LLM-based applications are becoming more capable and increasingly complex, making their behavior harder to interpret.
Each model output results from prompts, tool interactions, retrieval steps, and probabilistic reasoning that cannot be directly inspected. LLM observability addresses this challenge by providing continuous visibility into how models operate in real-world conditions. It enables organizations to monitor quality, detect failures, troubleshoot multi-step workflows, and manage performance and costs.
Tool | Best For |
|---|---|
Running frequent experiments and comparing prompts/models with strong versioning and dashboards. | |
Langfuse | Open-source and self-hosted observability with granular traces and customizable evaluations. |
Helicone | No-code setup for basic monitoring, cost tracking, and caching of LLM API calls. |
Langsmith | Building multi-step chains or agents (especially with LangChain) with detailed trace visibility. |
Braintrust | Automated evaluation, alerts, and production quality monitoring. |
Weights & Biases (W&B Weave)
W&B Weave is Weights & Biases‘ LLM observability platform for monitoring, evaluating, and optimizing language model applications. Weave automatically tracks every LLM call using the @weave.op decorator, capturing inputs, outputs, costs, latency, and evaluation metrics without manual setup.
The platform tracks token usage and calculates costs automatically, monitors response times to catch slow queries, and measures accuracy by comparing predictions against expected results. Different experiments can be compared side-by-side to see which model or prompt performs better. Error tracking shows which predictions failed and why, while automatic versioning preserves every configuration change for reproducibility. This makes it easy to test different approaches, identify what works best, and debug issues when models make mistakes.
Score Summary Dashboard
Figure 1: Graphs showing the model performance metrics dashboard, tracking accuracy, cost, and latency trends over time.
Performance metrics are shown across all evaluation runs. Total cost, token usage, and response times are displayed with graphs showing changes over time. Custom metrics, such as accuracy and error rates, appear in separate panels. Trend lines help spot when performance gets worse, or costs increase unexpectedly, with the dashboard updating automatically as new tests complete.
Traces View
Figure 2: Evaluation trace table showing model versions and their intent classification results.
Every test run is saved with complete details. Each trace shows which model was used, what prompt was sent, and all settings. Success or failure indicators indicate whether tests were completed correctly. The prompt column displays the text sent to the model for verification. This logging allows comparing different versions side-by-side, seeing what changed between runs, and repeating any test by using its saved configuration.
Model Comparison Leaderboard
Figure 3: Image showing the leaderboard comparing intent classifier model versions across accuracy and latency metrics.
Different models and settings can be compared on the same test data. Columns show accuracy, correct predictions, scores, and response times. Color coding highlights better performers in green. This comparison reveals trade-offs like higher accuracy at the cost of slower speed or faster responses with slightly lower accuracy, helping choose which configuration works best for production needs.
Model Versioning
Figure 4: Intent classifier configuration panel showing model settings and version details.
Every configuration change automatically creates a new version, keeping a complete history. Version details show when changes happened, who made them, and storage used. The Values tab displays exact settings, including model name, parameters, and function versions. This versioning ensures any test can be repeated with identical settings, allows tracking how performance changed over time, and enables reverting to older versions if needed.
Detailed Evaluation Results
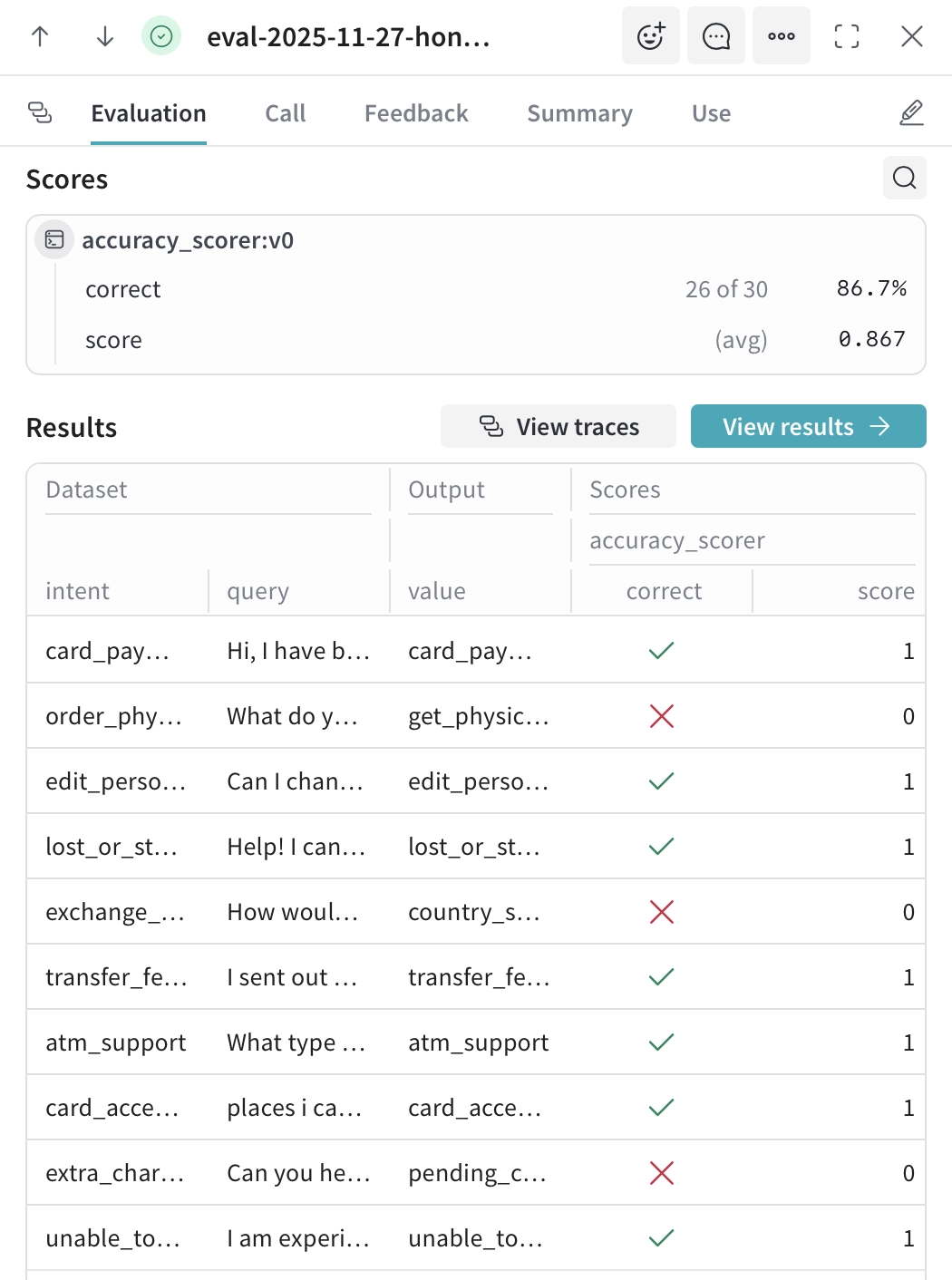
Figure 5: Evaluation results showing individual test cases with predicted intents and accuracy scores.
Individual test results are shown for every sample. The Scores section summarizes total correct predictions, accuracy percentage, and custom scores.
The Results table displays each query with its expected answer and the model’s prediction, using check marks for correct answers and X marks for incorrect answers. Failed predictions are easy to spot, often showing patterns such as confusion between similar categories.
Clicking any row opens the full trace, including the prompt, response, token counts, and timing, making it straightforward to debug failures and improve prompts or model selection.
Langsmith
LangSmith is LangChain’s observability platform for monitoring, debugging, and evaluating LLM applications. It automatically traces every LLM call, captures prompts and outputs, tracks costs and latency, and enables systematic evaluation through dataset-based testing. LangSmith integrates natively with LangChain but supports any LLM application through its SDK.
Per-Sample Evaluation Results
Figure 6: Image showing the individual test case evaluation on predictions and performance metrics.
Individual prediction outcomes are displayed alongside expected outputs, allowing you to identify where the model makes mistakes. Comparing expected versus actual predictions reveals confusion between semantically similar categories. Per-query latency and token counts show which input types are more expensive to process, enabling optimization of slow or costly queries.
Trace Volume and Health Monitoring
Figure 7: Graph showing the project traces visualization tracking success and error rates over time.
Application health is shown through trace volume trends and success/error ratios over time. Different views are available for analyzing LLM calls, cost trends, tool invocations, or feedback scores. Issues like error spikes or cost increases become visible, indicating problems that need investigation.
Model and Configuration Comparison
Figure 8: Experiment comparison view showing performance metrics across multiple test runs.
Different models can be compared side-by-side on the same test dataset. Tradeoffs between accuracy, latency (P50/P99), and token efficiency are displayed visually. Identifying which configuration best meets requirements – whether maximizing accuracy or minimizing cost and response time – is straightforward through these comparisons.
Langfuse
Langfuse is an open-source LLM observability platform designed for monitoring, debugging, and evaluating language model applications. Available as both self-hosted and cloud solutions, Langfuse provides comprehensive tracing with automatic capture of prompts, outputs, costs, and latency.
The platform supports any LLM framework through its flexible SDK and offers built-in evaluation capabilities, including LLM-as-a-judge for automated quality assessment. Langfuse tracks prompt versions across runs, enabling comparison of performance metrics between different formulations.
User feedback collection through thumbs-up/down ratings helps identify high- and low-quality outputs, while custom scoring allows tracking application-specific metrics. Automated evaluations can process thousands of traces at configurable sampling rates, enabling continuous quality monitoring at scale without manual review of every output.
Detailed Trace View
Figure 10: Trace logs showing API call details with performance and cost data.
Individual traces display complete execution details for each LLM call. The trace view shows exact latency measurements, token consumption (prompt and completion tokens separately), and calculated costs per request.
Model configuration is preserved, including temperature, max_tokens, and other parameters. The Preview section displays the full prompt sent to the model alongside the complete response, allowing you to understand precisely what the model received and generated.
This granular visibility enables debugging of specific failures by examining the precise input-output pair that caused an error.
Traces Overview Table
Figure 11: Individual trace inspection showing request details and model response.
All traces are aggregated in a filterable table showing outputs, observation levels, latency, token usage, and total costs. Each row represents a single LLM call with color-coded observation levels indicating trace hierarchy or importance. Token counts display both prompt and completion tokens, along with totals, while cost calculations are automatically calculated based on the model used.
The Columns selector allows customization of displayed metrics, and filters enable narrowing down traces by environment, time range, or other criteria. This tabular view makes it straightforward to identify patterns such as consistently slow queries or unexpectedly expensive requests.
Braintrust
Braintrust is an LLM observability platform combining evaluation and production monitoring. The platform enables testing models against datasets, comparing different prompts or configurations, and tracking quality metrics through automated scoring. Built-in and custom evaluation functions measure accuracy, relevance, or domain-specific criteria, with results displayed in comparison tables showing performance differences between versions.
For production monitoring, Braintrust tracks real-time metrics including latency, cost, and custom quality scores as traffic flows through applications. Alerts trigger when quality thresholds are crossed or safety guardrails are violated. Brainstore, the platform’s log storage system, ingests application logs at scale with optimized search for AI interactions. The dashboard displays aggregated metrics across experiments and production runs, capturing cost tracking, token usage, and response metadata for both evaluation and production requests.
Helicone
Helicone is a proxy-based observability platform that monitors LLM applications by routing API requests through its proxy server. Integration requires only changing the base URL without SDK installation or code modifications. The platform automatically captures requests, responses, costs, and token usage for monitoring application behavior.
The dashboard displays total request volumes, aggregated costs, and token consumption across all API calls. Request logs show complete input prompts and model outputs, enabling investigation of specific predictions or errors. Cost tracking breaks down spending by model type, user, or custom tags to identify expensive operations. Built-in caching detects duplicate requests and serves cached responses, reducing both API costs and response times. Rate limiting sets usage caps per user or endpoint to prevent unexpected spending spikes.
The platform focuses on monitoring individual API calls – each request appears as a separate log entry without built-in support for grouping related calls or visualizing sequences. This makes Helicone practical for applications such as independent LLM calls (e.g., single-turn chatbots), batch content generation, or classification tasks, but less suitable for tracking multi-step workflows where understanding relationships between sequential calls is important.
What is LLM observability?
LLM observability is the practice of collecting and interpreting continuous data from large language models to understand how they behave during real-world usage. It focuses on gathering metrics, traces, and logs that show how LLMs respond to different prompts, tools, and external API calls.
Since language models operate through probabilistic reasoning, their internal processes cannot be directly inspected. This makes LLM monitoring dependent on reviewing LLM outputs, LLM inputs, and the intermediate steps that appear in agentic workflows. By studying these traces, LLM developers gain visibility into system performance, model behavior, and usage patterns that influence application performance and output quality.
LLM observability is vital for several reasons:
- Quality assurance: Large language models can produce incorrect or low-quality outputs for a wide range of reasons, including unclear prompts, drifting data, or unexpected user behavior. Monitoring prompts and responses over time helps track evaluation metrics such as correctness, coherence, relevance, and factuality. This allows teams to detect when LLM outputs start to decline in response quality or when the model begins generating hallucinations. As LLM use expands across enterprise workflows, ensuring consistent accuracy becomes a common challenge.
- Troubleshooting: When issues occur inside LLM applications, the root causes can come from many areas. Examples include poorly tuned prompts, faulty fine-tuning, failed external API calls, or logic errors inside multi-step agent workflows. By collecting LLM traces that show intermediate steps, developers can perform root-cause analysis efficiently and pinpoint the exact stage at which the behavior diverged. This reduces the need for human intervention and shortens error-tracking time.
- Optimization: Tracking system performance, resource usage, and token usage helps organizations identify bottlenecks and improve LLM performance. Teams can measure latency, throughput, memory usage, and error rates to understand how LLMs behave under varying load levels. They can also track tokens to control costs and review usage patterns to improve performance and cost efficiency. Continuous monitoring of these key metrics is especially valuable in retrieval-augmented generation and agent workflows, where performance bottlenecks often emerge from inefficient tool calls or unnecessary round-trip during reasoning.
Core metric categories
LLM observability tools typically group relevant metrics into three categories that support both software development teams and operational teams.
System performance metrics
- Latency: Measures the time between receiving a prompt and delivering a response.
- Throughput: Indicates how many requests the model can process within a given period.
- Error rates: Reveal how frequently the system returns invalid or failed responses.
Resource utilization metrics
- CPU and GPU consumption: Help understand how efficiently the system uses hardware.
- Memory usage: Affects scaling decisions and capacity planning.
- Token usage: Influences cost efficiency and helps teams control costs during heavy LLM usage.
- Throughput-to-latency trade-offs: Show how the system balances speed and processing volume.
Model behavior metrics
- Correctness, factuality, and response quality: For identifying low-quality outputs.
- User engagement and user feedback: Provide insights into how well the model meets user needs.
- Faithfulness and groundedness metrics: Reflect how closely the model adheres to the source material.
Manual vs. autonomous observability
Relying on manual observation presents several challenges. Large language models generate high volumes of data, and multi-step reasoning chains produce numerous logs and traces. The need for real-time monitoring increases the operational complexity, and even experienced teams struggle to review every LLM call without missing essential signals. Manual workflows also make it challenging to keep up with continuous changes in user behavior and prompt variations.
Autonomous observability systems address these challenges by using software agents that continuously analyze LLM activity. These agents detect anomalies, diagnose issues, and perform root cause analysis without constant human intervention. Automated evaluations also help identify risky behavior, such as prompt injection.
A system of this type supports continuous monitoring and ensures consistent tracking of evaluation metrics across the entire model. As a result, organizations benefit from faster troubleshooting, improved application performance, and better control over operational risks.
Features of LLM observability tools
Quality and security evaluations
- Hallucination detection to identify when the model deviates from reliable data.
- Prompt injection and jailbreak detection for addressing security concerns.
- Toxicity scoring and safety evaluations that support compliance and risk reduction.
- Clustering that groups similar LLM outputs to identify drift over time.
Experimentation features
- A/B testing for prompt management and configuration changes.
- Rapid comparison across multiple LLM models or parameters.
- Evaluation of accuracy, token consumption, and latency before deployment.
- Testing model changes against real-world scenarios using production-like data.
Correlation with infrastructure
- Connecting LLM traces to backend application performance monitoring data.
- Linking response time and response quality to real user sessions.
- Identifying how system performance affects LLM performance and application stability.
LLMOps and governance
- Guardrails that filter unsafe prompts and block harmful responses.
- Dashboards for tracking PII exposure, hallucinations, and safety violations.
- Tools that support compliance, reporting, and analysis of security incidents.
Observability for agentic workflows
As LLMs power multi-step agent workflows, observability requirements expand beyond single request-response pairs. Agentic applications introduce additional layers of complexity that require dedicated tracing approaches.
Key observability dimensions for agents:
- Planning and reasoning traces: Visibility into how the agent breaks down tasks, selects actions, and refines its approach based on intermediate results
- Tool call monitoring: Tracking external API calls, database queries, and function executions to identify latency bottlenecks or failures
- Handoff tracing: For multi-agent systems, monitoring how tasks transfer between agents and whether context is preserved correctly
- State evolution: Understanding how memory and context change across multiple turns within a session
Together, these dimensions form the foundation of agentic monitoring. LLM observability tools such as Langsmith, Langfuse, AgentOps and Weights & Biases provide agent-specific tracing views that display full execution graphs.

Be the first to comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.