12 Process KPIs to Monitor Process Performance in 2024
There is pressure to manage, improve and automate processes since efficient process management can improve productivity by 30-50%. However, improvement and automation strategies are rarely monitored because establishing realistic and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) that measure process performance is time-consuming and error-prone. Thus, analysts are often unable to quantify the benefits of their process improvement efforts.
Process mining can help track relevant process performance metrics by deriving quantitative process performance metrics from system data. Leading process mining tools also enable businesses to act on those metrics.
In this article, we’ll go over 12 process performance metrics and how process mining helps establish realistic and effective indicators to assess the process effectiveness, efficiency, cycle time and compliance in your organization.
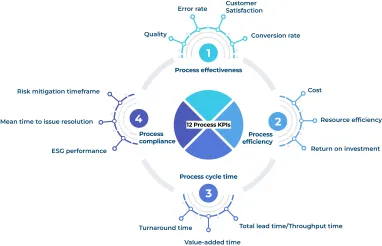
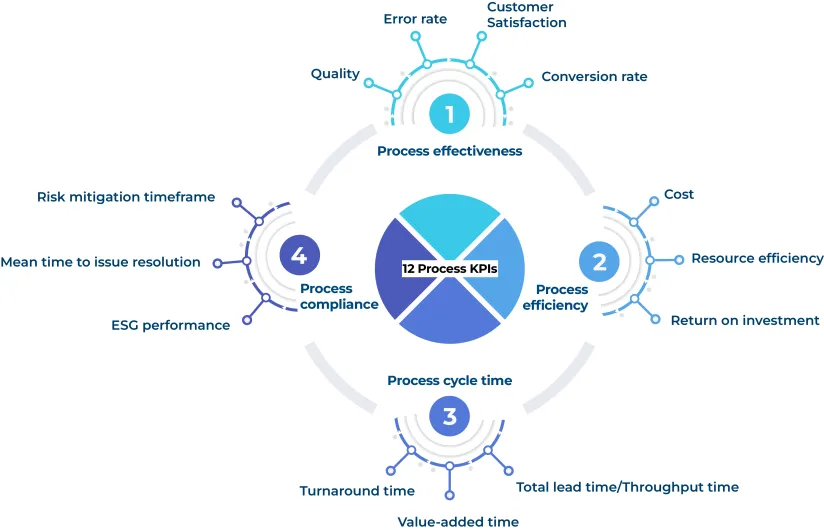
Process effectiveness
Process effectiveness is the delivery of a qualified service or product in a way that it satisfies the customers.
Some examples for process effectiveness KPIs include:
- Quality: The output (service or product) meets the client standards, internal QA and budget.
- Error rate: The number of units, products or service that failed during the entire process cycle.
- Customer Satisfaction: How well the process meets the customer’s expectations.
- Conversion rate: The number of prospects that company interacts and convinces to become customers (in a commercial process).
For example, the company can measure these to measure process effectiveness:
- in a manufacturing process:
- Percentage of non-conforming units produced
- The level of customer satisfaction (for the final product).
On the other hand, conversion rate metrics are used by IT, sales and marketing teams to measure the effectiveness of their ads, campaigns or banners.
Process mining can automatically estimate and deliver these factors while discovering the process in analysis. The results obtained from the process discovery phase can be compared to the strategy, business process management model or the ideal or standard process model with process mining’s conformance check capability. The difference between ideal and obtained process models indicates the process’s effectiveness.
In a process mining case study, Von Ardenne, a leading German equipment supplier, integrated a process mining software to elevate operational effectiveness. Thorough analysis of business processes unveiled hidden weak points and cost drivers, offering real-time visibility. Aligned with key performance indicators (KPIs) such as:
- Efficient delivery by increasing delivery reliability
- Error rate reduction
- Cost reduction by improving planning and analytics
- Improved customer satisfaction by tracking workflow for customer lifetime value
KPI dashboards ensure constant performance measurement, fostering a commitment to continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Process efficiency
Process efficiency measures the allocation and utilization of resources, the employee skills, proportion of non-value-added activities, delay times.
Some process efficiency KPIs examples are:
- Cost: The expenses spent on the necessary resources to complete the process, including workers’ salaries.
- Resource efficiency: The metrics compares the total value of the final process against the consumed resources considering environmental impact
- Return on investment: The amount of profit required to justify the investment on a particular campaign or process.
Process mining can help analysts achieve efficiency by showing resources and time waste involved in the process.
Process cycle time
Process cycle time measures how long time it takes to complete a given task. As a result, the cycle time reveals the inefficiencies within the process flow that slow down the delivery of the service or product.
The cycle time KPIs include:
- Total lead time/Throughput time: The time from the start until the end of the process, including each step the process contains
- Value-added time: It is the time that is spent completing a single task
- Turnaround time: The turnaround time refers to the time it takes to complete a customer’s request from order to delivery
For a logistics firm, turnaround time is important while measuring the time the firm should shorten to increase customer satisfaction.
For a manufacturer, the throughput time is a way to assess the performance for their entire production journey. Producers gather raw materials, put them in the production line, manufacture and then deliver them to the customer or logistics firm to complete delivery. They evaluate all the waiting time for materials, machinery downtime or delays occurring at any stage that might prolong the throughput time.
Process mining can allow analysts to predict the potential problems such as delays that might affect process performance negatively.
Process compliance
Internal process compliance provides insights into possible causes for non-conforming processes compared to standard operating procedures and best practices, while external compliance ensures tracking and complying with relevant government regulations and policies. As a result, process compliance protects organizations from fines and helps mitigate the risks.
Some KPIs used for compliance:
- Risk mitigation timeframe: It is to measure the time between the risk that occurs after the change implemented and the discovery of that risk
- Mean time to issue resolution: It is the time that takes to solve an issue after it’s identified
- ESG performance: Environmental, social and governance reporting shows the non-financial impact and compliance level with standard procedures and rules in the regions the firm operates through several metrics.
These KPIs are helpful for executive boards to get prepared for external compliance checks and guide relevant departments on operations that do not follow the strategy or standard procedures.
Compliance is one of the core use cases for process mining because process mining seamlessly portrays the complete process and identifies compliance issues with process discovery and conformance checks capabilities. Thus, many process mining vendors offer root cause analysis capability for ill-performing operations. With root cause analysis, process mining users can detect the responsible teams, parties or stages that create the non-compliant output.
For example, a logistics company leveraged process mining and detected around 70% compliance risks in its credit and collections management process.
Explore how process mining enhances auditing and compliance in-detail.
Further reading
Feel free to check our articles on process mining use cases, benefits and how process mining facilitates RPA:
- 33 Use Cases and Applications of Process Mining
- 11 Benefits of Process Mining
- 4-Step Guide to Facilitate RPA Deployment with Process Mining
If you believe your business can benefit from process mining, start reviewing our data-driven comprehensive vendor lists.
You can improve your process KPIs by deploying various other management and development tools. Check out our objective lists of:
- Workflow management software
- Business process management software
- Low-code/No-code development platform
- Onboarding software
And if you still have some doubts left, you can always let us help you:



Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.