What is Intelligent Automation: Guide to RPA's Future in 2024
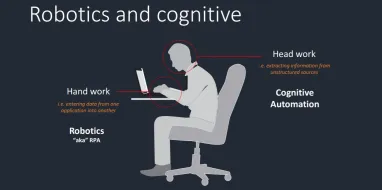
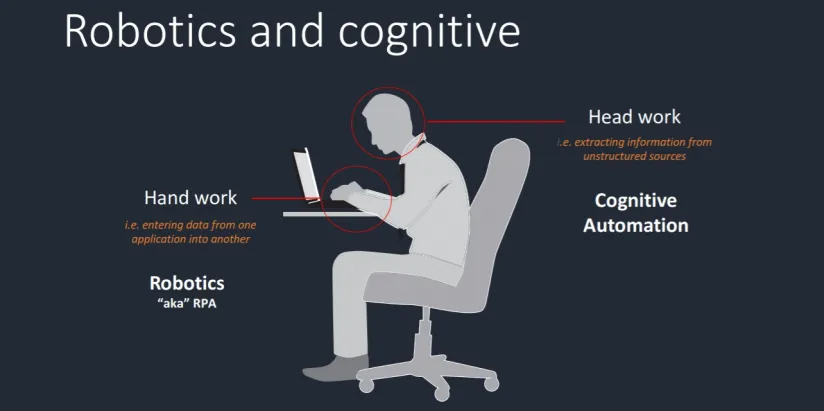
While automation is old as the industrial revolution, digitization greatly increased activities that could be automated. However, initial tools for automation, which includes scripts, macros and robotic process automation (RPA) bots, focus on automating simple, repetitive processes. However, as those processes are automated with the help of more programming and better RPA tools, processes that require higher level cognitive functions are next in the line for automation.
In this article, we explore RPA tools in terms of cognitive abilities, what makes them cognitively capable, and which RPA vendors provide such tools.
What is cognitive automation?
Intelligent/cognitive automation tools allow RPA tools to handle unstructured information and make decisions based on complex, unstructured input. Cognitive automation (also called smart or intelligent automation) is an emerging field that augments RPA tools with artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities like optical character recognition (OCR) or natural language processing (NLP). Cognitive automation is the future of RPA. It deals with both structured and unstructured data including text heavy reports.
These are the solutions that get consultants and executives most excited. Vendors claim that 70-80% of corporate knowledge tasks can be automated with increased cognitive capabilities. To deal with unstructured data, cognitive bots need to be capable of machine learning and natural language processing. See our cognitive automation guide for more info. Cognitive automation is the current focus for most RPA companies’ product teams.
What are the different types of RPA in terms of cognitive capabilities?
There are 3 types of RPA tools in terms of the cognitive capabilities they provide:
No cognitive capabilities
RPA tools without cognitive capabilities are relatively dumb and simple; should be used for simple, repetitive business processes.
While this seems like a big disadvantage, there is a mitigation. Even if the RPA tool does not have built-in cognitive automation capabilities, most tools are flexible enough to allow cognitive software vendors to build extensions. Therefore, required cognitive functionality can be added on these tools.
However, it is likely to take longer to implement these solutions as your company would need to find a capable cognitive solution provider on top of the RPA provider. Only the simplest tools, initially built in 2000s before the explosion of interest in RPA are in this bucket.
Built-in cognitive capabilities
Most RPA tools are in this bucket. Most RPA companies have been investing in various ways to build cognitive capabilities but cognitive capabilities of different tools vary of course. The ideal way would be to test the RPA tool to be procured against the cognitive capabilities required by the process you will automate in your company.
Marketplace supported cognitive capabilities
Realizing that they can not build every cognitive solution, top RPA companies are investing in encouraging developers to contribute to their marketplaces where a variety of cognitive solutions from different vendors can be purchased.
What makes RPA intelligent?
Key capabilities for cognitive automation:
Natural language processing (NLP): Even basic language understanding makes it much easier to automate most customer service processes or processes involving contracts.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Despite increased digitization, a mind-boggling amount of paper is still used, especially in heavily regulated industries like healthcare or banking. Processing these papers are required to automate any process end-to-end.
Machine learning: Processes require decisions. If those decisions can not be formulated as a set of rules, machine learning solutions are required to replace human judgement with machine judgement and automate processes.
You can check our article where we discuss the differences between RPA and intelligent / cognitive automation.
Let’s look at what bots will do with these capabilities.
Cognitive Automation Solution Providers
Cognitive RPA solutions by RPA companies
- Automation Anywhere is marketing IQ Bot as a cognitive RPA solution that incorporates AI capabilities.
- Blue Prism calls their bots advanced capabilities intelligent automation skills.
- IBM’s Cloud Pak automation solution, which incorporates RPA to automate repetitive rule-based tasks, also leverages different AI algorithms and applications to allow for an end-to-end execution of rule-based as well as complex processes. This is done by leveraging:
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to extract text from documents; use computer vision to interact with apps over a remote desktop
- Classification algorithms to identify the purpose of a document or email
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) to extract structured data from textual communications such as emails, documents, and instant messages
- Knowledge base to answer queries via web-chat or SMS
- Rules to make complex decisions with predictable outcomes
- Fuzzy logic to make decisions with variations and uncertainty
- R scripts to perform statistical analysis
- UiPath promotes cognitive automation under intelligent process automation. Its solutions suite includes bots to manage other bots which UiPath calls unattended automation. According to UiPath: “Automated bot managers reduce automation costs & meet service levels by synchronizing queued work and robot deployments with scheduled workflows and events; monitoring & triggering failover procedures, as needed”
- WorkFusion promotes their bots cognitive capabilities under Smart Process Automation.
Cognitive RPA solutions by RPA ecosystem
While these are efforts by major RPA vendors to augment their bots, RPA companies can not build custom AI solutions for each process. Therefore, companies rely on AI focused companies like IBM and niche tech consultancy firms to build more sophisticated automation services.
Cognitive plugins/bots in RPA marketplaces
Additionally, large RPA providers have built marketplaces so developers can submit their cognitive solutions which can easily be plugged into RPA bots. Read our article on RPA marketplaces to learn more.
Cognitive RPA use cases and application areas
You can check our comprehensive article on the use cases of cognitive / intelligent automation in different business functions and industries. You can also explore intelligent automation case studies we compiled from different sources. Here are some examples:
1. HR – New hire onboarding
RPA can automatically populate employee information into multiple systems, such as payroll, benefits administration, and IT provisioning, without the need for manual data entry. Additionally, RPA can assist in scheduling orientation sessions, sending out welcome emails, and generating personalized onboarding materials.
For more, check our article on intelligent automation in HR.
2. Discovering mismatches between contracts and invoices
Deloitte explains how their team used bots with natural language processing capabilities to solve this issue. You can also check our article on intelligent automation in finance and accounting for more examples.
3. Offering end-to-end customer service with chatbots
While chatbots are gaining popularity, their impact is limited by how deeply integrated they are into your company’s systems. For example, if they are not integrated into the legacy billing system, a customer will not be able to change her billing period through the chatbot. Cognitive automation allows building chatbots that can make changes in other systems with ease.
4. Banking – Fulfilling KYC requirements
Leverage public records, handwritten customer input and scanned documents to perform required KYC checks.
5. Banking – Processing trade finance transactions
Banks finance international trade. Processing these transactions require paperwork processing and completing regulatory checks including sanctions checks and proper buyer and seller apportioning.
For more, check our article on intelligent automation in banking.
6. Insurance – Servicing policies
Data mining and NLP techniques are used to extract policy data and impacts of policy changes to make automated decisions regarding policy changes.
7. Insurance – Claims processing
Make automated decisions about claims based on policy and claim data and notify payment systems.
Though cognitive automation is a relatively recent phenomenon, most solutions are offered by Robotic Process Automation (RPA) companies. Check out our RPA guide or our guide on RPA vendor comparison for more info. You can also learn about other innovations in RPA such as no code RPA from our future of RPA article.
Feel free to check our article on intelligent automation in insurance.
Read our in-depth whitepaper on RPA to explore underlying technologies, use cases, and case studies:
And if you are planning to invest in an off-the-shelf RPA solution, scroll through our data-driven list of RPA tools and other automation solutions.
And we can help you choose the right vendor:

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow onNext to Read
30 Intelligent Automation Case Studies / Success Stories in 2024
Intelligent Automation vs Hyperautomation Comparison for 2024
nice
Enjoyed reading the article above , really explains everything in detail,the article is very interesting and effective.Thank you and good luck for the upcoming articles
Hi dear!
Thank you for the amazing information about Cognitive automation . I appreciated your work.
![Intelligent Automation Tools: Key Features & Top Vendors [2024]](https://research.aimultiple.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/Intelligent-Automation-tools-landscape-190x107.png.webp)
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.