Hiding your IP address is no longer about bypassing geo-blocks. It also helps protect you from AI-based tracking and ‘Harvest Now, Decrypt Later’ data collection.
This guide offers solutions to help you stay anonymous online, from simple browser adjustments that require no installation to advanced encrypted tunnels for your entire operating system.
1. The “no-install” method: Browser-native masking
Major browsers have integrated native IP obfuscation via Oblivious HTTP (OHTTP). Without downloading any software, this is the quickest way to conceal your IP address online for free.
Google Chrome (v140+):
Turn on “IP Protection” under Settings > Security and Privacy. Chrome now hides your IP address from data brokers by using Google-owned intermediate relays to proxy traffic to “suspected trackers.”
Brave browser:
Brave now uses the native Leo Private AI Proxy. Go to Settings > Shields and toggle “Aggressive IP Obfuscation.” This decouples your IP address from both the websites you visit and the AI models you interact with.
SOCKS5 proxies:
For high-speed tasks such as web scraping or gaming, a SOCKS5 proxy is preferred over an HTTP proxy. It doesn’t encrypt data, but it is significantly faster than a VPN for simply changing your location.
2. Apple users: Activating “ultra-masking”
With the release of iOS 19 and macOS 16, Apple upgraded iCloud Private Relay to include a high-security tier called ultra-masking.
How it works:
Ultra-Masking uses a 3-hop setup, unlike regular VPNs. Your encrypted data passes through three separate relays: Apple, a third-party partner, and a local egress point. This way, no single group knows both your identity and your destination.
Setup:
Go to Settings > [Your Name] > iCloud+ > Private Relay. Select “Ultra-Masking (High Security)” for sensitive apps like Health, Finance, and Mail.
Limitation: This is currently limited to Safari and native Apple system services.
4. App-specific obfuscation (advanced)
If you want to hide your IP in specific applications without slowing down your entire device, use these 2026 app-level settings:
Telegram: Go to Settings > Data and Storage > Proxy Settings. Add an MTProto Proxy. This hides your IP address from Telegram’s servers and prevents it from leaking during peer-to-peer (P2P) calls.
Docker: To prevent a container from exposing your host IP, route it through a sidecar container. Command:
Gaming (steam/epic): Use a dedicated gaming proxy (Geo-fenced) to reduce ping while masking your home IP from DDoS attackers in competitive lobbies.
Hide Your IP with a VPN
Using a VPN, which provides an encrypted connection between your device and a remote server via the internet, is one of the most popular methods for concealing your IP address.
VPNs replace your IP address with an IP address from a server of your choosing. These services provide secure browsing by encrypting your internet traffic, particularly on public Wi-Fi networks where unprotected connections expose your data.
Numerous VPN services are available, ranging from free to paid options. Although free VPNs are available, keep in mind that their speed, security, and server availability are often constrained. Investing in a premium VPN service is necessary to get optimal performance.
You can check your new IP address by going to a website such as whatismyipaddress.com after connecting to the VPN server.
Hide IP with a proxy (HTTP/HTTPS/SOCKS)
Proxy servers assign an IP address from their pool and act as intermediaries between your device and the internet. When you access a website through a proxy, your request is sent to the proxy server, which forwards it to the website.
The proxy server uses its own IP address to forward your request, so the website only sees the proxy’s IP, not yours.
What a proxy server hides vs. what it doesn’t
What a proxy server hides
- Your actual IP address from the destination of the target site is replaced with the proxy’s IP address.
- Your location is based on IP geolocation.
- The origin of specific requests.
What a proxy server doesn’t hide
- Unless it’s an HTTPS proxy, your traffic is not encrypted.
- Your internet provider still sees you’re connected to a proxy.
- Sites can still identify you using other methods.
Configure a proxy on Mac/Windows
macOS proxy settings (system-wide)
- Open network settings
- Click the Apple menu → System Settings or System Preferences.
- Select your connection
- Choose Wi-Fi or Ethernet, then click Advanced.
- Go to the proxies tab
- Select Proxies from the top menu.
- Enable the proxy type
- Check Web Proxy (HTTP) or Secure Web Proxy (HTTPS).
- Enter proxy details
- Type the server address and port number provided by your proxy service.
- Apply settings
- Click OK, then Apply to activate the proxy.
Windows 11/10 proxy settings
- Open proxy settings
- Press Windows + I → Settings → Network & Internet → Proxy.
- Manual setup
- Under Manual proxy setup, select “Use a proxy server” and set it to “On”.
- Enter proxy details
- Fill in the Address and Port provided by your proxy provider.
- If authentication is required, enter your username and password when prompted.
- Save and close
- Click Save and restart your browser.
Free options (Tor & public proxy caveats)
TOR browser
Tor is a free browser that conceals your IP address by routing your internet traffic through a network of volunteer-operated servers.
However, Tor does not provide complete anonymity. Be aware of slower speeds and avoid logging in to personal accounts, such as email or social media, while using it.
- Avoid downloading or uploading sensitive files while using Tor.
- Do not use a proxy server with Tor, and avoid accessing personal accounts.
- Do not install browser extensions while using Tor, or download large files.
However, private browsing does not hide your IP address or prevent websites from tracking your activity. Browsers like Tor can conceal your IP address and block trackers or scripts.
Public Wi-Fi network
When you connect to a Wi-Fi network, the public router assigns your device a different IP address, temporarily hiding your real one. However, public Wi-Fi still poses security and privacy risks.
For example, your internet provider can monitor your online activity and track the websites you visit through your IP address. If you access sites without HTTPS, others on the same network may also view your data.
Hide IP on your phone (iOS & Android)
Safari built-in settings (Safari only)
Apple has a built-in privacy feature for hiding users’ IP addresses from trackers. However, this method doesn’t protect non-Safari apps and websites, as they can still use your browser fingerprinting and cookies.
- Open your settings, then scroll to the Apps section.
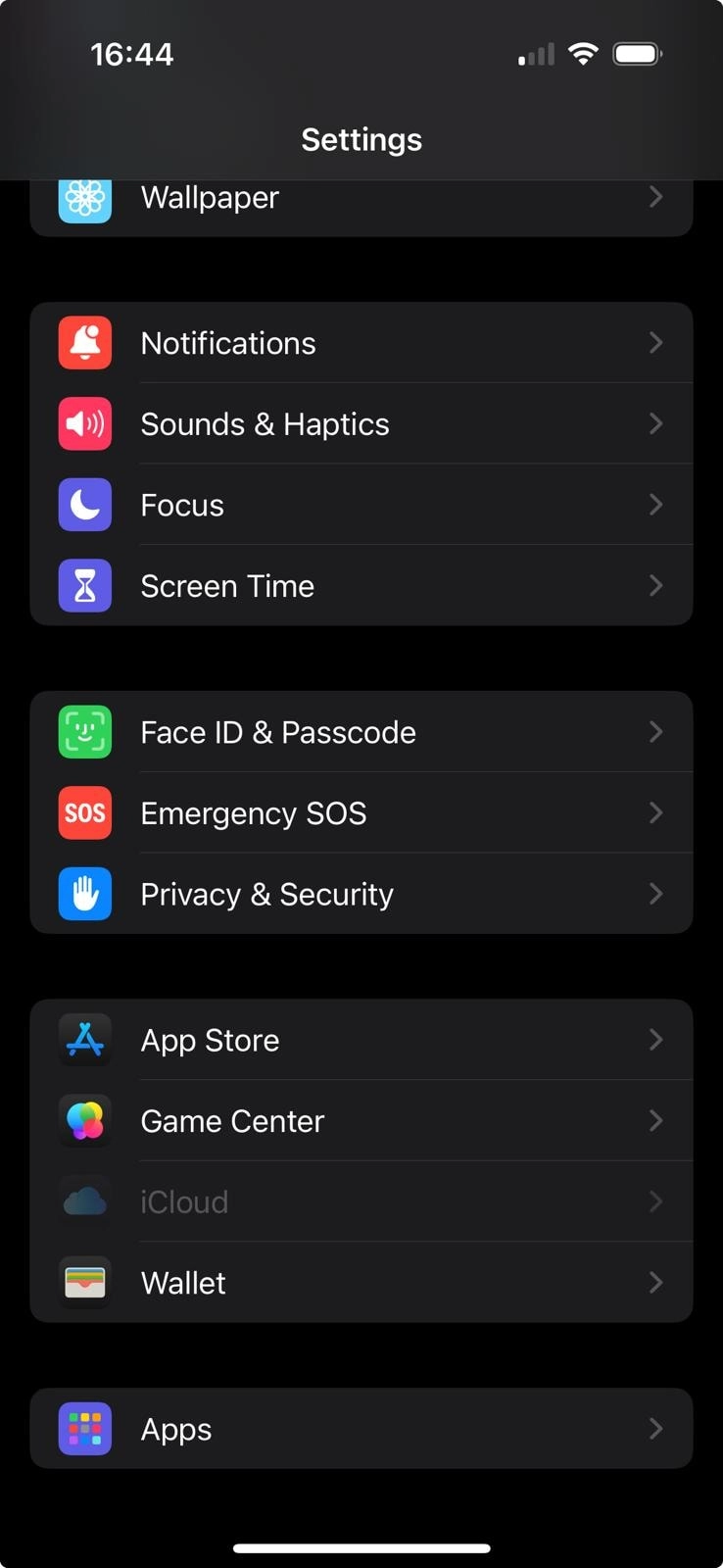
- Go to Safari and Scroll to Privacy & Security.
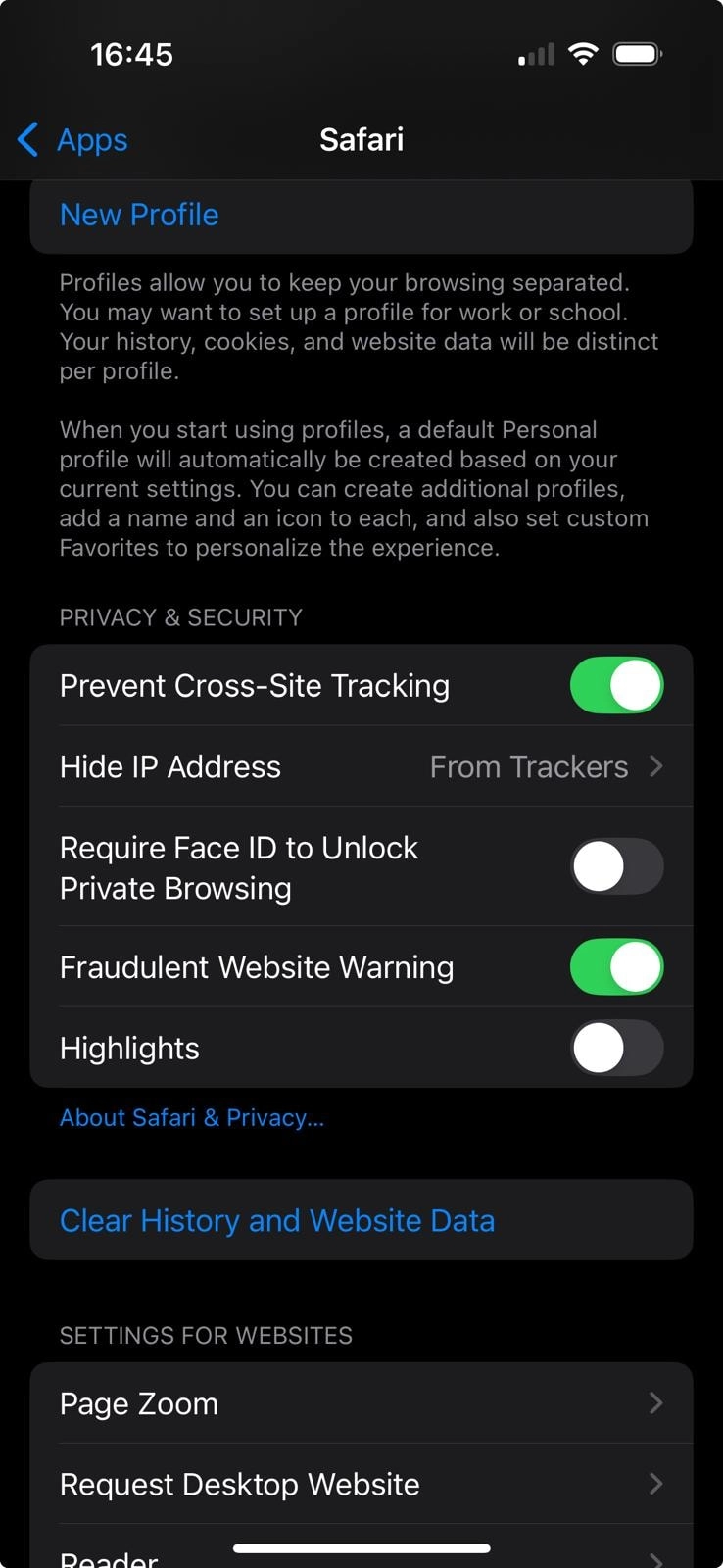
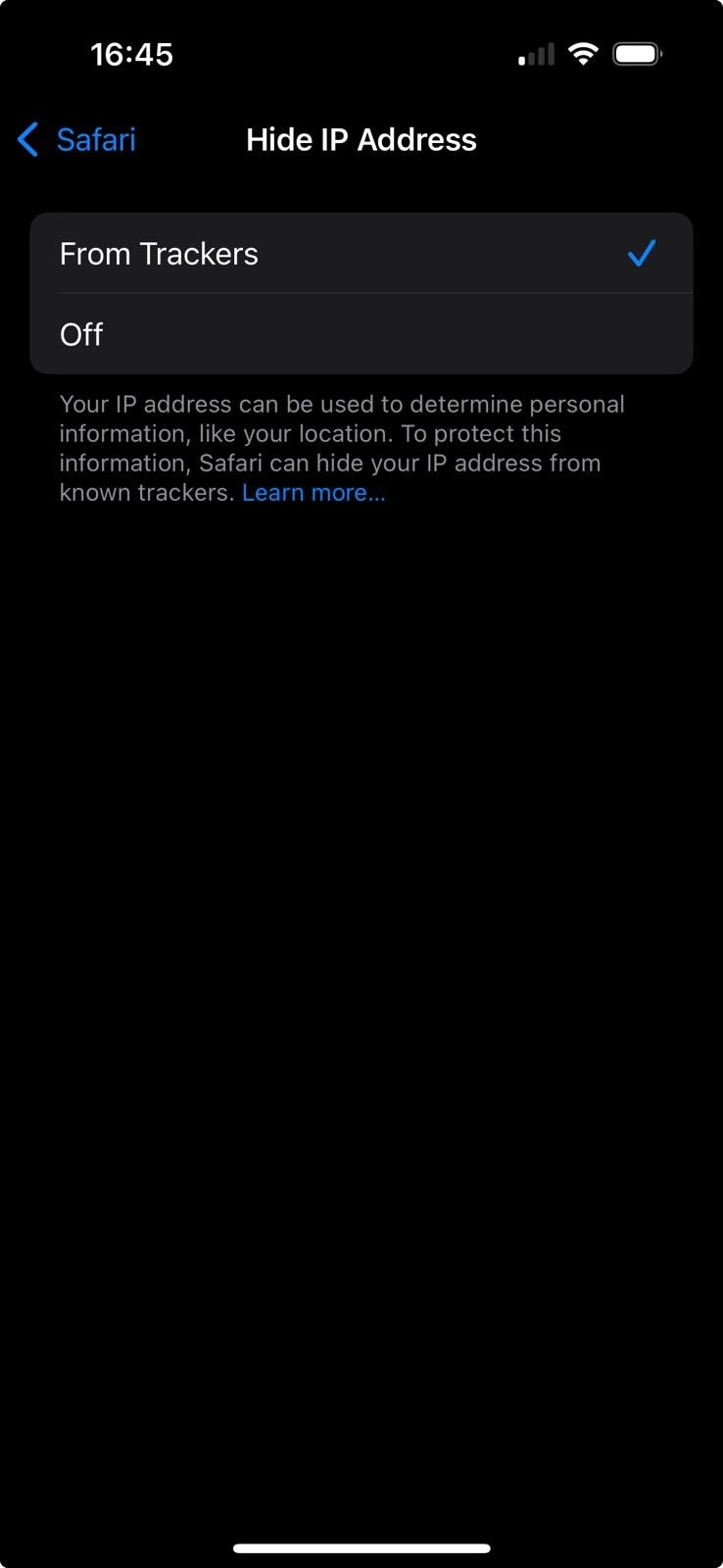
- Tap Hide IP Address.
See: How to Configure Proxy Server Settings on iPhone
iCloud Private Relay (iOS)
iCloud Private Relay is a feature available for iOS 15 and later. It protects user privacy by hiding their IP address when browsing with Safari. Apple can’t see the websites you visit, and websites can’t see your actual IP.
However, it only works in Safari and is not available for users who aren’t subscribed to iCloud+. You can enable iCloud Private Relay by:
- Go to Settings → Your Name → iCloud → Private Relay, then toggle the switch to turn it on.

Be the first to comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.