cybersecurity?
Penetration testing improves cybersecurity by proactively identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, enhancing incident response capabilities, and informing better security strategies and policies.
External Links
- 1. Cost of a data breach 2024 | IBM.
- 2. Your browser is not supported | usatoday.com.
- 3. The cost of compliance in the changing world of regulation | Thomson Reuters.
- 4. Cost of a data breach 2024 | IBM.
- 5. The Creeping Cost Of Compliance.
- 6. U.S. Government Laboratory Case Study | Penetration Testing.
- 7. 7 Sample Business Continuity Plan Examples to Learn From. Invenio IT
- 8. What Is the SolarWinds Hack and Why Is It a Big Deal? - Business Insider. Business Insider

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.