
There are already some open-source RPAs, and we are showing the top 6 ones and their source codes. Note that the ecosystem is still relatively immature. However, with the commodification of RPA technology, more vendors are offering similar solutions. And because open source is transparent and free, it can play a large role in RPA’s future.
If you don’t know where to start with using an open-source RPA solution, you could check out some of our data-driven and comprehensive benchmarks & guides, such as Python RPA tools, no-code RPA & Python RPA library.
List of open-source RPA software
Open-source RPA solutions are distributed software with their source code to enable users to modify and customize the bot code according to their needs. The following list includes the top open-source RPA software and their source codes on GitHub:
RPA | Licensing | Implementation | Platform | Stars on GitHub* | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Robot Framework | Apache 2.0 | Python Jython (JVM) IronPython (.NET) | Windows MacOS Linux | 9.7k | |
TagUI | Apache 2.0 | Python R | Windows MacOS Linux | 5.6k | |
Open RPA | MPL 2.0 | C# JavaScript | Windows MacOS Linux | 2.2k | |
UI.Vision | AGPLv3 | Python C# JavaScript TypeScript | Windows MacOS Linux | 1.2k | |
Taskt | Apache 2.0 | .Net C# | Windows | 1.1k | |
Robocorp | Apache 2.0 | Python | Windows MacOS Linux | 1.1k |
*As of October 2024.
Benchmark results
We have successfully executed our scenarios using:
The task is:
- Log in to the mail
- Search for “refund”
- Open and read emails
- Generate an AI-based response based on company policy.
Robot Framework
Robot Framework is an open-source test automation framework supported by the Robot Framework Foundation and continuously developed through community contributions. It can be used for Acceptance Testing, ATDD, and BDD. Using a single framework for mobile, web, API, and accessibility testing provides significant flexibility.
With the Robot Framework, users can use various programming languages such as Python, Java, and .NET.
Robot Framework offers an online editor for users to try out the framework and provides detailed documentation to support learning and implementation.
Pros
- Extensive ecosystem of libraries: A wide range of ready-to-use libraries (e.g., SeleniumLibrary, RequestsLibrary, MailClientLibrary) makes handling different automation tasks straightforward.
- Open-source & vibrant community: Maintained on GitHub with an active developer and user community, offering forums and continuous contributions.
- Test-driven approach: Clearly defined test cases and keywords improve the readability and maintainability of automation scenarios.
Cons
- Outdated or unsupported libraries: Some community-contributed libraries may no longer be actively maintained (e.g. IMAPLibrary)
- Complex environment setup: New users may find it tricky to coordinate multiple components (Selenium drivers, Python versions).
TagUI
TagUI is a RPA tool supported by open-source contributors and the community. It allows users to use human language scripting, which supports more than 20 languages, and cross-platform compatibility to simplify automation tasks.
Its integration with R and Python and support for visual and web automation makes it suitable for a wide range of applications. It is compatible with multiple platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, offering flexibility for diverse operating environments.
TagUI’s natural language-like syntax makes it easy to develop, deploy, and use for automation tasks.
TagUI also has a comprehensive YouTube learning series.
Pros
- Easy command syntax: Simple, script-based scripts can be prepared with clear commands such as type, click, js begin, and js finish.
- Terminal-based operation: TagUI supports running commands directly through a script or command line, which can be efficient for users comfortable with terminal environments.
Cons
- Lack of drag-and-drop interface: Compared to GUI-based RPA tools, the learning curve can be steeper for non-command typing users.
- Sensitivity to dynamic interface updates: The script may require frequent maintenance as ID/XPath changes in Yahoo or other services.
- Limited debug and log: While switching to “debug” mode for error analysis is possible, encountering errors instead of detailed messages can be challenging for beginners.
Open RPA
OpenRPA has a drag-and-drop interface supported by an active developer community. Its low-code design makes it accessible to both experienced programmers and users with limited coding experience. The platform provides an orchestration layer through the OpenFlow component.
Pros
- Founder is active: The project’s founder actively participates in the community and development.
- Drag-and-drop interface: Users can design automation workflows using a visual drag-and-drop interface.
- Integration with Node-RED: OpenRPA is compatible with Node-RED and allows users to visualize flows.
Cons
- Weak documentation: The available documentation can be less comprehensive, making it harder for new users to get started or troubleshoot.
Previously available open-source tools
1. Automagical
Automagica provided an open-source Python RPA library on Github with 12 contributors. Though Automagica was a free, open-source tool for noncommercial purposes, you needed to pay for the software if you were going to use it for business. The company was acquired, and the software is no longer open-source.
Recommendation to business leaders
Before investing in an open-source RPA solution, make sure to understand the open-source RPA ecosystem. Our up-to-date research on the future of open source RPA shows that:
- Open source does not yet have the momentum to shape RPA, as no big corporations have embraced open-source projects
- Current RPA providers face an innovator dilemma as open source will cause them to reduce their prices
- As the RPA market grows, projected to reach $11B by 2027, so will the open-source market
- The future of RPA will involve more open-source tools.
The future of open-source RPA
1. Open source does not yet have the momentum to shape RPA
Open-source projects often show how for-profit companies use the software to their benefit. Some, like Android and Chromium, are started by these companies, while others, like Linux and WordPress, are adopted for their competitive edge. However, this has not happened in Robotic Process Automation (RPA) yet.
In the modern software world, all four major cases of open-source success relied on for-profit corporations:
Successful open source software that benefited from for-profit companies making it part of their offering:
Linux: Without vendors like Red Hat, acquired by IBM in 2018 for 34B, the Linux ecosystem would have been much different today. Though Linux was not started by a for-profit company, its growth heavily relied on enterprise software vendors. This was a win-win situation.
These vendors could access a competent server operating system for free to reduce the total cost of ownership for their enterprise customers and still make healthy profits by offering support services. Linux ecosystem also benefited as these vendors contributed to the software.
WordPress: WordPress, the content management software powering ~30% of the web, is commercialized by numerous companies. 1 The most prominent company commercializing WordPress is Automattic, founded by the founders of WordPress. Automattic was valued at >3bn in 2019. 2
Successful open-source software started by for-profit companies:
Android: Google started Android to break Apple’s hegemony over mobile operating systems and protect its mobile advertising business.
The fastest way for Android to gain traction was to make it open source and freely available so device manufacturers would have every incentive to use it. And that’s what Google did. Android became one of the most successful recent open-source projects, dominating the majority of the mobile OS market.
xChromium (the code on which Google Chrome is based): It’s almost the same story for Android, but this time, Google’s aim was to break Microsoft’s hold on the browser market.
However, major corporations in the RPA space have not yet embraced such open-source projects. This could change if RPA implementation companies found an open-source solution as strong as the existing closed-source solutions.
If such strong open-source RPA software existed, they could support it and offer it to their customers. This would reduce their customers’ total cost of ownership and, therefore, increase their addressable market.
2. The future of RPA is likely to involve more open-source
As technologies like operating systems matured, open-source adoption increased. For example, the smartphone OS market, which Apple’s proprietary iOS kickstarted, is now dominated by Android in terms of the number of users.
There are a few driving factors to increasing open-source adoption as solutions mature. As solutions mature,
– Core functionality becomes clear, and in most cases, it becomes easier to replicate. As a software component matures, it becomes easier to build it from scratch using modern tools
– Solutions need to rely more on outside developers for components to cover the needs of specific customer segments. Both customers and component developers don’t want to get locked into a proprietary system and support open source efforts as technologies mature.
We see this trend already happening in RPA as well.
3. Python RPA has gained more importance
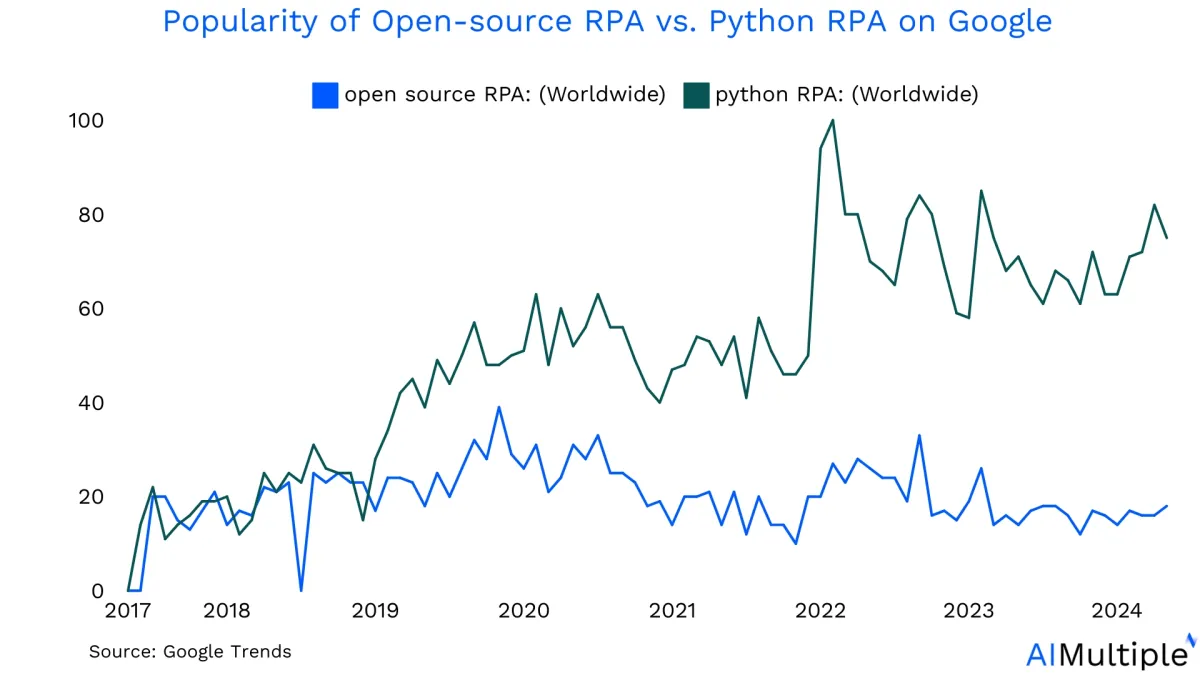
As seen in Google searches, Python RPA has gained more attention than open-source RPA (See Figure 2). This is because Python is becoming increasingly popular. Python provides a wide range of tools, is easy to integrate with existing systems, and has strong community support. This makes it a preferred choice for tasks in data science, automation, and web development.
As companies focus on scalable and flexible automation solutions, Python’s ability to adapt meets these changing needs better than other technologies.
4. Open-source RPA will benefit from the growth in the RPA ecosystem
While RPA was a standalone solution until a few years ago, now there is a wide range of companies, such as process mining and AI vendors, that are crucial for RPA deployments. For example:
– Process mining vendors enable companies to easily identify automation opportunities.
– No code AI tools enable companies to build flexible AI solutions quickly, with limited effort.
Open-source RPA vs. Proprietary RPA
Aspect | Open-source RPA Tools | Proprietary RPA Tools |
|---|---|---|
Initial Cost | Typically lower or free | Higher licensing fees may apply |
Customization | Highly customizable | Customization options may vary |
Support | Community-driven support | Dedicated customer support available |
Updates and Features | Regular updates, features may vary | Regular updates, consistent features |
Integration | May require more effort for integration | Often designed for seamless integration |
Scalability | Scalability may vary depending on community | Generally designed for scalability |
FAQ
For more on RPA
For more info on RPA, feel free to read our research on:
- RPA pricing
- RPA implementation best practices
- Pitfalls to avoid in RPA development
- Low-code/no-code RPA
If you are ready to invest in an off-the-shelf RPA solution, check out our data-driven list of RPA vendors and other automation solution providers.
Reference Links

Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE and NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and resources that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised enterprises on their technology decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.


Comments 10
Share Your Thoughts
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.
How did the author miss OpenRPA? As the name clearly shows it’s an open-source RPA tool and one of the best around that can compete directly with UiPath.
We never heard about it. Feel free to reach out with case studies to our info email
Model-Based Testing (MBT) could act as the automation flow (path) to run RPA, if you can build the state machine that represents state changes as result of robotic actions. MBT tools can use the state machine to find the optimal (shortest) path to get to the desired state and execute automation. Another benefit of using MBT is that the same state model can be used to drive testing of RPAs, just by letting the model running using random sequencer for hours or days. Check out TestOptimal for more details.
Thanks! Had to remove the link since if we allow them, we get too many comments.
Hi Cem. Did you consider AHK when writing this guide? They do not use the term “RPA” anywhere in their website, but as a “scripting language for Windows”, they’re very fit for RPA development.
Open RPA is another promising free RPA software with alot functionalities that are very similar to UiPath.
Hi Fadi Abu, thank you for contributing. So do many open source/community edition RPA software: https://research.aimultiple.com/open-source-rpa/ What makes open RPA different? And I would call it freemium as I am sure they have a business model for monetizing enterprise users.
Hi Cem, There is a new free and open source software company who recently launched this month called OpenBots. Their RPA automation tool suite provides discovery, development, and bot orchestration capabilities to all users through its RPA Studio, Server, and Discovery software.
Thanks! Please make sure that they sign up @ https://grow.aimultiple.com
Automagica is no longer open source.
Thanks for the heads up. Hope the acquisition price was worth it. I am sure the user community is not happy, it is not good to invest in the code of an open source project and integrate it into your work, to see it taken offline. Maybe we should also think harder before adding providers to our lists.
Hi Cem, Can you list Auteros RPA as a free option?. Auteros RPA community version is completely free without any restriction. Many thanks for that and also for your great blog’s information.
I am so happy I found your blog and I absolutely love your information about open source rpa. I liked and it is wonderful to know about so many things that are useful for all of us! Thanks a lot for this amazing blog!!
It’s free for personal use. Just because they are open source and their sourcecode is on Github – it’s not free. If you want to use the bots in a commercial environment you need to pay per bot. Its not the same as Chromium / Linux / WP.
Thanks Mohamed, you are 100% right, we clarified that above
Sorry, Automagica is not open-source , but free for non-commercial use only
Then why is their code on github and they call their solution open source on their own website? Happy to learn from you if we are missing something.