Data Lake: What It Is, Benefits & Challenges in 2024
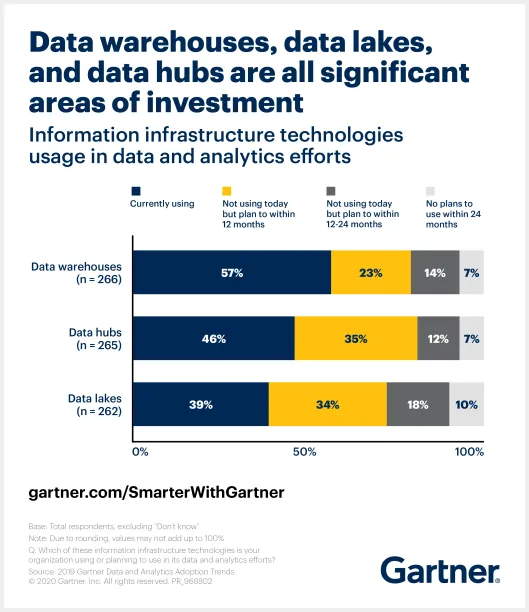
Data lakes have become one of the most popular repositories used to store large amounts of data. A study by Gartner shows that 57% of data and analytics leaders are investing in data warehouses, 46% are using data hubs and 39% are using data lakes. We’ll explore data lakes, their features, benefits, and challenges in this article what are the maturity levels of a data lake in an organization.
What is a data lake?
A data lake is a centralized repository that holds a large amount of structured and unstructured data until it is needed. A unique identifier and metadata tags are assigned for each data in the data lake. The purpose of this is to access data faster. Unlike most data warehouses and databases, data lakes can handle all types of data (including unstructured and semi-structured data such as images, video, and audio) that are required for machine learning use cases.
What are the maturity levels of data lake in an organization?
- Data source identification: In the first stage, the data lake serves to store the raw data indefinitely before making it available for use. Data from different sources is stored in a raw form. At this stage, a correct and secure management practice should be decided to label and classify the data to be stored.
- Testing and learning a data lake environment: At this stage, organizations begin to use the data lake more actively. While collecting data in the first stage, this stage focuses on transforming and analyzing the collected data. Experiments are conducted with unmodified data and the most appropriate tool for the company is decided.
- Integrate data lake with existing data warehouses: Companies use data warehouse and data lake together for data analytics.
- Data lake as a service: At this stage, the data lake becomes a core part of the organization’s data infrastructure as a service that provides data to the company.
What is the difference between a data lake and a data warehouse?
Data lakes and data warehouses are two different approaches for storing big data. Fundamentally, both are storage repositories that combine various data stores. However, there are some key distinctions between the two approaches:
- A data warehouse has a predetermined scheme for the data it stores. However, a data lake does not have a predetermined schema.
- Data lake processes all types of data such as structured, semi-structured, and unstructured (raw) data while data warehouses process and store only structured data.
- For large data, data warehouses are usually more expensive when compared to data lakes. However, it provides higher performance and faster query results.
- Typical users of data warehouses are business analysts while typical users of data lake are data scientists, business analysts, and data developers.
What is data lake architecture?
There is no single recipe to define the data lake architecture. However, there are three fundamental data lake architectural principles:
- All data is loaded in the data lake whether it is structured or unstructured
- The data is stored in the data lake in an unconverted or partially converted form
- In accordance with the business need, the data is converted and fit into a schema
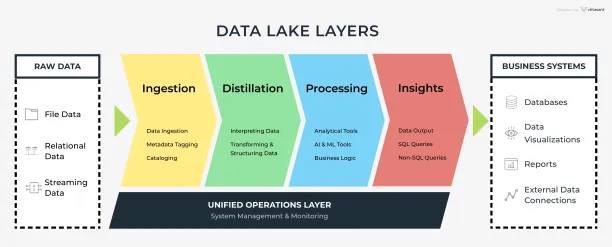
- Ingestion Layer: The ingestion layer is the first step of the data lake layers. It gathers data and ingests raw data from various sources into the data lake. The ingestion layer prioritizes and categorizes raw data.
- Distillation Layer: The distillation layer takes the data from the ingestion step and converts it into structured data for better and easier analysis. Data preparation begins in this step. The distillation layer cleans and transforms raw data from the ingestion layer for efficient analysis.
- Processing Layer: The processing layer runs analytical tools and user queries with interactive, real-time, and batch on structured data.
- Insights Layer: The insight layer represents the query interface. SQL or NoSQL queries can be used for data analysis.
- Unified Operations Layer: The Unified Operations Layer is tasked with governing system monitoring and management. It performs data management and workflow management.
What are the benefits of data lake?
- The data lake is highly agile. Data scientists can prepare and analyze data models rapidly.
- Data lakes require low-cost hardware and most technologies used to manage data in a data lake are open source like Hadoop. It is cheaper to implement compared to a data warehouse.
- Data lakes reduce unnecessary resource usage in the organization. They store any kind of data and it provides resource savings to businesses. Resources are only expended when data is used.
What are the challenges of data lake?
- Data lakes can store large amounts of data. Thus, organizations need to have good data management practices. Otherwise, the data lake may turn into a data swamp and become unusable. Organizations need to keep the data up-to-date and perform the necessary merges and deletions. In this way, valuable data wouldn’t be wasted.
- Sometimes data requiring confidentiality can also be stored in the data lake. In these cases, the biggest challenge would be storing such data in the lake without a measure and monitoring.
- Data lake provides accessibility to everyone in the organization. However, its use in practice is not equally accessible to everyone. Since the data lake also stores unstructured data, it is not easy for non-technical users to parse the data.
What are some popular data lake solutions?
If you have questions about data lakes or other data storage methods, we would like to help:

Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.