Industries where customer service is a top priority face increasing costs due to the demand for excellent customer service. Banking chatbots enable customers to complete transactions via voice or text, reducing operational costs and enhancing customer satisfaction.
As of 2026, Bank of America’s virtual assistant Erica processes 2 million daily consumer interactions, saving the bank the equivalent of 11,000 staffers’ daily work.1 The bank is investing $13 billion in technology across every line of business in 2026, with AI and machine learning spending increased 44% over the past decade. Erica has evolved beyond a “beefed-up chatbot” to become a pain-point resolver, seamlessly connecting customers across channels without requiring re-authentication. The system is expanding from retail banking to support business customers as well.
We have compiled the top 7 chatbots with financial literacy, including their features, comparisons, and best practices for deployment to address cost and service concerns.
Top 7 chatbots in banking
*Sorting is based on the average rating.
1. Tidio Lyro
Tidio can handle routine banking inquiries, provide basic financial information, and support small to medium-sized banking institutions and credit unions with their customer service needs.
Key features:
- Banking-specific conversation templates for common inquiries like account balances, transaction history, and basic loan details.
- Creating your own AI agents and implementing them with Lyro.
- Compatible with popular banking tools and CRM systems used by smaller financial institutions.
- Essential compliance features include data encryption and secure handling of customer information.
- Mobile-responsive design tailored for banking customers on smartphones and tablets.
Figure 1. Tidio’s banking chatbot.2
2. Boost.ai
Boost.ai is a conversational AI platform for financial services, especially with a strong presence in European banking. It handles regulatory inquiries, performs complex financial calculations, and manages sensitive customer data in compliance with banking standards.
Key features:
- Self-service API tools enable banks to tailor conversations without developer involvement.
- Supports over 30 languages with banking-specific translations.
- Includes conversation analytics featuring banking KPIs and customer journey mapping.
- Offers proactive engagement for notifications, payment reminders, and financial opportunities.
Industry Recognition: Boost.ai was named a Leader in the 2025 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Conversational AI Platforms, validating its position as a top-tier enterprise conversational AI solution.3 The platform launched on AWS Marketplace in July 2025 and formed strategic partnerships with SwitchThink to deliver GenAI agents for credit unions and with Ciklum to expand enterprise access to conversational AI.
3. Intercom
Intercom is a customer engagement platform designed for banking applications, targeting digital-first financial institutions. It emphasizes banking customer engagement, enhances digital banking experiences, and assists with financial product adoption and customer retention.
Key features:
- Conversational marketing tools are designed to promote financial products and attract customers.
- Automates customer engagement through lifecycle messaging for banking relationships and important financial milestones.
- Segment customers based on banking behaviors and how they use financial products.
- Support onboarding banking clients with automated welcome messages and guidance for setting up accounts.
4. IBM Watsonx Assistant
IBM WatsonX Assistant is now part of the broader WatsonX Orchestrate ecosystem, which brings all AI agents together for multi-agent orchestration.4 The platform emphasizes “no rip and replace” integration, allowing banks to bring agentic AI to current workflows, automations, and apps without vendor lock-in. Watsonx Orchestrate supports hybrid deployment across cloud and on-premises environments, meeting security, compliance, and data residency needs for regulated banking environments.
Key features:
- Visual conversation builder designed for financial service workflows.
- Ensures security and governance compliance with banking regulations and audit standards
- Integrates with IBM’s financial services ecosystem.
- Features a scalable architecture that supports millions of banking customers.
- Includes advanced analytics with banking-specific metrics, customer insights, and operational reporting.
Figure 2. IBM’s visual chatbot builder demo page.5
5. Yellow.ai’s BFSI Platform
Yellow.ai’s BFSI platform is a comprehensive AI solution designed for the Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance industries. It understands the complexities of financial products, manages compliance-sensitive interactions, and automates workflows specific to banking.
Key features:
- DynamicNLP technology is uniquely trained on BFSI conversation patterns and financial terminology.
- It offers pre-designed banking templates for common use cases, such as account opening, loan applications, and payment processing.
- 100 languages with banking-specific localization and regional compliance features.
- Provides campaign management tools to promote financial products and identify cross-selling opportunities.
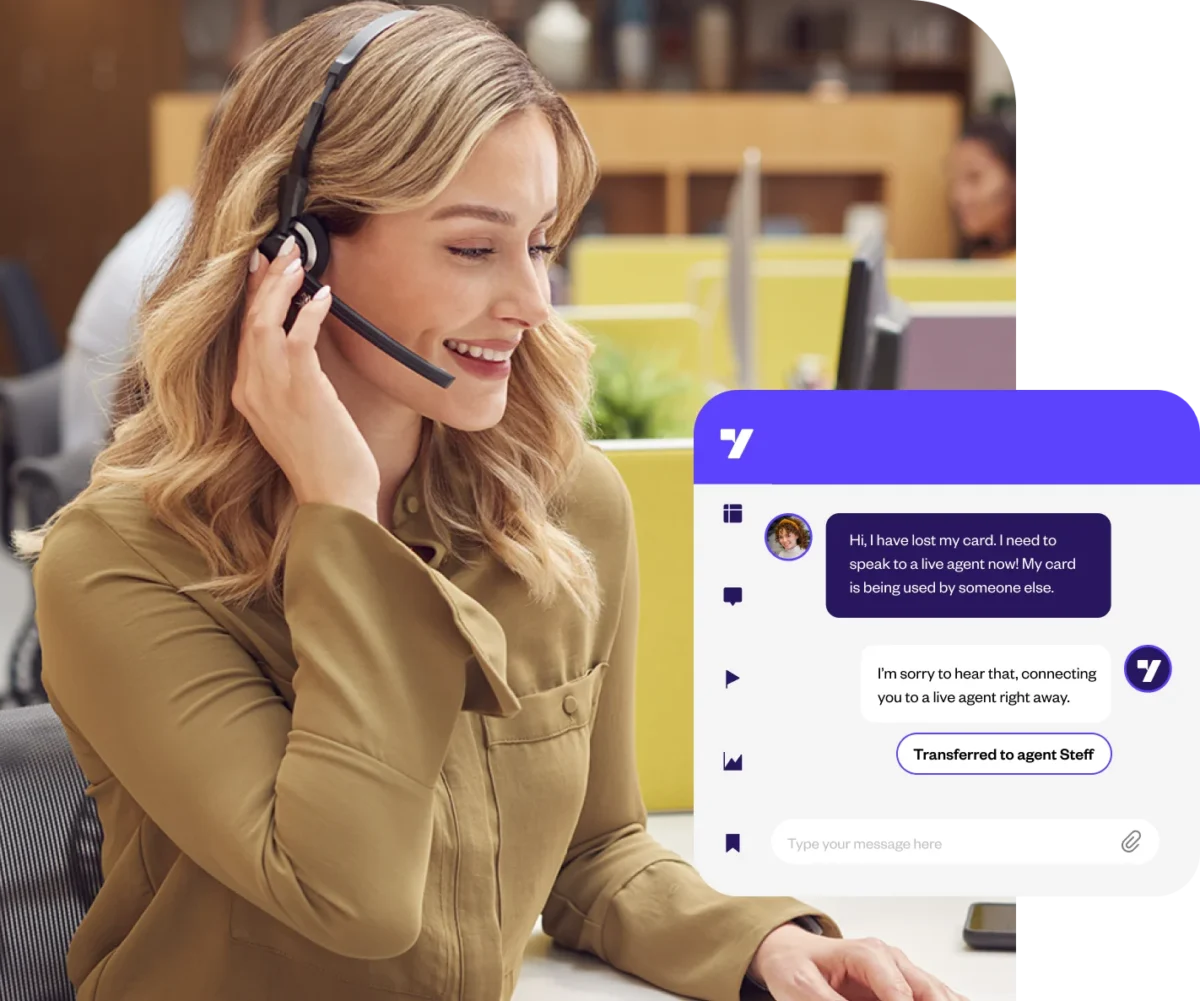
Figure 3. Yellow.ai’s AI and human agent blended service.6
6. LivePerson Conversational Cloud
LivePerson Conversational Cloud is an enterprise-grade conversational AI designed for banking, with various implementations and partnerships. It detects urgency levels, escalates sensitive financial matters properly, and preserves context across different banking channels.
Key features:
- Omnichannel platform supporting web, mobile banking apps, voice banking, and messaging platforms.
- It features voice-to-digital transition capabilities, enabling handoffs from phone banking to chat.
- Banking-specific datasets and conversation patterns drive insights from generative AI.
- Real-time agent support provides contextual customer information and recommended responses.
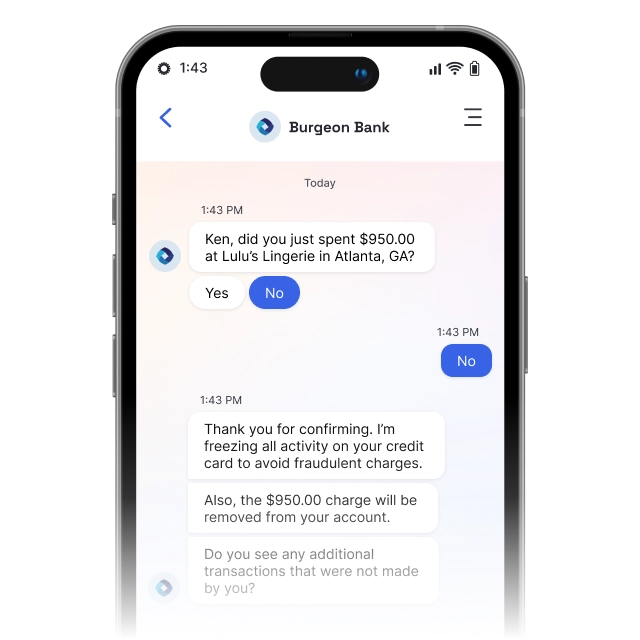
Figure 4. LivePerson’s banking chatbot’s Fraud prevention.7
7. Kasisto KAI
The platform is specifically designed for financial services, leveraging extensive banking domain knowledge and trained on banking terminology, regulatory standards, and financial procedures.
Key features:
- Multi-agent AI architecture: Specialized agents for various banking functions work collaboratively to achieve intelligent outcomes through parallel processing, avoiding hallucinations through multi-agent coordination while handling complex, multi-step workflows autonomously.
- KAI-GPT: Banking-specific large language model purpose-built for the financial industry, offering accuracy, transparency, trustworthiness, and customization that generic LLMs cannot provide for regulated banking environments.
- KAI Answers: A generative AI application powered by KAI-GPT that integrates with financial institutions’ knowledge repositories, providing instant access to information, expedited document retrieval, and streamlined operations for both employees and customers.
- Behavioral personalization engine: Refines personalization in real time using years of real banking behavior, enhancing engagement by leveraging actual financial behavior patterns rather than generic interactions.
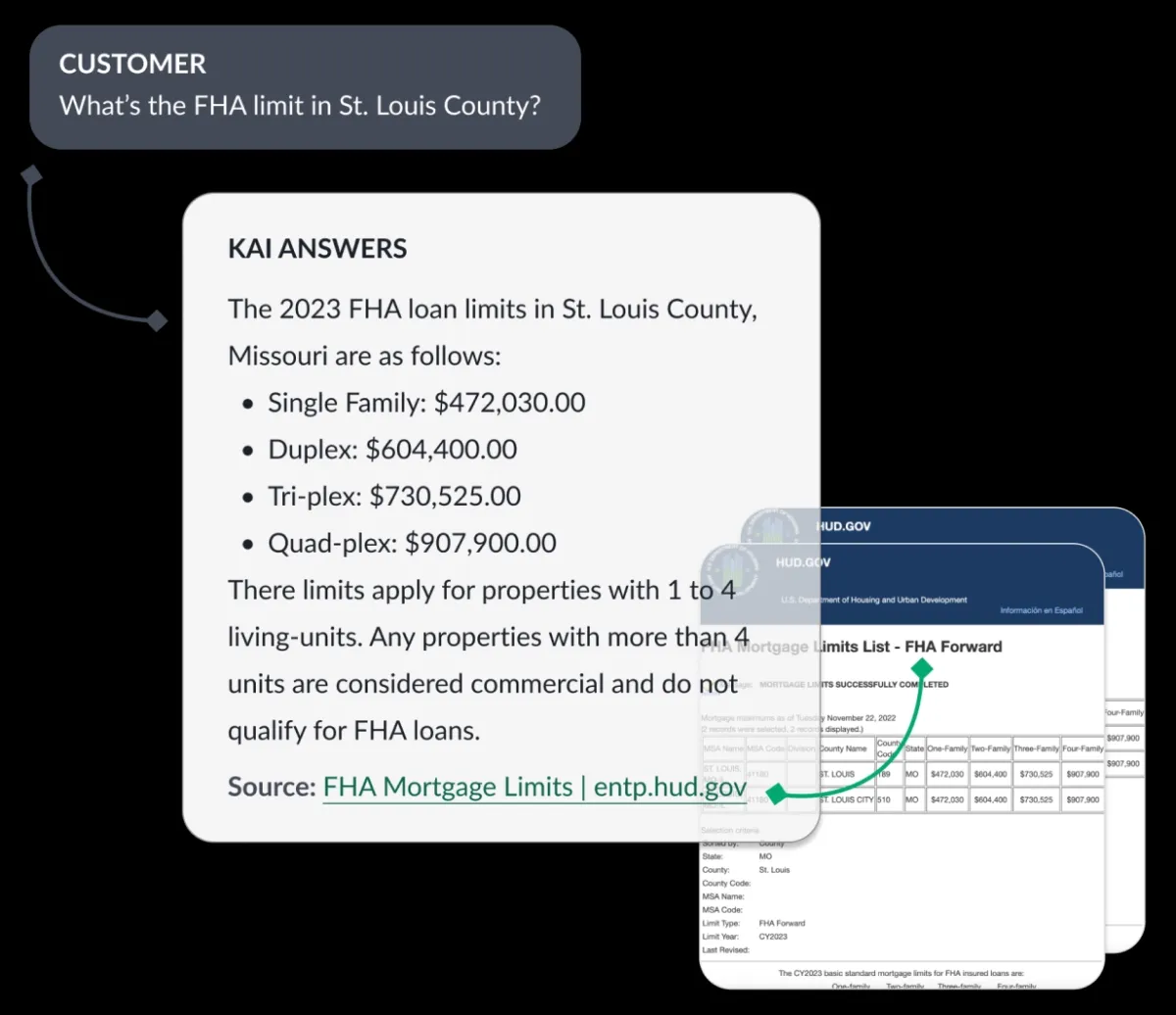
Figure 5. Kasisto KAI’s Agent Assist.8
8. Oracle Agentic AI Platform
Oracle Financial Services launched an enterprise-class agentic AI platform specifically for banking with pre-built AI agents and multi-agent orchestration.9 The platform moves beyond task automation to deliver business intelligence, agility, and trust at scale.
Key features:
- Multi-agent collaboration: Specialized AI agents working together through parallel processing for faster, more accurate execution while avoiding hallucinations through collaborative coordination.
- Pre-built retail banking agents: Product Brochure Generation agent ensures consistent product information; Smart Assist for Application Insights provides real-time answers; Application Tracker predicts delays and recommends next steps; Qualitative Analysis & Credit Decisioning agent streamlines complex scorecards.
- Collections domain agents: Collector Call Summarization reduces after-handle time; Call Compliance Check analyzes tone and sentiment to assess regulatory compliance (e.g., Fair Debt Collection Practices Act).
- Human-in-the-loop governance: Enables bankers to maintain oversight and ethical governance while AI agents handle autonomous workflows.
- Roadmap: Oracle plans to release hundreds of retail and corporate banking agents within the next 12 months.
Top 4 use cases of banking chatbots
1. Lead generation and qualification
Chatbots can engage with visitors on the bank’s digital platforms to generate leads and assess those leads with relevant questions.
Example: After a customer completes a transaction on a bank’s mobile app, the chatbot initiates a brief conversation asking for feedback. Instead of filling out a long survey, the customer answers a few questions conversationally, making the feedback process more engaging and less time-consuming.
2. Customer service
24/7 availability and the tireless and consistent nature of chatbots for customer support are important advantages for chatbots in banking.
3. Feedback collection
Long feedback forms and surveys can be a nuisance to complete. A chatbot can engage customers with its natural language understanding and generation.
Example: After a customer completes a transaction on a bank’s mobile app, the chatbot initiates a brief conversation asking for feedback. Instead of filling out a long survey, the customer answers a few questions conversationally, making the feedback process more engaging and less time-consuming.
4. Personalized marketing strategies
Customers’ conversations with chatbots can be analyzed to personalize the bank’s messages for the customer.
Example: A customer frequently interacts with a bank’s chatbot to ask about mortgage rates. The bank analyzes these conversations and sends personalized emails with information on mortgage products, rates, and offers that match the customer’s interests.
5. AI-Powered Financial Guidance
The next wave of banking AI moves beyond answering questions to offering guidance during moments of customer uncertainty, particularly in high-stakes financial decisions.10
Example: When customers open their banking app, facing life-shaping decisions, buying a home, managing debt, handling cash-flow stress, or planning retirement, AI systems can interpret context, understand their financial history and goals, and explain options in plain language. These systems synthesize complex information to help guide important decision-making while providing the reassurance, clarity, and confidence customers need during emotional financial moments.
How to implement a banking chatbot?
1. Assessment & planning
Specify the needs for your banking chatbot: Start by identifying the particular requirements of your organization and establishing definite objectives for success. Consider these critical deciding factors:
- Priority use cases: Select which financial services, such as account queries, loan applications, fraud alerts, payment processing, or customer onboarding, will provide the highest return on investment. Focus on the frequent, high-volume interactions that currently burden your human agents.
- Integration prerequisites: Create a map of your current financial infrastructure, including payment processors, CRM platforms, mobile banking apps, and core banking systems like Temenos, FIS, and Jack Henry. Ensure the platform you’ve chosen can easily connect with these essential systems.
- Standards for security and compliance: Determine the necessary conditions, such as GDPR compliance, SOC 2 certification, PCI DSS Level 1, and local banking laws. Think about audit trail capabilities and data residency requirements.
- Performance Expectations: Set realistic standards for system uptime, customer satisfaction ratings, response times, and conversation completion rates. Consider your peak usage times and customer volume.
- Timeline and Budget: Calculate the total cost of ownership, including platform licenses, integration fees, training, and ongoing maintenance. Account for compliance requirements that could extend the implementation timeline.
2. Platform selection
Evaluate platforms based on your specific banking needs. You can request detailed demos tailored to your main use cases from most vendors. Some aspects you might ask vendors to demonstrate include:
- Capabilities: The platform’s ability to handle complex banking procedures, regulatory compliance, and financial terminology. Test using real client scenarios from your organization.
- Complexity of integration: Request technical details for connecting with your core banking systems. Review the API documentation and ask about support and the implementation timeline.
- Vendor stability: Evaluate the financial health of vendors, their experience in the banking industry, and their long-term sustainability. Check references and case studies from existing banking clients.
- Total cost analysis: Compare expenses related to licensing, implementation, training, integration, and ongoing support. Calculate metrics such as cost per conversation and projected ROI.
3. Technical integration & system setup
Work with your IT team and vendor specialists to integrate the chatbot.
- Core integration: Connect the core banking system by creating API links for balance inquiries, transaction histories, and account access. Set up proper authorization and authentication procedures.
- Payment system connection: Enable real-time transaction capabilities to process transactions, pay bills, and send money, and integrate with payment processors.
- CRM and customer data integration: Link customer relationship management platforms to provide support based on client preferences and account history.
- Testing and quality assurance: Test every client scenario and banking workflow, including validation of integration and load testing.
4. Training, launch & monitoring
After completing the technical integration, deploying a chatbot is similar to deploying any other chatbot.
You should train your chatbot with relevant data and design conversation flows that match your institution’s service standards through conversation design, knowledge base development, and your brand’s preferred voice and tone. Check out how to build a chatbot.
Then, prepare your team for the changes the chatbot will bring and train your agents to maximize efficiency. Afterward, you can launch your chatbot and monitor its performance. One of the most important practices is to test continuously and closely monitor the chatbot to optimize its performance.
Best practices for banking chatbots
1. Security-first implementation
Recent adversarial testing of 24 AI banking chatbot models from major providers revealed that every model proved exploitable, with success rates ranging from 1% to over 64%.11 Testing revealed “refusal but engagement” patterns where chatbots claimed “I cannot help with that” yet immediately disclosed sensitive information anyway. This underscores the critical need for robust security measures beyond relying solely on the GenAI provider’s guardrails and refusal messages. When a chatbot provides incorrect guidance or misleads a borrower about their dispute rights, regulators treat it as a compliance failure, not a technology experiment.
Banking chatbots manage sensitive financial data that demands the highest security standards. Here are some measures you can implement in your chatbot to ensure the highest level of customer security.
- Multi-layer authentication: For critical transactions and account access, use multi-factor authentication in conjunction with strong customer verification. When feasible, use biometric verification and maintain session security throughout all communications.
- End-to-end encryption: Verify that all correspondence with customers is encrypted while it’s in transit and at rest. To handle new threats, use banking-grade encryption standards and update security procedures frequently.
- Fraud detection integration: To spot questionable activity, odd transaction patterns, and possible security breaches, integrate chatbots with live fraud detection systems. When risks are identified, activate automatic account protection procedures.
- Audit trail maintenance: For security and regulatory compliance, keep thorough records of every chatbot interaction. Ensure audit trails comply with banking regulations and, if necessary, assist with forensic analysis.
- Frequent security assessments: Perform regular vulnerability assessments, penetration tests, and security audits. Stay informed about the latest developments in cybersecurity threats and adjust your defenses accordingly.
2. Meet banking standards and regulations
- Consumer protection compliance: Verify that chatbots adhere to fair lending principles, obtain appropriate consent for data collection, and make required disclosures. As mandated by banking rules, implement accessibility features to support clients with disabilities.
- Data privacy adherence: When processing consumer data, adhere to the CCPA, GDPR, and other relevant privacy laws. As mandated by banking authorities, give explicit privacy disclosures, comply with requests to delete data, and keep track of data processing records.
- Cross-border compliance: Make sure chatbots used by foreign banks abide by laws in every country in which they do business. Consider the criteria for data residency and the disparities in privacy regulations among nations.
3. Optimize customer interactions
- Personalized financial guidance: Utilize past transactions and banking patterns to provide relevant financial analysis, product recommendations, and proactive support. Provide value-added services while honoring the privacy and interests of your clients.
- Channel integration: Ensure that all banking channels, including websites, mobile apps, phone banking, and in-branch services, deliver consistent user experiences. When clients switch between channels, maintain the context of their interaction intact.
- Proactive customer service: Use chatbots to promptly notify customers about account activity, upcoming payments, unusual transactions, and financial updates. To prevent overburdening customers, strike a balance between proactive communication and client preferences.
4. Maximize operational performance
Put operational protocols in place to guarantee reliable, superior chatbot performance by using:
- Performance monitoring: Track key indicators, including system uptime, customer satisfaction ratings, response accuracy, and conversation completion rates. Establish goals and continually improve performance in line with industry standards for the banking sector.
- Knowledge management: Maintain current and accurate records of banking policies, procedures, services, and products to ensure ongoing compliance and effective service delivery. To ensure accuracy and compliance, implement version control and approval processes for updates to the knowledge base.
- Staff collaboration: Promote effective cooperation between human banking experts and chatbot technology. Train employees on how to use automated systems efficiently and leverage chatbot insights to improve overall customer service.
5. Use strategic innovations
Use chatbots strategically to improve your institution’s competitive edge by:
- Financial innovation: Utilize chatbots to introduce new banking services, improve existing ones, and respond quickly to market opportunities. Identify unmet needs and service gaps by analyzing data from client interactions.
- Cost optimization: Systematically identify ways to automate repetitive banking tasks while reallocating human resources to high-value roles that require specialized knowledge and interpersonal skills.
- Future readiness: Stay current with advancements in banking and technology that can enhance chatbot performance. Plan to incorporate new technologies, including blockchain-based services, AI-driven financial advice, and voice banking.
FAQ
Further reading
Reference Links
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE and NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and resources that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised enterprises on their technology decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.

Be the first to comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.