Have you ever wondered how search engines such as Google and Bing collect all the data they present in their search results?
Search engines index all the pages in their archives so they can return the most relevant results for queries. Web crawlers enable search engines to handle this process.
The best web crawlers of 2026
Vendors | Price per 1k pages (mo) | Free trial | PAYG per 1k pages |
|---|---|---|---|
$0.98 | 7 days | $1.50 | |
$0.50 | 7 days | ❌ | |
$0.88 | 3K free requests | ❌ | |
Nimbleway | $1.00 | 7 days | ❌ |
Apify | $2.00 | $5 free usage | ❌ |
Zyte | $0.13 | $5 free | $1.27 |
What is a web crawler?
A web crawler, sometimes called a “spider” or “agent,” is a bot that browses the internet to index content.
Crawlers have moved beyond search engines and now serve as the Agentic Data Layer. They act as the eyes for autonomous AI agents like Claude Code and OpenAI Operator, assisting with real-time tasks such as competitive research and multi-step transactions.
Major industry shifts & trends
1. The move to permission-based crawling
- After a major update in early 2026, all new Cloudflare domains must be configured to allow or block AI crawlers when they are set up.
- Cloudflare and other CDNs are testing systems that let publishers charge AI companies for access to their data via bots. This offers publishers a new way to monetize web traffic.
Old methods for detecting bots, such as IP address blocking, are now considered outdated.
- Modern websites use machine learning to spot non-human mouse movements and browser fingerprints.
- Crawlers now use managed cloud browsers that mimic real user behavior, such as typing naturally and matching TLS 1.3 fingerprints, to avoid detection by security systems.
2. Real-time retrieval (RAG) vs. static indexing
There has been a big increase in traffic from user-action bots like ChatGPT-User. These bots fetch pages when users request them, rather than indexing sites for databases. Because of this, many websites now provide llms.txt files, which are simple Markdown-only versions of their content for AI.
What does a web crawler do?
Web crawling was split into three modes, each designed for a different crawler goal.
- Discovery mode (traditional): Search engine bots like Googlebot crawl URLs for indexing, helping people find results through search engines.
- Retrieval Mode (RAG): AI bots like ChatGPT-User or PerplexityBot fetch specific pages in real time to answer user prompts. They use markdown instead of HTML to fit the AI model’s token limits.
- Agentic Mode (Action-Oriented): This new type of crawler in 2026 does more than just read content. Using Model Context Protocol (MCP), these bots can interact with websites to book flights or run software commands.
In the past, crawlers used selectors such as XPath or CSS to extract data. AI-Native Extraction has become the norm.
Tools such as Firecrawl and Crawl4AI use natural language instructions to find data. Instead of writing rules for each element, developers can tell the crawler to “extract the product price,” and the AI will find the right value even if the website’s code changes.
Build vs. buy web crawlers in the AI era
1. Building Your Own Crawler
Ideal for protecting core intellectual property and enabling deep customization. Building now requires developing a proprietary agent layer, not just writing basic Scrapy scripts.
- When to build: Select this approach if your crawler provides a unique competitive advantage. For instance, build your own if you are developing a specialized search engine or require complete control over sensitive or regulated data.
- The toolset: You no longer need to start from scratch. Developers now leverage the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to enable internal AI agents to interact with the web.
2. Using Web Crawling Tools & APIs
Managed tools have advanced from basic scrapers to autonomous agents.
- Zero-maintenance extraction: Modern tools such as Kadoa and Firecrawl use self-healing AI. You specify the required data, such as “Product Price,” rather than its location in the code. If the website layout changes, the tool adapts automatically.
- Compliance as a service: Many providers offer built-in compliance with the EU AI Act. They manage required audit logs and copyright opt-out checks, which are challenging to implement independently.
- Speed to value: Purchasing a platform can move your project from concept to production within weeks.
Figure 5: An explanation of how a URL frontier works.
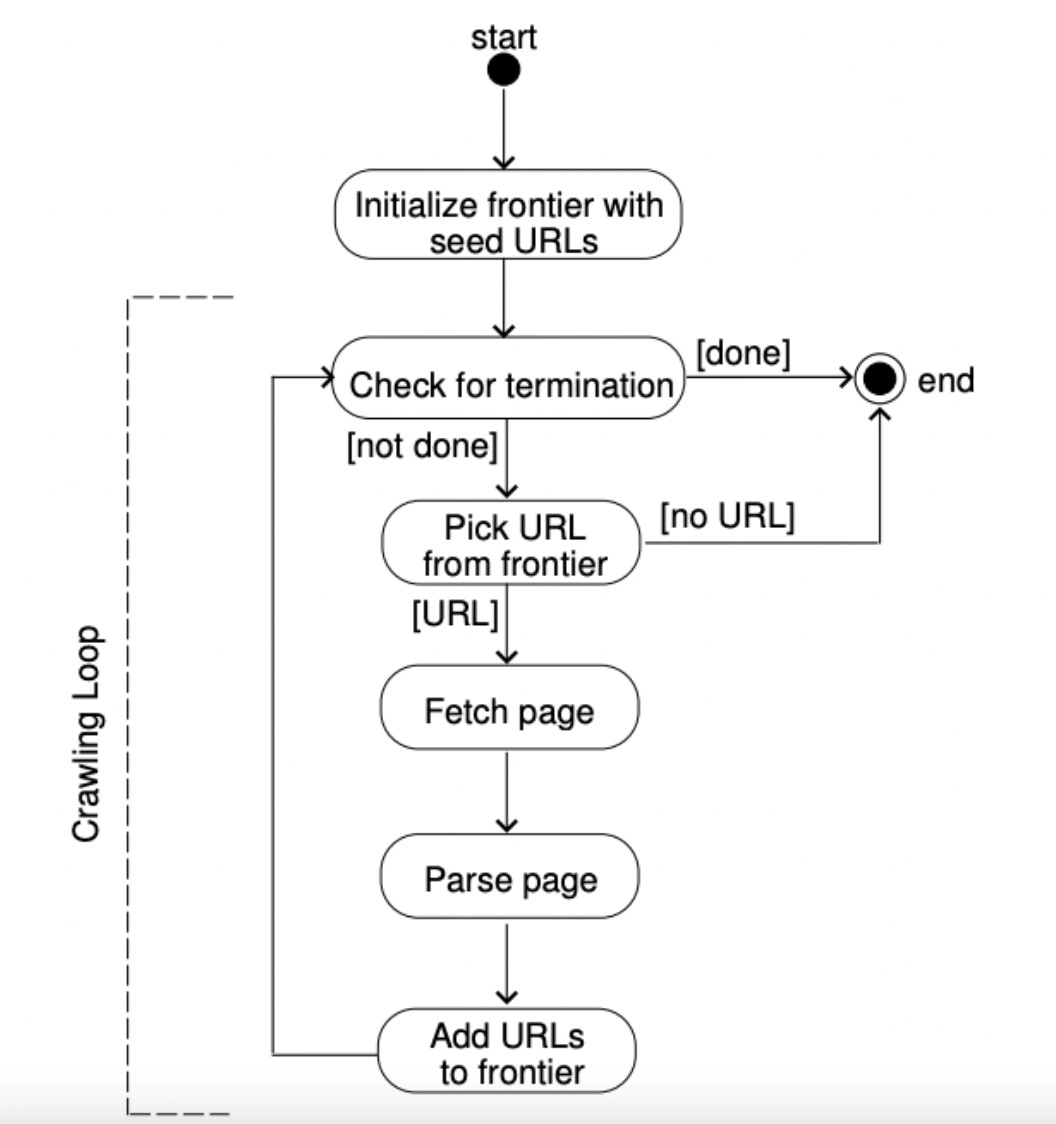
Are web crawlers legal?
In general, web crawling is legal, but depending on how and what you crawl, you could quickly find yourself in a legal bind. Four major pillars determine whether crawling (and the scraping that typically follows) is legal:
1. Public vs. private: Only crawl data that is openly available to the public without an account.
2. Personal information: Steer clear of PII (names, emails, and addresses) unless you have a lawful basis.
3. Server health: Use rate limits to avoid slowing down the server; avoid “DDOSing” a website.
4. Copyright: Articles and images are protected by copyright, but facts (prices, dates) are not.
What is the difference between web crawling and web scraping?
Web scraping is using web crawlers to scan and store all the content from a targeted webpage. In other words, web scraping is a specific use case of web crawling to create a targeted dataset, such as pulling all the finance news for investment analysis and searching for specific company names.
Traditionally, once a web crawler has crawled and indexed all of the elements of the web page, a web scraper extracted data from the indexed web page. However, these days scraping and crawling terms are used interchangeably with the difference that crawler tends to refer more to search engine crawlers. As companies other than search engines started using web data, the term web scraper started taking over the term web crawler.
What are the different types of web crawlers?
Web crawlers are classified into four categories based on how they operate.
- Focused web crawler: A focused crawler is a web crawler that searches, indexes and downloads only web content that is relevant to a specific topic to provide more localized web content. A standard web crawler follows each hyperlinks on a web page. Unlike standard web crawlers, focused web crawlers seek out and index the most relevant links while ignoring irrelevant ones (see Figure 4).
Figure 4: Illustration of the difference between a standard and focused web crawler
- Incremental crawler: Once a web page is indexed and crawled by a web crawler, the crawler revisits the URLs and refreshes its collection regularly to replace out-of-date links with new URLs. The process of revisiting URLs and recrawling old URLs is referred to as incremental crawling. Recrawling pages helps to reduce inconsistency in downloaded documents.
- Distributed crawler: Multiple crawlers are operating simultaneously on different websites to distribute web crawling processes.
- Parallel crawler: A parallel crawler is a crawler that runs multiple crawling processes in parallel to maximize the download rate.
What are the challenges of web crawling?
1. Database freshness
Websites’ content is updated regularly. Dynamic web pages, for example, change their content based on the activities and behaviors of visitors. This means that the website’s source code does not remain the same after you crawl the website. To provide the most up-to-date information to the user, the web crawler must re-crawl those web pages more frequently.
2. Crawler traps
Websites employ different techniques, such as crawler traps, to prevent web crawlers from accessing and crawling certain web pages. A crawler trap, or spider trap, causes a web crawler to make an infinite number of requests and become trapped in a vicious crawling circle. Websites may also unintentionally create crawler traps. In any case, when a crawler encounters a crawler trap, it enters something like an infinite loop that wastes the crawler’s resources.
3. Network Bandwidth
Downloading a large number of irrelevant web pages, utilizing a distributed web crawler, or recrawling many web pages all result in a high rate of network capacity consumption.
4. Duplicate pages
Web crawler bots mostly crawl all duplicate content on the web; however, only one version of a page is indexed. Duplicate content makes it difficult for search engine bots to determine which version of duplicate content to index and rank. When Googlebot discovers a group of identical web pages in search result, it indexes and selects only one of these pages to display in response to a user’s search query.
Top 3 web crawling best practices
1. Politeness/Crawl rate
Websites set a crawl rate to limit the number of requests made by web crawler bots. The crawl rate indicates how many requests a web crawler can make to your website in a given time interval (e.g., 100 requests per hour). It enables website owners to protect the bandwidth of their web servers and reduce server overload. A web crawler must adhere to the crawl limit of the target website.
2. Robots.txt compliance
A robots.txt file is a set of restrictions that informs web crawler bots of the accessible content on a website. Robots.txt instructs crawlers which pages on a website they may crawl and index to manage crawling traffic. You must check the website’s robots.txt file and follow the instructions contained within it.
3. IP rotation
Websites employ different anti-scraping techniques such as CAPTCHAs to manage crawler traffic and reduce web scraping activities. For instance,browser fingerprinting is a tracking technique used by websites to gather information about visitors, such as session duration or page views.
This method allows website owners to detect “non-human traffic” and block the bot’s IP address. To avoid detection, you can integrate rotating proxies, such as residential proxies, into your web crawler.
What are examples of web crawling?
All search engines need to have crawlers, some examples are:
- Amazonbot is an Amazon web crawler for web content identification and backlink discovery.
- Baiduspider for Baidu
- Bingbot for Bing search engine by Microsoft
- DuckDuckBot for DuckDuckGo
- Exabot for French search engine Exalead
- Googlebot for Google
- Yahoo! Slurp for Yahoo
- Yandex Bot for Yandex
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE and NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and resources that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised enterprises on their technology decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.

Comments 1
Share Your Thoughts
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.
Hi Cem, I think there is a misunderstanding regarding the robots.txt role in the crawling context. The web bots can crawl any website when indexing is allowed without having the robots.txt somewhere on their top domain, subdomains and ports and so on. The role of a robots.txt is to keep control of the traffic from web bots so the website is not overloaded by requests.