We have been experimenting with AI development tools in our code generation and code editing benchmarks for months. We have seen that AI agents like Claude Code are highly capable of software development, achieving ~%90 success rate.
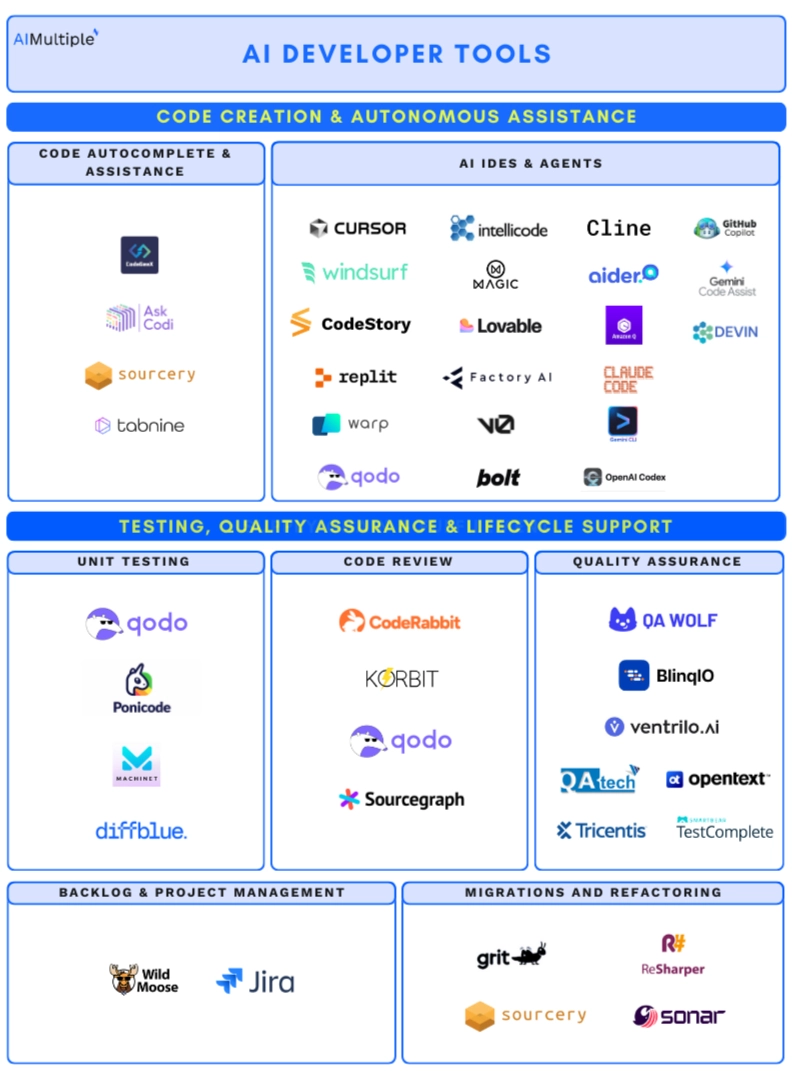
To provide a clearer picture of the current state of AI agents for software development, below, we listed 40+ AI developer tools for end-to-end software development. Our list includes the best performers from our tests, along with other tools for unit testing, code review, and software QA, etc.
We also outlined how the landscape evolved, from early autocomplete tools to AI tools that now handle unit testing, code review, and quality assurance.
The shift toward AI-enabled development
Software development is no longer just about code autocomplete. It has evolved from basic code autosuggestions to automated software testing and code migrating & refactoring, etc. Below, we walk through each stage of this evolution:
Wave 1: Code creation & autonomous assistance (2020–present)
- Early tools: code autocomplete & assistance (2020–2021): Tools like Tabnine improved efficiency with multi-language support (e.g., Python, JavaScript, Java, C++, Go) and context-based completions. This phase marked the first widely adopted step beyond traditional IDE autocomplete.
- AI IDEs + early conversational context (around 2022): The first generation of AI IDEs began to emerge, with tools like Cursor, CodeStory, and Replit Ghostwriter integrating AI directly into the development environment. Unlike traditional IDEs with autocomplete plugins, they were designed from the start to make AI a core part of the workflow.
In 2022, Replit also introduced Ghostwriter Chat, adding conversational elements so developers could interact in natural language.
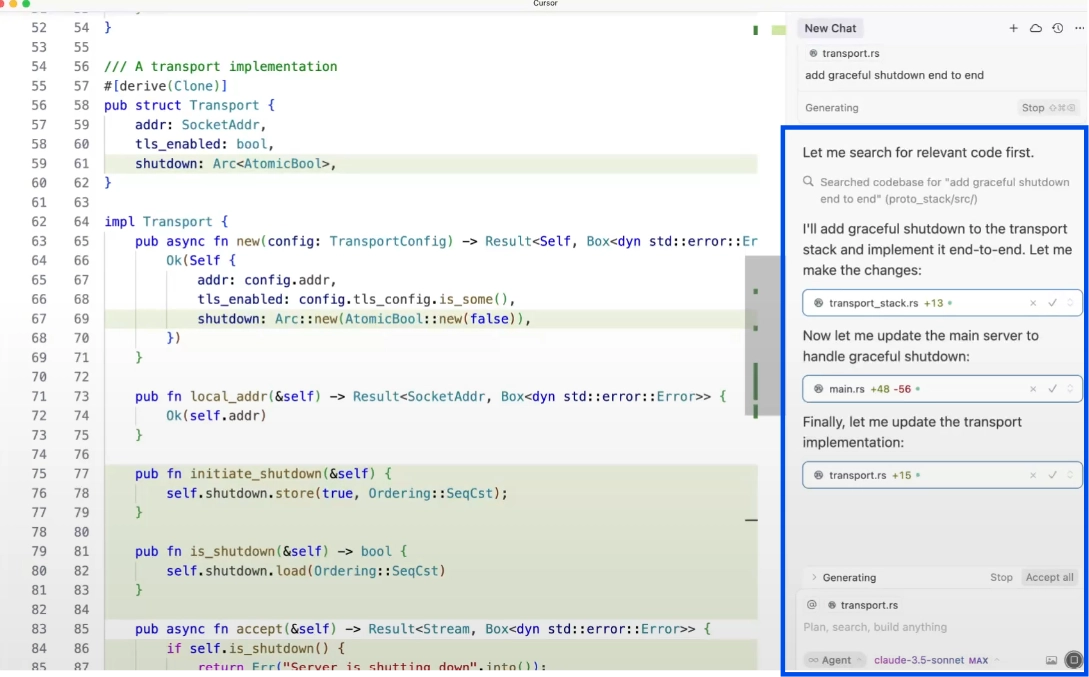
- AI-led development and agents (2023–present): Tools like Magic, Factory, and Bolt enabled AI agents to take on multi-step tasks, build apps from prompts, and automate parts of the development process that previously required frequent human intervention.
Cursor also released agent features like Bugbot (automated code review/fixes) and introduced AI agents within the IDE.
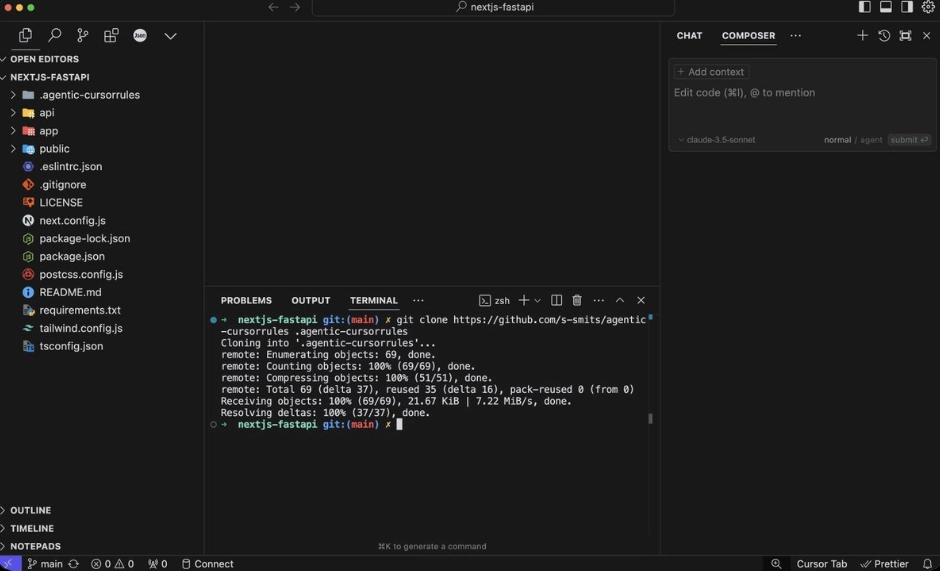
An example of an agent-enabled coding workflow: a Next.js + FastAPI project on the left, an agentic ruleset being pulled in via terminal, and Claude 3.5 (Sonnet) integrated as an in-IDE assistant on the right.3
Wave 2: Testing, quality assurance & lifecycle support (2023–present)
Expansion across the development lifecycle: We are now seeing tools that go beyond just coding assistance to automate key parts of the development process:
- Unit testing: AI helping with repetitive test writing. Tools like Qodo (formerly CodiumAI) began automatically generating and maintaining unit tests.
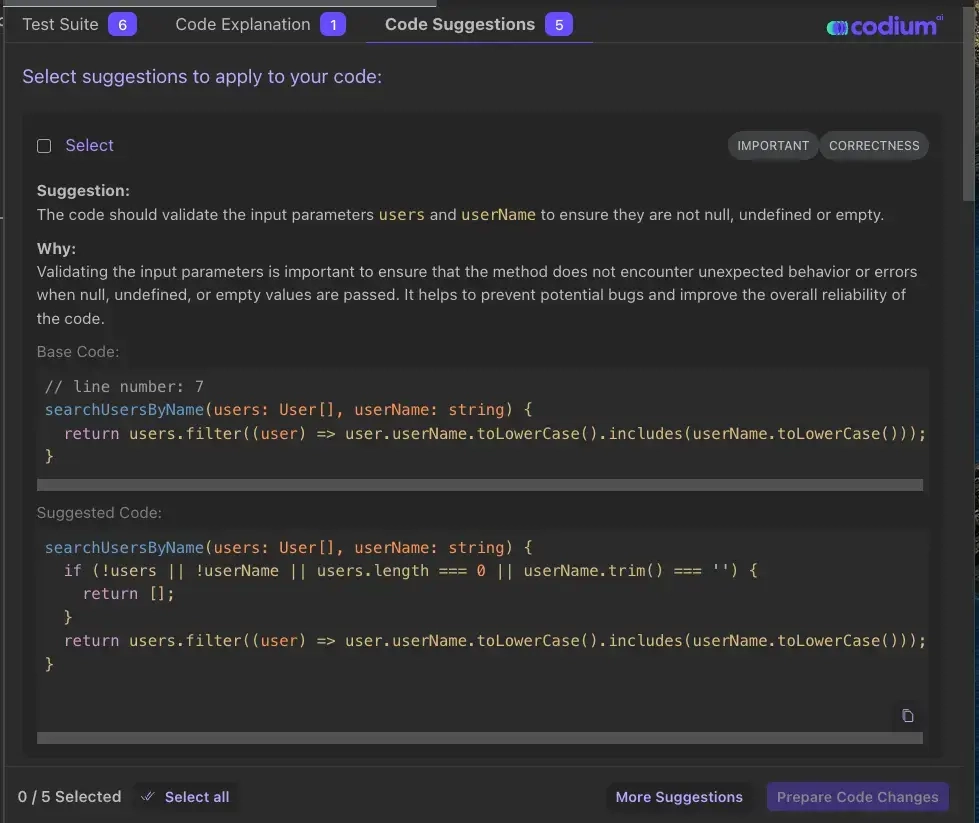
Qodo (formerly CodiumAI)’s suggestions that could fix several edge cases4
- Code review: AI assisting in pull request reviews, flagging potential issues, and suggesting fixes before human reviewers stepped in.
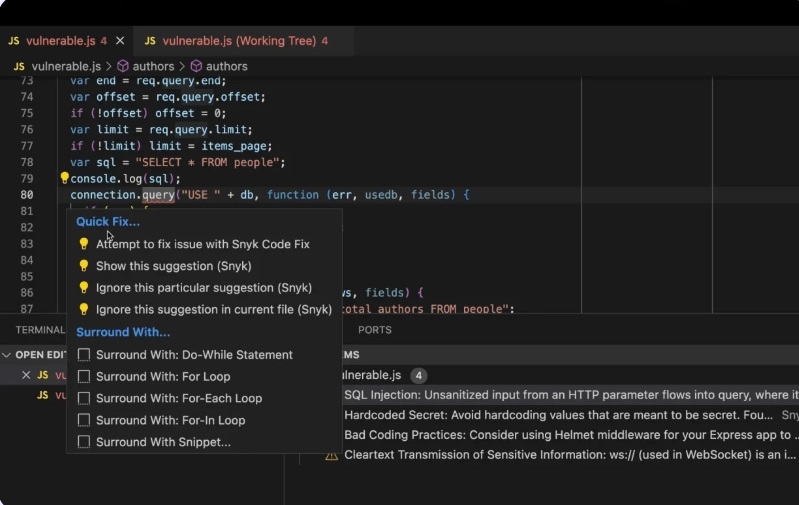
An example of AI-assisted code review: Flagging vulnerabilities like SQL injection and offering quick fixes directly in the IDE.5
- Quality assurance: AI tools helping with regression and end-to-end testing, with automated platforms reducing reliance on manual QA and helping teams catch bugs.
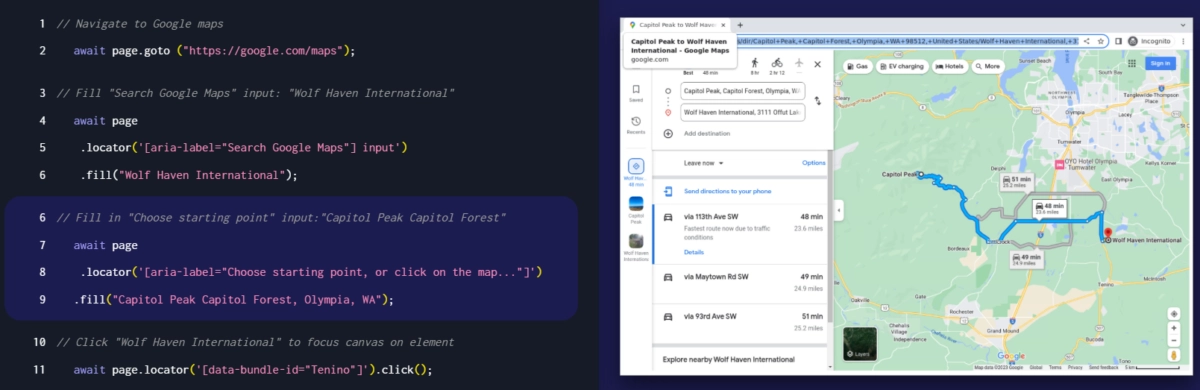
An example of automated end-to-end testing: a script interacts with Google Maps to simulate real user flows and validate outputs.6
- Backlog & project management: AI moved beyond coding tasks, with systems prioritizing tasks, restructuring backlogs, and integrating into project management tools.
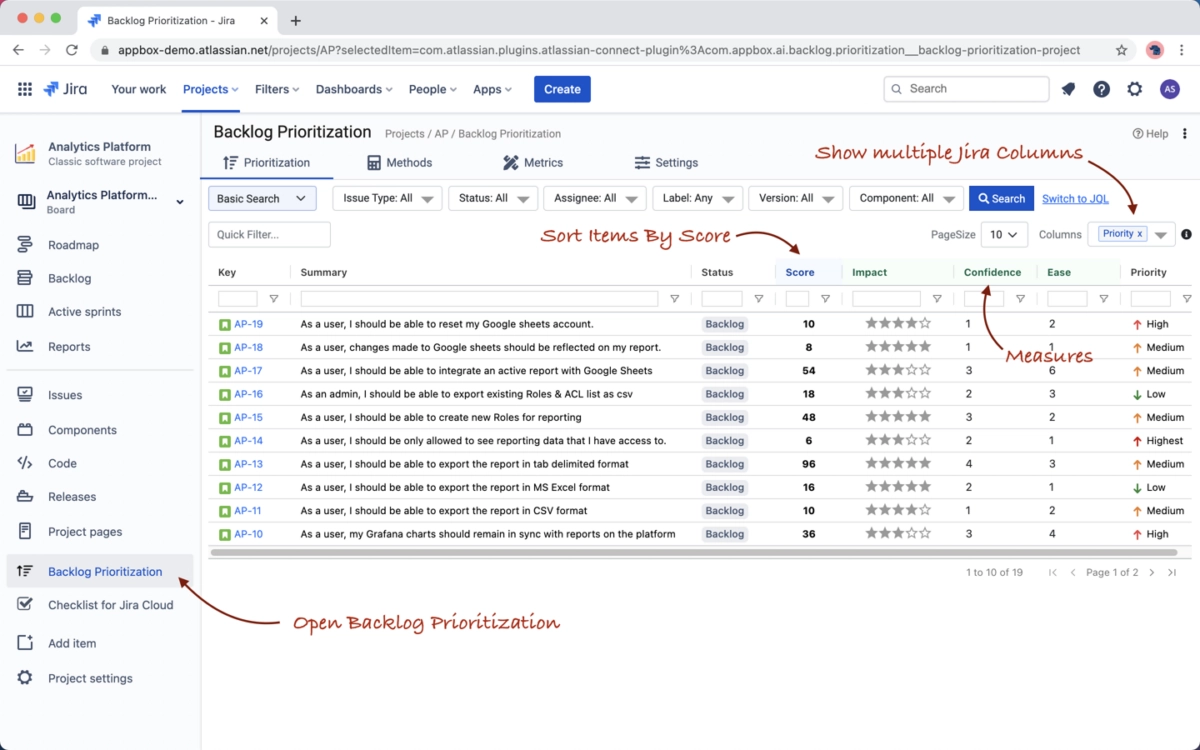
An example of AI-assisted backlog management: Jira uses scoring and measures like impact, confidence, and ease to help teams prioritize tasks more effectively.7
End-to-end AI development track
Code autocomplete & assistance:
- Code completion:
- Codeium: Free, privacy-first autocomplete.
- Tabnine: Code completion tool trained on open-source and private datasets, with enterprise deployment options.
- Multilingual code generation:
- CodeGeeX: Multilingual code generator available as open-source.
- Coding assistance & tools:
- AskCodi: Coding assistant with modules for tests, configs, and documentation.
- Sourcery: Tool for refactoring and improving code quality.
2. AI IDEs & agents
Startups:
- Cursor: context-aware AI IDE with deep codebase integration. In our coding benchmarks, Cursor ranks among tools with high spec code quality.
- Windsurf: It has similar features to Cursor, but its agent systems work differently. We found that its answers tend to be simpler and contain more errors compared to Cursor.
- Intellicode (Microsoft): AI-enhanced coding features integrated into Visual Studio.
- Amazon Q Developer: AI coding assistant integrated into AWS ecosystem.
- Replit: browser-based IDE with AI completions. Ranked among the top tools in our AI coding benchmark.
Natural language-to-code assistants (integrated within AI-native IDEs):
- Claude Code (Anthropic): natural language–to-code assistant, best for lighter, more conversational / vibe coding; context management is critical.
- Gemini CLI (Google): command-line interface tool for Google’s Gemini models.
- OpenAI Codex: model that translates natural language into code, also used in GitHub Copilot.
- GitHub Copilot: AI-powered code completion integrated into IDEs, based on OpenAI Codex. In 2025 introduced an agent mode was introduced as an autonomous and agentic real-time, synchronous collaborator that performs multi-step coding tasks based on natural language.
- Gemini code assist: Code Assist runs in the same way as Gemini CLI. It introduced an agent mode in July 2025 to analyze your codebase, but struggles with complex logic, multi-file context.
- Devin: Still in private beta purgatory. Early testers found it useful for automating repetitive work, though many noted it still struggles with complex tasks. Costs $500/month, more expensive than tools like Cursor ($20/month)as of 2025.
- Warp: terminal with AI command suggestions and agent workflows.
- Qodo (formerly Codium): platform for AI-powered code integrity and productivity.
- Gemini CLI (Google): Command-line interface tool for Google’s Gemini models.
Autonomous development platforms:
- Magic: platform aiming to provide fully autonomous software development.
- Lovable: tool for building applications with AI-first workflows. good when iterative refinement is possible; somewhat less complete under strict single-prompt criteria.
- v0: high success (~90%) in baseline “website creator” tasks under screenshot-to-code style benchmarks.
Agent-based development frameworks:
- Factory: framework for agent-based development workflows.
- Bolt: coding assistant with autonomous features and collaboration support.
- Cline: agent for CLI-based workflows; supports file editing, command execution, git operations, good for test-driven loops.
- Aider: open-source CLI agent; strong in multi-file editing, instruction following, and integrating with Git.
Orchestration & workflow automation:
- Cadence: AI system for orchestrating development projects.
- Augment Code: workflow automation with AI support.
For more on AI-code editors operating from the terminal, see agentic CLI tools: Claude Code vs Cline vs Aider.
4. Unit testing
- Qodo (CodiumAI): generates unit tests for multiple programming languages.
- Ponicode: VS Code extension for AI-generated unit tests.
- Diffblue: generates unit tests for Java applications.
5. Code review
- CodeRabbit: AI assistant for pull request reviews
- Korbit: AI tool for reviewing code with learning-based feedback.
- CodiumAI: combines test generation with code review functionality.
- Sourcegraph Cody: AI tool for exploring large codebases and assisting with reviews.
6. Quality assurance
End-to-end QA:
- QA Wolf: framework for AI-driven end-to-end testing.
Regression & functional QA:
- Meticulous: tool to detect regressions during development.
- BlinqIO: platform that creates, runs, and maintains functional tests to validate that applications work as intended, reducing manual QA effort.
Conversational & specialized QA:
- Ventrilo.ai: tool for conversational and voice-based QA.
- QA.tech: testing platform that generates and executes automated QA tests across apps.
Enterprise QA solutions:
- Tricentis: enterprise test automation platform with AI-enhanced features for regression testing.
- OpenText UFT (formerly Micro Focus): functional and regression testing suite with automation capabilities.
- SmartBear TestComplete: testing platform with AI-powered object recognition.
7. Backlog & project management
- Wild Moose: experimental AI-driven project planning platform.
- Jira AI Assistant: AI functionality for Jira project management.
8. Migrations and refactoring
Automated migrations:
- Grit: tool for automated framework and code migrations.
Code refactoring:
- Sourcery: tool for inline refactoring suggestions.
- JetBrains ReSharper / IntelliJ: refactoring and cleanup tools integrated into enterprise IDEs.
- SonarQube: enterprise code quality and refactoring platform, with AI-powered insights.
Reference Links

Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE and NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and resources that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised enterprises on their technology decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.




Comments 0
Share Your Thoughts
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.