How Digital Twins Change the Insurance Sector in 2024
Digital twins are one of the technological breakthroughs that are transforming insurance practices. They can be both a useful and disruptive technological innovation. Digital twins offer improvements in core insurance practices such as underwriting, claims processing and fraud detection. Moreover, digital twins combination with the Internet of Things (IoT) can change the insurance sector that has existed for centuries, as they can prevent damages before they occur.
But a monitored environment by technological devices also creates new areas of risk, such as cyber risk that is insured by companies. Thus, the insurance practices of the future remain blurry. Consequently, the insurance companies of the future will be those that adapt to this rapidly changing environment. In this respect, understanding digital twins could help unravel the mystery.
What are the digital twins and why are they important for insurance companies?
Digital twins are computerized representations of any physical objects such as people, houses or cars. They help companies create simulations or exercises which help to derive “virtual data”. Insurance is inherently a data-centric business, and Accenture argues that implementing digital twins as a data source represents a breakthrough innovation for the future of the insurance sector.
Until the introduction of modern technologies, insurance companies could only use historical data for risk assessment. Thanks to simulations, insurance companies can assess their readiness to deal with rare disasters such as volcanic eruptions, large earthquakes or floods, pandemics, and so on. From this perspective, digital twins provide a virtual platform for insurance companies where any risk scenario can be predicted and evaluated.
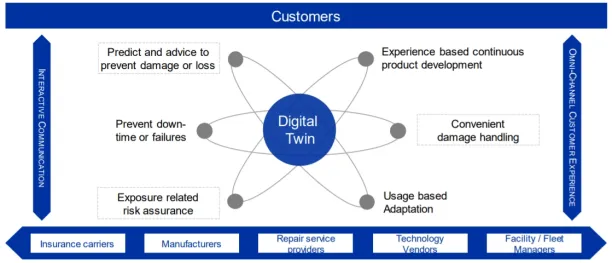
How do digital twins transform the insurance sector?
With the rapid spread of digital twins and IoT technologies, the insurance sector is undergoing rapid changes. Old-fashioned insurance policies that cover damage from unintended events are being replaced by insurance services that reduce risks before they cause problems.
Digital twins combined with the Internet of Things (IoT) are forcing insurance companies to adopt a new business model in which they mitigate or prevent rather than compensate for damages. This new business model is called Assurance.
Digital twins and the networking of smart devices have the potential to prevent damage before it occurs. Under these circumstances, no one is asking for old-fashioned insurance policies anymore. To understand this better, let’s take an example:
Consider a ship transporting goods from one port to another. Telematics of nearby objects warns that the ship will soon be exposed to a tropical storm. The ship’s digital twin takes real data from all of the ship’s systems. Thus, a simulation is performed that reflects the effects of the storm on the ship. Based on the simulation results, the captain decides to return to port. Similar logic could be applied to smart cars, smart houses, and so on.
Customers expect insurance companies to quickly adopt technological improvements and assure their assets.
Digital twin technology also allows companies to generate a digital replica of their organizations, a digital twin of an organization (DTO). A DTO simulates the activities and tasks of an insurance firm and allows the firm to improve its operations. A DTO can be helpful to predict client behaviour, simulate a scenario of catastrophic events, and provide insights to implement RPA for automating the processes. Therefore, a DTO can improve organizational operations by exploring the process data stored in event logs.
Which insurance practices can be improved through digital twins?
The following insurance practises can be enhanced thanks to digital twins:
- Underwriting: More accurate prediction of the future risks thanks to data streams via simulations.
- Claims processing: Expedited claims processing thanks to computer-assisted replication.
- Fraud detection: Using the data provided by the IoT, replicate the environment in which the damage occurred and assess whether or not the claim is fraudulent is possible thanks to the digital twins.
Underwriting
Digital twins lead insurance companies to expand their datasets. Underwriting is the process by which insurers price risk. Therefore, risk assessment is the core of underwriting. Risk assessment is related to the computational power and volume of data evaluated. The simulation capability of digital twins improves the underwriting process and enables insurance companies to set competitive premiums.
Thanks to digital twins, insurers can expand the data set they had for everyday risks such as car accidents, heart attack or house fires, but they can also collect data for catastrophic events that occur very rarely. For example, an insurance company can estimate the potential damage of an earthquake that could happen in California.
Claims Processing
Claims processing is an insurance practice that impacts both operational efficiency and customer satisfaction for the insurance company. Since claims are liabilities to insurance companies and customers expect a quick response when they experience an undesirable situation, it pays to improve the process.
Thanks to digital twins and telematics, it is possible to reproduce the conditions of the damage that occurred, and using this data, it is possible to simulate the accident and its impact on the property. This helps to speed up the claims processing and reduces the necessity for expert examination.
Engineers can regularly check the success of their damage simulation. In small car accidents, for example, insurance company chatbots instruct customers to take photos and videos of the damage to create a damage report. By comparing real and virtual damage reports, engineers can improve their digital twins.
Fraud Detection
According to the FBI, the cost of insurance fraud (excluding health insurance) is $40 billion per year in the U.S. alone. Such a burden on insurance companies is reflected on innocent customers in the form of higher premiums. So improving fraud detection is for the good of all involved.
Thanks to digital twins, some of the fraudulent claims could be detected. As we discussed above, it is possible to reproduce the damage-causing event using digital twins. It is plausible that the simulated claim may not perfectly reflect the real damage. However, with a known standard deviation, the real damage can be replicated. As a result, statistically inconsistent claims can be more closely examined by insurance companies to determine whether fraud is involved or whether the digital twin model decays.
Further readings
You can also read our selection of 5 insurance/insurtech articles
- Top 5 Insurance Technologies & Their Use Cases: This article highlights the impact of five key technologies, namely Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing, Internet of Things, Blockchain, and Digital Twins on everyday insurance practices such as underwriting, claims processing, customized insurance policies, and fraud detection.
- 3 Ways Blockchain will Change Insurance Sector: This article explains how blockchain technology is changing the insurance sector with a similar structure to the article you read.
- Small Business Insurance: An Emerging Industry for Insurers: We believe that SME insurance will be the future of commercial insurance. To find out the latest trends on SME expectations, you can read this article.
- Top 7 Innovative Insurtech Companies of 2023: Detailed Guide: Introduces 7 innovative insurtech companies that implement a variety of technologies to enhance insurance practices.
You can also check our articles on Digital Twins:
- Top 5 Use Cases of Digital Twin in Automotive Industry
- The Ultimate Guide to Digital Twin Applications in Supply Chain
- Best Digital Twin Applications & Use Cases in Healthcare
- Ultimate Guide to Top 6 Digital Twins Use Cases in Manufacturing
- 15 Digital Twin Applications/ Use Cases by Industry
It might be also beneficial for your company to check our top insurance suites and digital twin software lists.
If you need more information about finding an insurtech that help your digital transformation please, contact with us.

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.