We benchmarked 9 leading multimodal AI models on visual reasoning using 200 visual-based questions. The evaluation consisted of two tracks: 100 Chart Understanding questions testing data visualization interpretation, and 100 Visual Logic questions assessing pattern recognition and spatial reasoning. Each question was run 5 times to ensure consistent and reliable results.
Visual reasoning benchmark
See our benchmark methodology to learn our testing procedures.
- Gemini 2.5 Pro and GPT-5.2 Chat tied for the highest overall accuracy at 62%, but demonstrated distinct performance patterns:
- Gemini 2.5 Pro scored 79% on Chart Understanding versus 44% on Visual Logic, showing a 35-point gap.
- GPT-5.2 Chat achieved 78% on Chart Understanding and 45% on Visual Logic, with a 33-point gap.
- While both models excel at chart interpretation, GPT-5.2 shows marginally better balance with slightly stronger visual logic capabilities.
- Qwen3-VL-8B-Thinking demonstrated solid mid-tier performance with 66% on Chart Understanding but dropped to 35% on Visual Logic, revealing a 31-point performance gap.
- Claude Sonnet 4.5 achieved 59% on charts but fell to 32% on logic tasks, showing a 27-point difference and clear specialization in data visualization interpretation.
- Gemini 3 Pro Preview maintained moderate performance at 56% on Chart Understanding and 31% on Visual Logic, with a 25-point gap.
- Grok-4.1-Fast scored 55% on charts and 27% on Visual Logic, displaying a 28-point performance difference.
- Claude Haiku 4.5 showed 48% on Chart Understanding and 25% on Visual Logic, with a 23-point gap.
- Gemini 2.5 Flash demonstrated the most consistent cross-category performance with 44% on Chart Understanding and 24% on Visual Logic, showing only a 20-point gap, the smallest disparity among all models tested.
- Llama 4 Maverick revealed the most pronounced weakness in visual reasoning:
- 44% on Chart Understanding but only 18% on Visual Logic, the lowest visual logic score across all models.
- This 26-point difference indicates severe limitations in abstract pattern recognition and spatial reasoning tasks, positioning it as the weakest performer in visual logic capabilities.
Benchmark questions on where LLMs excel and struggle most
Chart question with the lowest LLM success rate
Figure 1: Bar chart showing Star Sales Volumes across 12 months with four clustered bars per month (1998-2000 data). Each month displays solid, white, and striped bars in close grouping.
Note: All charts were obtained from Hitbullseye.1
Question: If the sales of three consecutive years are steadily increasing or steadily decreasing, then it is called a steady trend. Which months show a steadily increasing trend across three consecutive years?
Only GPT-5 and Gemini 2.5 Pro correctly answered this question.
For example, in June 1999, Actual was lower than in 1998, showing a decrease, but the model incorrectly interpreted it as steadily increasing. Most models make the same mistake on this question.
When 4 bars are clustered together per month, models struggled with bar-to-year mapping and relative height perception. They could not accurately distinguish which striped/solid/white bar belonged to which year, leading to bars being read in the wrong order or to confusing their heights.
This revealed a fundamental limitation in visual-spatial reasoning: current models lacked the pixel-precise perception needed to correctly measure and sequence densely packed bars, leading to systematic misidentification of trends.
Chart question with the highest LLM success rate
Figure 2: Bar chart showing voter turnout percentages in Indian general elections from 1952 to 1998. One bar per election year with clear spacing between bars.
Question: The highest and lowest ever voter turnout (in percentage) were respectively in which years?
All models answered this question correctly. This success shows models excel at simple min-max identification, finding the tallest and shortest bars.
Unlike the clustered 4-bar groups, which are confusing, this chart has a single bar per year with clear spacing, making direct visual comparison straightforward. Models perform well on purely observational tasks that require no complex bar-to-category mapping.
Visual logic question with the highest LLM success rate
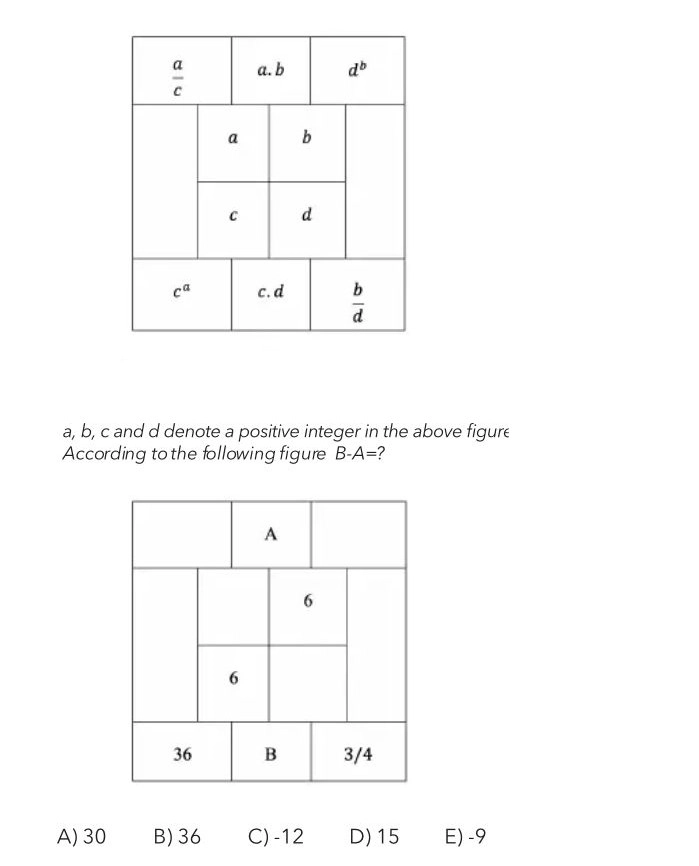
Figure 3: Two aligned 3×3 grids showing algebraic pattern matching. The top grid contains variables and their operations (multiplication, division, exponents). The bottom grid shows numerical values, with some cells filled (6, 36, 3/4) and two unknowns (A, B). The question asks to find B-A.
All models answered this question correctly. Success came from the clear mathematical pattern visible in the table structure (algebraic relationships like a×b, c×d). The simple grid layout, with no visual complexity, allowed models to focus solely on numerical inference and logical deduction.
Models excel when problems involve explicit mathematical patterns that can be solved through step-by-step reasoning, demonstrating their strength in symbolic logic and pattern recognition when visual distractions are minimal.
Visual logic question with the lowest LLM success rate
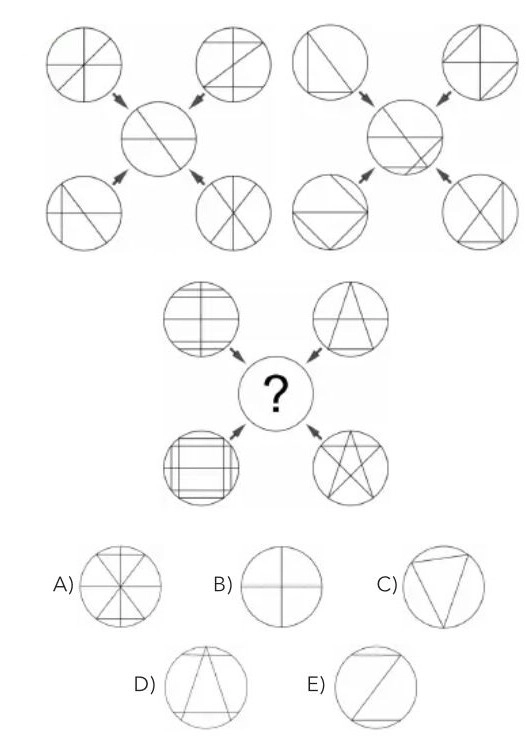
Figure 4: Pattern recognition puzzle with circles containing different internal line patterns and geometric shapes. Two example sequences with arrows shown at the top, followed by a question asking to complete the third sequence from five multiple-choice options.
All models failed this question. The difficulty stems from requiring abstract visual pattern recognition, identifying geometric transformation rules across multiple examples.
This demands pure spatial reasoning to understand how shapes rotate, transform, and relate to each other. Models struggle with rule inference from visual sequences when no explicit numerical or textual guidance is available, only spatial patterns.
What is visual reasoning?
Visual reasoning refers to the ability of a model to interpret an image, connect its elements, extract structure and associations, and produce a correct answer to a visual reasoning question. This capability brings together computer vision and language analysis, enabling an LLM to handle multimodal tasks that require understanding both visual and textual inputs.
Recent research and studies present multiple frameworks showing that LLMs can interpret objects, edges, positions, and patterns in an image, and then explain how they arrived at an answer through a reasoning process.
For example, the Cola framework organizes multiple vision-language models to answer visual reasoning questions by asking each model to provide captions and plausible answers, then letting an LLM select the correct answer.
Two approaches are presented: Cola-FT, which is instruction-tuned, and Cola-Zero, which relies on in-context learning without extra training. The framework focuses on the reasoning process, using structured prompts to coordinate models and analyze their contributions.
Figure 5: Graph showing how Cola leverages a coordinative language model for visual reasoning.2
Another example is the CVR-LLM framework, which improves reasoning by converting images into context-aware descriptions using the CaID method and selecting relevant examples with the CVR-ICL procedure. This framework treats image information as text-based representations, enabling the LLM to analyze associations more effectively across various types of multimodal tasks.3
How visual reasoning works in LLMs
LLMs do not perceive images directly. They rely on vision models that convert images into representations the LLM can understand. The mechanisms below summarize how recent models achieve visual reasoning.
Image interpretation and representation
Models first extract structured visual information using a vision encoder. The vision encoder identifies objects, textures, lines, edges, the lower part or upper part of an image, and the relations between them. This step is similar to classic image recognition, but the output format is tailored for language models.
LLMs then receive this representation along with the question. The model must combine these inputs to build a reasoning chain. For example, when asked a water-image question, such as identifying what people are doing in the middle of a river, the LLM must connect the appearance of the people, the positions of the objects, and the context clues provided.
Coordination or refinement
Recent research suggests two types of mechanisms for solving complex visual scenarios.
- In the coordination form, an LLM serves as a central hub that integrates outputs from multiple vision models. Each model may focus on different patterns, and the LLM merges these descriptions to reach the endpoint. This mechanism allows the LLM to cross-check plausible answers and choose one that fits the question and the visual evidence.
- In the refinement form, the LLM guides the image captioner through several steps. The LLM may point out missing information or ask clarifying questions. This feedback loop reprocesses the image, aligning the caption with the multimodal reasoning process. The refined description helps the LLM detect symbols, signs, or associations that the initial caption may have overlooked.
Both mechanisms address limitations found in existing methods where a single model often fails to analyze complex scenarios.
In-context learning for multimodal reasoning
Some frameworks extend the process by retrieving similar examples from training data. The LLM receives a set of demonstrations that match the structure of the target question. These examples provide the model with a template for interpreting similar diagrams or images.
For instance, when the model is evaluated on a visual reasoning benchmark for selecting the correct water-related figure, in-context examples help it understand the task’s theory and follow the same reasoning structure.
Producing the final explanation
The LLM then produces an answer supported by a reasoning process. This explanation helps users understand how the model interpreted the image, which part of the image it relied on, and the associations it used.
Business applications of visual reasoning in LLMs
LLMs with visual capabilities can support multiple business scenarios. These applications depend on the model’s ability to analyze images, link them with text data, and produce reliable insights.
Document and content analysis
Businesses handle diagrams, engineering drawings, scientific journal figures, and various forms of visual data. A visual reasoning model can:
- Detect missing or incorrect elements.
- Identify objects or signs in the lower part or corners of the diagrams.
- Connect text and image segments for quality checks.
- Extract structured information for further deployment or reporting.
This is especially useful for industries where compliance documents include complex image-based sections.
Quality inspection and operations
In manufacturing and logistics, models can inspect products or packages. Visual reasoning helps detect defects, misalignments, or unusual patterns. The model can compare images against a reference and generate an explanation of what changed or what is missing.
Retail and eCommerce
Models can analyze product images, identify key attributes, and match them to catalog data. They can also identify inconsistencies between the written description and the image. This enhances product classification and reduces manual work.
Security and monitoring
Visual reasoning supports video and image inspection tasks. For example, a model can analyze the sequence of frames, find unusual associations between objects, or detect scenarios that require attention. The ability to explain its reasoning improves reliability for high-stakes environments.
Marketing and user experience
Visual reasoning helps teams understand how users interact with digital content. A model can evaluate screenshots or creatives and provide insights about layout, object placement, and potential issues. This is especially relevant when assessing different categories of visual assets.
Comparative landscape: major players and their approaches
Chance AI
Chance AI is among the first commercial tools built around vision-first understanding. Its visual reasoning system analyzes images through cultural, historical, functional, and aesthetic lenses. Instead of assigning simple labels, it delivers structured insights that explain why an object, figure, or scene matters, such as the artwork’s style, symbolism, and historical context, alongside its subject.
The design prioritizes user experience by enabling meaning-driven exploration through images without typed queries. This moves beyond traditional computer vision toward interpretation, storytelling, and human-like explanation, making it especially relevant for creative industries, education, and tourism, where context adds value beyond recognition.4
Meta AI
Meta’s UniBench framework introduced a unified approach to evaluating visual reasoning by combining over fifty benchmarks for spatial understanding, compositional reasoning, and counting. Testing nearly sixty vision-language models, Meta found that scaling data and model size improves perception but not reasoning, with even advanced models failing at simple tasks like digit recognition and object counting.
These findings changed how visual reasoning progress is measured, highlighting the need for higher-quality data, targeted objectives, and structured learning rather than relying solely on larger models. For businesses, UniBench offers a transparent way to compare reasoning performance across multimodal tasks before deployment.5
Figure 6: The graph shows the median performance of 59 VLMs on 53 benchmarks, revealing that, despite progress, many models still perform near-chance level, particularly on tasks like Winoground, iNaturalist, DSPR, and others (blue: zero-shot median; grey: chance level).6
OpenAI
OpenAI advanced visual reasoning with the o3 and o4-mini models, which can think with images by integrating image manipulation into their reasoning. During analysis, they zoom, crop, or rotate images to focus on relevant details, mirroring how humans adjust visual attention when interpreting diagrams or drawings.
Tested across multimodal benchmarks such as chart interpretation, visual problem-solving, and mathematical reasoning, the models showed clear gains in accuracy and contextual understanding. However, results also exposed limitations, including inconsistent reasoning and occasional perceptual errors, underscoring the ongoing challenge of reliability in visual reasoning systems.
Figure 7: The graph shows the results of all models evaluated under high “reasoning effort” settings.7
Academic and open research efforts
VisuLogic: A Benchmark for Evaluating Visual Reasoning in Multi-modal Large Language Models
This paper introduces VisuLogic, a benchmark for evaluating the performance of multimodal models on visual reasoning tasks. It combines over fifty datasets covering various types of reasoning, including spatial relations, compositional logic, and object counting.
The authors analyze dozens of existing models and find that increasing size or data scale improves image recognition but not reasoning. Models often detect patterns without understanding relationships among objects. The paper emphasizes that reasoning-specific training, better data quality, and detailed evaluation are essential for meaningful progress.
VisuLogic offers a unified framework that helps researchers and enterprises analyze reasoning capabilities rather than relying solely on perception metrics, making it a valuable resource for assessing multimodal reasoning systems.8
Explain Before You Answer: A Survey on Compositional Visual Reasoning
This survey reviews current approaches to compositional visual reasoning, focusing on how models combine visual and textual cues to reach a correct answer. It identifies weaknesses in existing methods that rely on recognition rather than structured reasoning.
The authors propose training models to explain before answering, ensuring that each reasoning process is transparent and interpretable. They discuss techniques for aligning visual and linguistic representations so that models can better understand diagrams, figures, and object associations.
The paper concludes that aligned and explainable reasoning enhances reliability and interpretability in multimodal tasks. It highlights that the future of visual reasoning research depends on integrating explanation-based learning into model design.9
Challenges and ethical considerations
The progress in visual reasoning also brings technical and ethical challenges that researchers and companies must address.
- Reliability remains a central concern. Models can generate different results when an image is slightly rotated or when parts of the visual field are transparent or missing.
- Bias and interpretation issues emerge because models may reflect cultural assumptions embedded in their training data.
- Explainability is critical for building trust. Users need clear visualizations or diagrams showing how the reasoning developed.
- Privacy and security concerns arise from using large image datasets that may include sensitive or proprietary information.
Benchmark methodology
All models were evaluated via OpenRouter API with standardized parameters: temperature set to 0.8 and max tokens set to 10,000. Models were instructed to respond with only a single letter (A-E) without explanation, though some models still provided detailed reasoning, which we parsed to extract final answers. Evaluation ran in parallel across all models simultaneously. Each question was run 5 times to ensure consistent and reliable results.
The benchmark consisted of 200questions split into two categories: Chart Understanding (100 questions) covering bar charts, line graphs, scatter plots, and complex data visualizations, and Visual Logic (10 questions) testing pattern recognition, spatial reasoning, and mathematical visual logic. All questions were presented in multiple-choice format with five options (A-E), requiring models to analyze images and select the correct answer.
Questions:
1. Chart Understanding We evaluated models on their ability to extract, interpret, and analyze information from various data visualizations:
- Bar Charts: Horizontal and vertical configurations, stacked and grouped formats
- Line Graphs: Single and multi-series trends, time-series data
- Scatter Plots: Correlation analysis, pattern identification with labeled axes
- Pie Charts: Percentage distributions and proportional reasoning
- Complex Visualizations: Combination charts, dual-axis graphs, and multi-panel displays
2. Visual Logic We assessed abstract reasoning and spatial intelligence through:
- Pattern Recognition: Identifying sequences and completing visual patterns
- Spatial Reasoning: 3D visualization, cube nets, and geometric transformations
- Mathematical Logic: Numerical patterns, algebraic reasoning, and combinatorics
- Abstract Thinking: Symbol manipulation, logical deduction, and rule inference
Question Format
- Answer Format: Multiple choice (A, B, C, D, E)
- Image Types: PNG/JPEG with varied complexity levels

Be the first to comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.