We analyzed ~80 RPA tools in the market and prioritized those with a low code approach. The below are either market leaders due to metrics like number of reviews and features or provide exceptional pricing. Learn more by following the links to visit their websites:
- Argos Labs for cost-effective RPA that is integrated into the Python ecosystem
- UiPath RPA for market leading enterprise-focused RPA
- Microsoft Power Automate for integrations with Microsoft ecosystem
Explore what is low-code and no-code Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and its benefits:
What are low-code and no-code RPA?
No-code RPA
No-code RPA aims to remove the need for programming in automation. Traditional RPA tools often include user interfaces (UIs), but these are usually limited. Developers still rely on coding to automate tasks.
Real-life example:
General Electrics used a no-code application (EASA platform) to automate their bidding/tender process.1
Type of RPA: No-code solution
Outcomes: Reduced time for preparing tender documents; faster responses to customer requests; more precision and personalization in offers.
Low-code RPA
Low-code RPA reduces but does not remove programming. These platforms allow simple automation through drag-and-drop features, but also give flexibility with coding when needed. They strike a balance: easier than coding-heavy RPA, but more flexible than no-code tools.
Real-life example:
Coca-Cola United automated order management and invoicing to handle increasing demand (especially for cartridge delivery and Freestyle vending machines). Used Microsoft Power Automate + unattended RPA bots.2
Type of RPA: Low-code RPA
Outcomes: Freed up staff time; scaled high-volume tasks; handled inbound/outbound order channels, CRM, and self-service interaction more smoothly.
What are different RPA tools in terms of UI?
We mainly see 3 types of vendors in the space:
1. Code-based RPA
- Users must write code (e.g., Python) to build bots. For example, Python-based RPA developers leverage Python RPA tools or libraries to develop and customize RPA software.
- Very flexible and customizable.
- Best suited for developers with programming skills.
- Not ideal for business users (“citizen developers”) since they must rely on IT teams.
- This slows down development, as business experts and developers need constant communication.
2. Low-code RPA
- Most RPA vendors fall into this group.
- Two interfaces:
- Drag-and-drop or recording for simple tasks.
- Coding options for complex tasks.
- Designed for citizen developers to handle common tasks such as Excel work, automated emails, or reports.
- For harder tasks, they may need support from IT teams or build technical skills.
- Users can code bots to automate complex processes.
3. No-code RPA
- Some newer RPA companies claim to be no-code. But almost all RPA solutions allow users to access the RPA code, therefore the difference between no-code or low-code solutions is not clear.
- The line between low-code and no-code is often unclear.
- Users should test tools with real processes to see how simple they are, rather than rely on marketing claims.
- Citizen developers may struggle with complex bots that span departments or require frequent updates. In such cases, IT support or coding is still needed.
Learn more about the types of RPA.
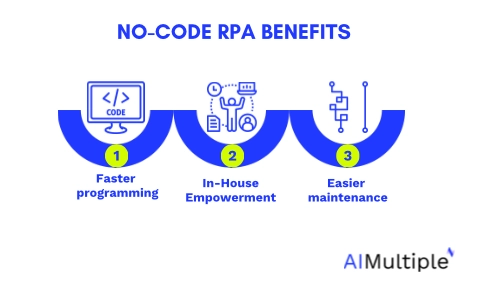
What are the benefits of no-code RPA?
DTraditional RPA requires programming, which means:
- Training or hiring programmers.
- Long programming and debugging phases.
- Reprogramming every time a process changes.
To deal with this, 63% of RPA solutions rely on outsourced programming, making maintenance complex, according to the latest RPA statistics. A new crop of companies is tackling this by developing low-code and no-code RPA solutions, enabling businesses to enjoy RPA benefits faster and more cost-effectively.
No-code RPA addresses this by:
- Cutting programming time.
- Allowing in-house staff to take on automation.
- Making maintenance simpler.
However, it is not a full solution. Businesses still need to understand and document their processes before automation.
What are the best practices for no-code/low-code RPA bots?
1. Code quality
- Even no-code tools use building blocks like boxes and connectors.
- These must be simple and well-structured.
- Poorly designed bots are harder to maintain than well-written code.
2. Keeping RPA and process know-how in house
- It is difficult to improve a bot created by someone else.
- Companies can set up Centers of Excellence (CoEs) and identify process experts to ensure that RPA and process knowledge remain in-house.
3. Process intelligence
- Bots need updates when processes or systems change.
- A deep understanding of processes makes maintenance easier.
- Process intelligence tools can provide insights to guide updates.
FAQ
Further readings
To learn more about no-code technology, read:
And if you believe your business will benefit from an RPA solution, feel free to scroll down our comprehensive list of RPA tools and automation software and solutions.
Reference Links
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE and NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and resources that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised enterprises on their technology decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.

Be the first to comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.