To prevent circumvention, CAPTCHA systems evolve. By early 2026, the focus has shifted from simple image recognition to behavioral biometrics and identity correlation. Web scrapers must adopt agentic workflows to stay effective in this changing environment.
4 Ways to Handle reCAPTCHA & hCaptcha in 2026
There are generally three primary strategies for bypassing CAPTCHA systems:
1. Using an agentic stealth browser
This method simulates complex physical behaviors to make automated browsers appear human.
- Neuromotor interaction: Cloudflare and AWS WAF easily detect basic randomized mouse movements. Modern stealth layers should use neuromotor jitter models that mimic Fitts’ Law, reflecting the natural acceleration and deceleration of human cursor movements.
- Hardware fingerprint spoofing: To prevent identity correlation across different IP addresses, scrapers should randomly generate GPU canvas fingerprints and font-rendering quirks and mask the navigator.
2. Applying zero-shot reasoning and Generative AI
Older methods no longer work well when training deep learning models on large datasets.
Modern scrapers use multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) to solve puzzles with logical reasoning. These models can handle new CAPTCHA types without training data because they understand the spatial context of each puzzle, not just by spotting objects like a fire hydrant.
AI agents can now fix their own mistakes. If a bypass fails, the agent checks the error code, like Cloudflare 403, and then changes its browser fingerprint or proxy before trying again.
3. Using hybrid CAPTCHA solving services
CAPTCHA-solving services are frequently regarded as the most reliable method. These services act as intermediaries between automated systems and CAPTCHA challenges:
Human solvers:
The CAPTCHA image is sent to a pool of human workers who solve it in real-time. Services like 2Captcha, Anti-Captcha, or DeathByCaptcha fall into this category.
For example, when your scraper captures the CAPTCHA image, it sends this information via an API call to the CAPTCHA solving service. The human worker solves the CAPTCHA and submits the solution back to the service. The service then returns the solution to your scraper via its API.
Hybrid solvers:
These systems utilize artificial intelligence models to address simple, well-understood CAPTCHA challenges and rely on human solvers for more complex or novel challenges. The CAPTCHA is routed to either an AI engine or a human solver based on its complexity.
4. Using AI for image recognition
AI, specifically deep learning models, can be trained to solve image-based CAPTCHA. This includes:
Training a model to interpret CAPTCHA images requires a large dataset of labeled CAPTCHA images paired with correct responses. Data collection and annotation are typically the most resource-intensive components of this approach.
CAPTCHA images may be collected and submitted to human solver services to obtain solutions, which are subsequently used to build a training dataset. However, if a website modifies its CAPTCHA, existing datasets may become outdated.
Why is CAPTCHA a challenge for web scraping?
The biggest challenge now is the risk score that gets assigned before you even see the puzzle, rather than the puzzle itself.
- In Google reCAPTCHA v18.9.0, the new SDK uses a feature called Fluid Risk Scoring. This system watches how someone interacts with the whole page, not just the CAPTCHA box. If your scraper clicks a button too quickly or too perfectly, the risk score goes up right away.
- Biometric entropy: Websites now measure the randomness of human input. True human movement has micro-fluctuations that are difficult for basic scripts to replicate without advanced mathematical modeling.
What are the common types of CAPTCHA?
CAPTCHAs are categorized into six types, each offering varying levels of security against automated programs. The most common CAPTCHA types include the following:
1. Image-based CAPTCHA
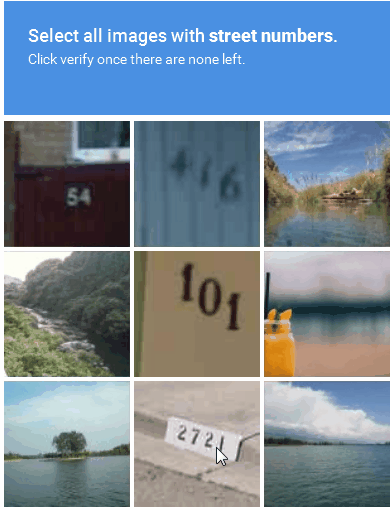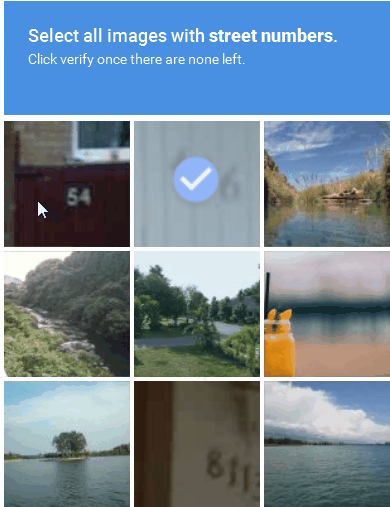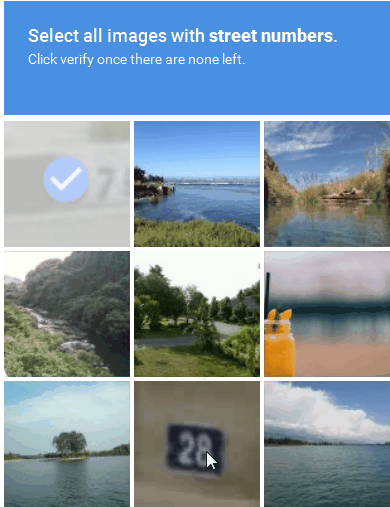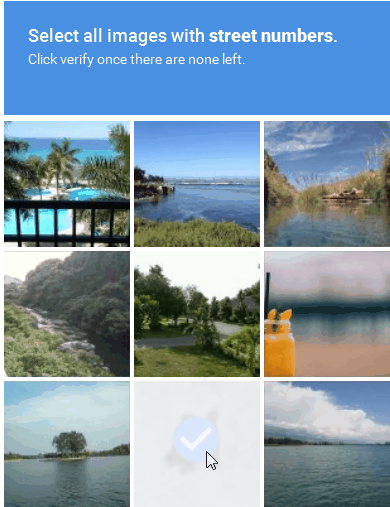
Image-based CAPTCHA presents a distorted image containing a word or sequence of characters that users must identify and enter into a text field (Figure 1).
The image distortion is designed to impede automated algorithms from recognizing characters while remaining solvable by humans. Image-based CAPTCHA effectively prevents bots from accessing websites, although it can be more challenging and time-consuming for users.
However, specific machine learning algorithms, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and support vector machines (SVMs), can accurately solve various image-based CAPTCHA. These methods analyze large CAPTCHA image datasets to train models that recognize character patterns.
Consequently, many websites have adopted more complex CAPTCHA challenges, including interactive CAPTCHA and ‘No CAPTCHA’ systems. These approaches use various methods to differentiate between human users and automated bots.
Figure 1: An example of an image-based CAPTCHA solution
2. Audio-based CAPTCHA
Audio-based CAPTCHA presents a distorted audio recording containing a word or sequence of characters (Figure 2). Users must listen to the audio and accurately identify the spoken content. This CAPTCHA type is frequently used to accommodate individuals with visual impairments.
Figure 2: An example of audio-based CAPTCHA
3. Text-based CAPTCHA
Text-based CAPTCHA is presented in unusual and distorted formats. Users must accurately identify the text and enter it into a designated field to complete the challenge.
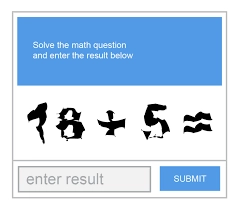
4. Math-based CAPTCHA
Math-based CAPTCHA provides users with a basic arithmetic problem to solve and enter into a text field, for example, ‘What is 3 + 2?’
Figure 3: Example of a math-based CAPTCHA
5. Interactive CAPTCHA
Interactive CAPTCHA requires users to complete a series of puzzles or tasks to verify their human identity.
6. Checkbox-based CAPTCHA
Checkbox-based CAPTCHA is a variant of reCAPTCHA, a free service developed by Google to help websites protect against unauthorized and fraudulent activities.
Checkbox reCAPTCHA prompts users to select a box to confirm they are not automated bots. Additional challenges may include selecting images that meet specific criteria or solving simple arithmetic problems.
FAQs about bypassing CAPTCHA
Bypassing a CAPTCHA isn’t always illegal by itself. Whether it’s legal depends on why you’re doing it and what you do next.
Yes, it is possible, but it is becoming increasingly difficult and requires complex approaches. The safest technique for valid and ethical web scraping is to follow website policies and search for official APIs.
When you try to access a website, you will notice a CAPTCHA as a security measure established by the website owner.
Typically, a CAPTCHA will present you with a challenge and need you to enter the necessary information to show you are human. This could include inputting distorted words, recognizing objects in photos, or checking a box.
Traditional CAPTCHAs are based on the reality that people are generally better at pattern recognition, deciphering distorted visuals, and comprehending context than computers.
When you solve a CAPTCHA, you are effectively conducting a “Turing test” in reverse. The target website is testing you to see if you have a human-like intellect.
Modern CAPTCHA, particularly reCAPTCHA, has experienced tremendous development. Instead of focusing solely on one difficulty, they frequently employ a combination of factors, such as behavioral analysis, browser fingerprints, and machine learning.
reCAPTCHA is a form of CAPTCHA system developed by Google. It’s one of the most popular and advanced CAPTCHA services on the internet.
Initially, reCAPTCHA aided in the digitization of books by presenting users with words from scanned texts that optical character recognition (OCR) failed to recognize.
CAPTCHA (Completely Automatic Public Turing Test to Tell Computers and Humans Apart) is an automatic challenge-response test used on computing systems to validate that the user is human rather than a bot.
Common implementations include Google reCAPTCHA (v2 checkbox, image challenges; v3 score-based), hCaptcha, and invisible reCAPTCHA.

Be the first to comment
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.