Comparison of Chatbots vs. Conversational AI in 2024
Managers might have a hard time choosing between a chatbot or a conversational AI application for their business.
That; however, is no fault of their own. Because at the first glance, both are capable of receiving commands and providing answers. But in actuality, chatbots function on a predefined flow, whereas conversational AI applications have the freedom and the ability to learn and intelligently update themselves as they go along.
In this article, we will explain the differences between chatbots and conversational AI, look at what each one does, go over some of their use cases, and help you decide for yourself which is a better fit for your company.
What is a chatbot?
Chatbots are computer programs that can talk to you, introduce themselves, ask you questions, receive your answers, and provide you with a solution. Today, they are used in education, B2B relationships, governmental entities, mental healthcare centers, and HR departments, amongst many other fields.
What are chatbots used for?
Chatbots have various functionalities, including, but not limited to:
- Automating responses by fetching answers from databases.
- Routing inquirers to human agents.
- Making sales and generating leads.
- Generating meaningful conversations with users (e.g. mental healthcare chatbots or emotional chatbots)
What is conversational AI?
Conversational AI is the name for AI technology tools behind conversational experiences with computers, allowing it to converse ‘intelligently’ with us.
Conversational AI lets for a more organic conversation flow leveraging natural language processing and generation technologies. Conversational AI is the umbrella term for all chatbots and similar applications which facilitate communications between users and machines.
What is the difference between chatbots and conversational AI?
Whereas all conversational AI applications are basically chatbots, not all chatbots utilize conversational AI to the same degree, and that is because chatbots’ specifications vary with the respect to the field in which they are used.
Chatbots primarily use natural language text interfaces that are constructed via pre-determined guidelines. This setup requires specific request input and leaves little wiggle room for the bot to do anything different than what it’s programmed to do. This means unless the programmer updates or makes changes to the foundational codes, every interaction with a chatbot will, to some extent, feel the same.
Conversational AI, on the other hand, combines sentiment analysis, user intent recognition, and continuous machine learning to enable the software to understand requests and questions which have not been already programmed and answer them by leveraging both structured and unstructured data in the business database. Thus, conversational AI has the ability to improve its functionality as the user interaction increases.
Advice for executives: Familiarize yourself with the basic differences between chatbots and conversational AI platforms before adopting either.
What does conversational AI do?
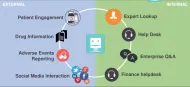
Conversational AI applications rely on different technologies, such as natural language processing, natural language understanding, machine learning, deep learning, and predictive analytics. These elements allow conversational AI applications to:
- Learn at scale: By feeding off various sources (e.g. websites, databases, APIs) conversational AI not only can provide you with a larger domain of answers, but can modify the output based on information updates.
- Adapt: Having full access to business databases (e.g. FAQs, supply chain) provides conversational AI with the contextual elasticity to carry out fluid interactions with the user, answer FAQs or provide information about shipments. This implies that if the user changes their mind mid-conversation or deems it necessary to require a different service, the conversational AI has the ability to adapt itself to the new commands mid-task.
- Personalize answers: Most conversational AI applications keep users’ data in data warehouses for certain periods. Therefore, they can then use historical data to make current interactions with users smoother and more personalized.
- Autonomously update: Because conversational AI leverages machine learning algorithms which train continuously on new data, most users do not need to manually update it. It does that on its own through automated testing and extensions.
- Speak various languages: Conversational AI systems, which have been trained using multilingual data, can work simultaneously in different languages while sharing the same overall logic and integrations.
Should you use a chatbot or a conversational AI platform?
The decision to choose between either a chatbot or a conversational AI platform depends on the nature of your business, for even though conversational AI is more intelligent, the market size of chatbots is expected to reach $1.3B by 2025. That is because not all businesses necessarily need all the perks conversational AI offers.
For example, if you are the owner of a candle shop looking to increase your online sales, you might need a chatbot making suggestions and streamlining purchases more than you would need it to understand the tone or the context of the conversation with your customer.
Or if you are running a pizzeria, you would expect all the digitized conversations to revolve around delivery times, opening hours, and order placement. You would not need to invest in an expensive conversational AI platform to, let’s say, offer pizza recommendations based on the user’s ethnicity or dietary restrictions.
But a chatbot would simply be inefficient in institutions, such as a hospital, where an extensive array of services get provided. Institutions of this nature are in perpetual flux: Surgeons get delayed in ERs, appointments get canceled, insurance policies change, and new treatments get offered. So you would normally want an advanced conversational AI application on the hospital’s website to constantly be able to keep itself in sync with the latest changes, happenings, and circumstances.
Advice for executives: Unless your enterprise is data-heavy, a chatbot is a better choice than a conversational AI application.
What are some case studies of conversational AI?
Wiley Property
Wiley Property is a real estate company in Virginia. On their website, home-buyers use conversational AI to either use voice or text to search for properties by dozens of different attributes, such as the number of bedrooms, square footages, amenities, and more. Buyers also have the ability to compare and contrast different listings and leave their contact info for further communications. Wiley’s Head of Content claims after having implemented the application, their bounce rate dropped from 64% to only 2%.

Coop Sweden
Coop Sweden is one of Sweden’s largest grocery chains. Through the implementation of conversational AI on their mobile app, they are able to:
- Recommend recipes that matches shoppers’ preferences.
- Help shoppers buy ingredients that can be combined with what they already have in their fridge into a unique meal.
- Allow shoppers to take pictures of items (e.g. lemons, bread, etc.) and have them automatically added into their shopping cart.
Conversational AI has so far allowed Coop to create an individual relationship with more than 3 million cooperative members, conduct 6,000 conversations each month, and successfully answer 91% of common questions.
For more on conversational AI:
- To learn more about the different versions of conversational AI, feel free to read our in-depth guide into four types of Conversational AI.
- To learn more about what the market looks like for conversational AI, skim through our Conversational AI market overview.
- And to learn more about the weaknesses of Conversational AI, read our article on 8 epic chatbot/conversational AI failures.
If you believe your business can benefit from the implementation of conversational AI, we guide you to our Conversational AI Hub where we have a data-driven list of vendors.
We have data-driven lists of chatbot agencies as well, whom can help you build a customized chatbot.
Lastly, we also have a transparent list of the top chatbot/conversational AI platforms.
And we can guide you through the process:

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.