We’ve compared the top DNS security solutions and their key features and pricing to help you find the best protection for your organization’s network. See our rationale for these recommendations by following the links on the product names:
| Software | Best For | |
|---|---|---|
1. | Large enterprises and organizations with existing Cisco infrastructure | |
2. | Simple admin interface with essential filtering controls | |
3. | AI-based threat detection with easy roaming client deployment | |
4. | Combines DNS security with SWG, CASB, and ZTNA in one platform | |
5. | High configurability, real-time logs, and privacy-first approach | |
With over 20 DNS security tools available on the market, selecting the right solution can be a complex task. When choosing a DNS security tool, users often consider the following factors:
- Threat Detection Capabilities: Ability to detect and block malicious domains, phishing attempts, and DNS tunneling.
- Response Time: Speed at which the tool identifies and reacts to threats to minimize exposure.
- Integration with Existing Security Stack: Compatibility with firewalls, SIEMs, and endpoint protection tools.
- Admin Panel Functionality – Ease of use, configurability, and depth of control in the tool’s administrative dashboard.
- Policy Management: Granular control over DNS queries based on users, devices, or network segments.
Top 5 DNS Security Tools Compared
| Vendors | Reviews** | Free Trial*** | Employees | Price | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisco Umbrella | 4.3 based on 343 reviews | ✅ | 100,466 | Not shared publicly | |||||||
| DNS Sense | 4.9 based on 67 reviews | ✅ | 51-200 | From $119 to $600 per year (Basic to Unlimited Plan) | |||||||
| DNSFilter | 4.6 based on 239 reviews | ✅ (30-day) | 51-200 | Basic Plan: $1.15 Pro Plan: $2.30 Enterprise Plan: $3.00 (1 User Per Month) | |||||||
| Zscaler | 4.5 based on 532 reviews | ✅ (7-day) | 2,100 | Pro Plan: $20.00 Business Plan: $200.00 | |||||||
| NextDNS | 4.4 based on 88 reviews | ✅ (30-day) | 10,000 | Not shared publicly |
Features of DNS Security Solutions
| Key Features | Cisco Umbrella | DNS Sense | DNSFilter | Zscaler | NextDNS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Threat Detection | With Cisco Talos | Limited | AI-Based Detection | With Zscaler ThreatLabZ | Basic threat blocklists |
| User/Device-Level Policies | With AD or client agents | Per IP or subnet | Roaming Clients & Active Directory | Zero Trust | Per device/profile |
| API Support | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| DNSSEC Support | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | Limited | ✅ |
| DDoS Protection (DNS) | ✅(via Cisco Anycast) | ❌ | via edge DNS | ✅ (Enterprise-grade) | ✅ (rate limiting) |
| Client/Group Based Rulesets | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Client Based Reporting | ✅ | ✅ Through DNSEye module | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Integration with Security Stack | Deep integration (Cisco stack) | Integrates with security tools | Easy integration | Works with broader Cloudflare stack | Full security stack integration |
| DNS over HTTPS (DoH) Support | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| SSL/TLS Traffic Inspection | Partial (via SWG integration) | ❌ | Limited | ✅ | ❌ |
All providers — Cisco Umbrella, DNS Sense, DNSFilter, Zscaler, and NextDNS — offer essential features such as real-time DNS filtering, customizable blacklist/whitelist controls, category-based website blocking, and a centralized admin dashboard for monitoring and policy management.
Cisco Umbrella
Cisco Umbrella is one of the most recognized DNS security solutions on the market, featured in Gartner reports and widely adopted by large enterprises. Its standout features include agent-based Zero Trust integration, DNS-layer threat prevention, and exceptionally low response times, all while placing zero load on the network. Cisco’s intuitive admin panel offers powerful visibility and quick policy enforcement across distributed environments.

Cisco Umbrella excels in environments where roaming users and remote branches need to be secured without deploying full-stack firewalls. It also supports DNSSEC, ensuring DNS integrity and authentication.
However, while its grouping and segmentation capabilities are robust, it is not designed explicitly for dynamic grouping based on roles, IP blocks, or VLANs—a feature more commonly requested by SMBs or multi-tenant environments.
DNS Sense
DNS Sense is an emerging player gaining traction in markets that need dynamic, role-based segmentation. Unlike many traditional DNS tools, administrators can assign DNS policies based on user roles, network segmentation (such as WLAN or IP block), and even dynamic DNS records.
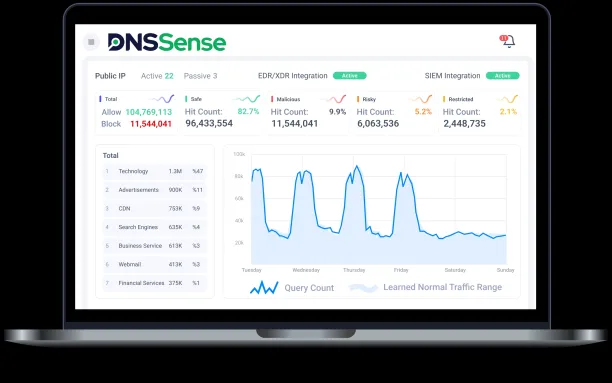
Although its response time and UI are not yet on par with Cisco Umbrella, DNS Sense offers excellent flexibility in grouping and a relatively lightweight infrastructure footprint. It supports DNSSEC, giving it a standards-compliant baseline for DNS integrity.
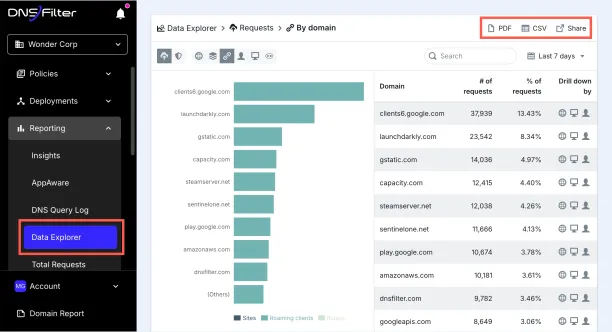
DNSFilter
A cloud-first DNS security solution that uses AI to detect new threats in real time. Offers robust content filtering, roaming client support, and per-user or per-location policies. Integrates easily with MSPs and enterprise setups.
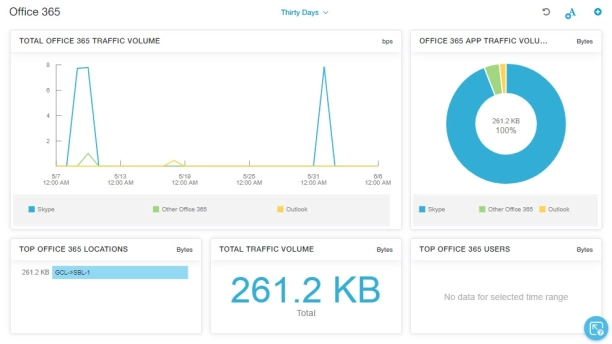
Zscaler Internet Access (ZIA)
Zscaler is a cloud-native security platform primarily used by enterprises for secure internet and cloud access. While it goes far beyond DNS filtering, it includes DNS security as part of its broader Zero Trust model.
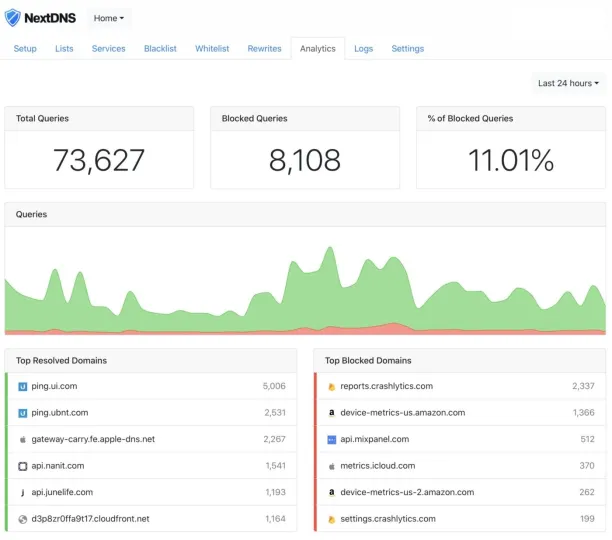
NextDNS
A privacy-focused DNS firewall offering real-time analytics, device-level rules, and extensive customization. You can set per-profile rules, access detailed query logs, and block trackers, ads, and threats. Consumer and SMB-friendly DNS filtering service offering customizable blocklists, analytics, and encrypted DNS protocols (DoH, DoT). Focused on privacy and parental control.
Why are the differentiating features important?
1. DNSSEC Support
DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) adds a layer of authentication to DNS lookups by using digital signatures to verify that the DNS responses come from a legitimate source and haven’t been altered.
DNS does not verify the authenticity of responses by default, making it vulnerable to attacks such as DNS spoofing or cache poisoning. DNSSEC helps protect against these threats by ensuring the integrity of DNS data.
When a DNS resolver queries a domain, DNSSEC verifies the cryptographic signatures in DNS records to confirm their validity. The response is rejected if the signature doesn’t match, preventing potentially harmful redirection.
2. DNS Firewall / Filtering
A DNS firewall, also known as DNS filtering, is a security mechanism that monitors and filters DNS queries to block access to domains associated with harmful or unauthorized content.
DNS is critical in internet traffic because every website visit starts with a DNS query. By filtering these queries, organizations can prevent access to known malicious domains (such as those used for phishing, malware distribution, or botnet control). It also allows organizations to enforce internet usage policies by restricting access to specific content categories like gambling, adult content, or social media.
3. DDoS Protection (DNS)
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) protection for DNS is a set of techniques used to safeguard DNS servers from being overwhelmed by massive volumes of malicious traffic that attempt to make services unavailable.
DNS servers are high-value targets for attackers. A successful DNS-based DDoS attack can result in widespread service outages, as users would be unable to resolve domain names to IP addresses.
This type of disruption can affect websites, applications, and communication systems. DNS DDoS protection ensures that services remain operational even under attack.
DDoS protection mechanisms can include various methods. One approach is anycast routing, where DNS queries are distributed across multiple geographically dispersed servers to absorb traffic spikes. Other methods include rate limiting, which restricts the number of queries from a single source; traffic filtering, which blocks known bad actors; and challenge-response tests, which verify whether a request is from a legitimate user or a bot. These strategies work together to keep DNS infrastructure responsive during high-load conditions.
4. Integration with Security Stack
Integration with a broader security stack means that DNS security tools are designed to share data and coordinate actions with other security systems, such as firewalls, endpoint detection and response (EDR), security information and event management (SIEM), and identity providers..
Isolated security systems can result in fragmented threat detection and response. When DNS security integrates with other tools, it becomes part of a unified defense system.
This enables faster threat detection, better contextual analysis, and coordinated responses across different layers of the network.
5. Cloud Deployment
Cloud deployment refers to delivering DNS security through cloud infrastructure, eliminating the need for organizations to manage their own DNS servers or on-site security hardware.
Cloud deployment offers several advantages, including reduced infrastructure costs, simplified setup and maintenance, and consistent protection for remote users and distributed offices.
It also allows DNS security to scale more easily with organizational growth and adapt quickly to new threats without manual updates.
FAQ
What is the purpose of a DNS security benchmark?
A DNS security benchmark evaluates and compares the capabilities of different DNS security solutions. It helps organizations understand how well each tool performs in terms of threat protection, filtering, performance, and administrative features. The goal is to select the most suitable solution based on specific business needs, infrastructure, and risk tolerance.
How were vendors selected for this benchmark?
Vendors were selected based on their market presence, feature sets, and relevance to common business use cases (e.g., enterprise, SMB, remote teams). Solutions vary in complexity, from lightweight tools suitable for small teams to enterprise-grade platforms.
Why is DNSSEC important in a DNS security tool?
DNSSEC adds authentication to DNS responses, ensuring they haven’t been tampered with during transmission. This helps prevent attacks such as DNS spoofing or cache poisoning, which could redirect users to fraudulent or malicious websites.
How does DNS filtering improve security?
DNS filtering prevents users from accessing known malicious domains or unwanted content. By blocking harmful requests at the DNS layer — before a connection is established — organizations can reduce their exposure to malware, phishing, and data exfiltration.
How should I choose the right DNS security solution?
Start by identifying your organization’s specific needs — such as compliance requirements, remote workforce support, threat exposure, and budget. Then compare the tools based on the features that matter most to your environment. Use this benchmark as a guide to narrow down your shortlist.







Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.