Top 12 Hyperautomation Use Cases & Examples in 2024
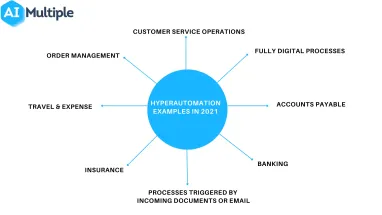
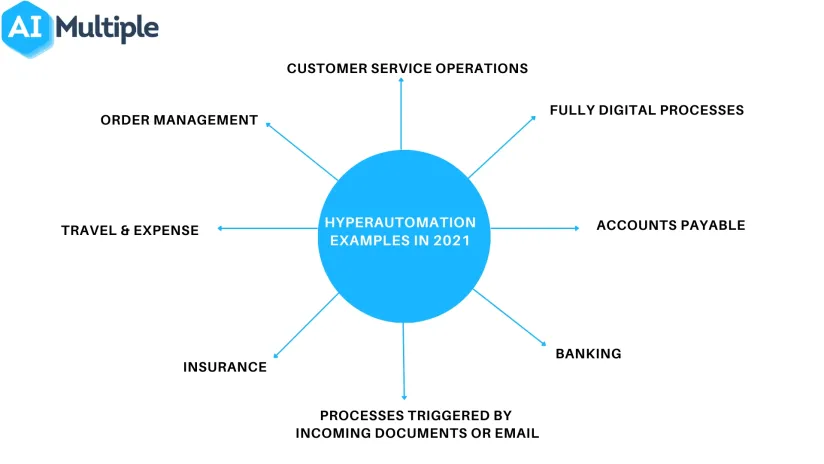
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) provided various benefits to organizations in the last decade. It is still an important opportunity for businesses since the payback period of RPA implementation (9 months) is shorter than most other digital technologies. However, RPA technology has its unique limitations such as its inability to automate via unstructured data and companies are working on end-to-end automation approaches like hyperautomation to solve this problem.
We’ve explained what hyperautomation is and how it differs from regular automation. In short, hyperautomation is the end-to-end automation of processes through a combination of technologies including:
- Robotic Process Automation
- Intelligent Business Process Management Suites (iBPMS)
- Process Mining
- Artificial Intelligence/ Machine Learning
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
- Digital Twin of an Organization (DTO)
We’ve discussed hyperautomation trends and benefits of hyperautomation for businesses. In this article, we’ll explore 12 repetitive business processes where hyperautomation is possible with today’s technology.
What is hyperautomation used for?
There are 2 types of processes where hyperautomation can be leveraged:
1. Processes triggered by incoming documents or email:
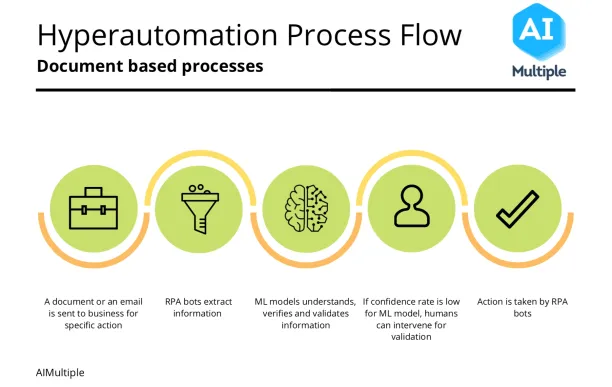
In these processes,
- Incoming documents or emails are collected by a script or RPA bot. This document or email can contain semi-structured or unstructured data.
- Document or email is processed using a machine learning model which extracts machine-readable data from the document
- Machine-readable data is validated by either rules or ML models. For example, invoices could be validated for VAT compliance or to ensure that they are not fraudulent.
- Validated data is enriched by database lookups or ML models. For example,
- Supplier ID can be looked up from the company’s master data
- Cost center can be added to the invoice based on the company’s historical transactions
- If machine learning model confidence is low, the output can be reviewed by a human using a human-in-the-loop software
- Finally, this validated and enriched machine-readable data is passed to the next system of record (e.g. ERP)
2. Fully digital processes:
Not all processes require unstructured or semi structured data. Some processes get triggered with structured data from the client or the company’s internal processes. These should be already automated or are candidates for an easy automation implementation.
The following are the specific process candidates for hyperautomation across common business functions like finance, sales, marketing and customer service as well as industries like insurance and banking:
1. Accounts Payable (AP)
Accounts payable process includes receiving, processing, and paying out invoices from suppliers that provided goods or services to the company. Manual processing
- is expensive
- leads to longer processing time,
- increases the risk of errors
With the addition of machine learning and document extraction technologies such as Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to the RPA, businesses can automate most of the tasks in AP processes.
For more on AP automation, feel free to check our comprehensive article on the topic.
2. Travel & Expense
Travel & Expense (T&E) processes involve paperwork and repetitive tasks that can be automated through hyper automation. Some T&E processes are:
- collecting travel expense paper receipts of employees
- extracting data from receipts
- checking receipts to see whether they are compliant with the expense policies of the company
- completing payments or requesting approval on items that are not in line with expense policies
You can also check our in-depth article on travel & expense automation.
3. Claims handling
Claims handling is a broad category seen in various settings. We will mainly focus on insurance claims and workplace claims.
Insurance claims
Insurers can automate almost the entire claims processing without interruption from humans. Claims handling contains following processes
- claims intake: extracting data from documents
- claims assessment: understanding and analyzing claims to identify whether they are in line with the customers’ policy
- claims settlement: automating transactions for valid claims
Workplace claims
Workplace claims, or HR claims, refer processing requests and claims made by employees to the HR department of a company in regards to vacation requests, expense reimbursements, complaints, and more.
4. Order to Cash (O2C)
Order management involves processes such as
- retrieving email and relevant attachments
- extracting information about what customers want. Some possibilities are
- new order
- order update
- order cancellation
- updating internal systems based on the newly placed order or modifications to existing orders
- taking necessary actions regarding customer query
For more on order management, feel free to check our related article.
5. Other document processing
Manual document processing is a challenge for every industry. Different industries need to process different documents such as invoices, bill of lading, purchase orders, receipts, pay slips, medical records & prescription. Businesses can automate the processing of these documents via hyperautomation. Document automation involves the following steps:
- Document processing
- data extraction
- validation
- enrichment
- In some cases, document generation will also be necessary. For example, orders may need to be generated from the quotes sent from suppliers. This includes:
- data capture
- transforming data to the desired format
- arranging content
- generating output document
With the combination of OCR and machine learning, a business can automate document processing end-to-end.
For more on document automation, please check our related article.
6. Customer Service Operations
Three technologies are involved in the end-to-end automation of serving simple customer requests:
- NLP: Customer input (e.g. email, document, query) understanding
- Machine learning algorithms to classify customer requests and match them to potential actions
- RPA bots or scripts for output (e.g. sending response emails or messages)
7. Lead generation from anonymous site visitors
Most visitors do not provide companies with their contact information. Using IP and other data, website/mobile app owners can identify the businesses that are browsing their digital applications. This data can be automatically fed into an outreach platform which can identify relevant profiles in those companies based on the profiles of companies’ customers. For example, if a company sells to the specialists in the procurement department, those profiles would be prioritized. The outreach platform could
- display advertising to these profiles
- send a series of emails to these profiles and once they respond, they can be routed to the sales team
All touchpoints until sales rep responses can be automated in this process.
8. Underwriting processing
Traditional underwriting relies on manual labor in data collection, data extraction, and risk scoring. Insurers can automate manual efforts and improve risk assessment with AI.
For more, check our article on AI in underwriting.
9. Redaction for privacy preservation
Redaction is necessary to protect personal data. For example, in the US courts subpoena insurers for their customers’ medical records and insurers need to ensure that those records include only the requested data and nothing more. For example Nonpublic Personal Information (NPI) such as social security numbers or telephone information need to be removed from these documents.
ML based solutions can automatically identify NPI and remove it from documents.
10. Anti Money Laundering (AML)
To prevent fraud in transactions, companies can either work with end-to-end AML solutions or combine RPA bots to provide automation:
- RPA bots collect related data and processes to validate customer records
- Fraud detection models identify unusual patterns through ML algorithms
- RPA bots perform follow-up actions
11. Loan underwriting
The underwriting process of loan transactions can also be automated via RPA & AI. It includes these steps:
- collect data from external and internal sources
- fill required data fields in internal systems
- assess risk via ML models
- analyze the historical transactions of customers and provide pricing & interest options
12. Banking customer onboarding
In banking, customer onboarding is a document-heavy area due to know-your-customer (KYC) regulations. The processes involves
- identity verification
- screening
- customer due diligence
- scoring
- reporting
- account activation
Automation of customer onboarding is provided by
- pre-trained bots to extract information from documents, input data into their systems and build risk profiles via machine learning
- human-in-the-loop and machine learning models to enable verification and validation of information
- intelligent bots are trained by historical data to improve their accuracy
If you are looking for vendors that can provide the necessary technologies to achieve hyperautomation, don’t hesitate to contact us:

Cem has been the principal analyst at AIMultiple since 2017. AIMultiple informs hundreds of thousands of businesses (as per similarWeb) including 60% of Fortune 500 every month.
Cem's work has been cited by leading global publications including Business Insider, Forbes, Washington Post, global firms like Deloitte, HPE, NGOs like World Economic Forum and supranational organizations like European Commission. You can see more reputable companies and media that referenced AIMultiple.
Throughout his career, Cem served as a tech consultant, tech buyer and tech entrepreneur. He advised businesses on their enterprise software, automation, cloud, AI / ML and other technology related decisions at McKinsey & Company and Altman Solon for more than a decade. He also published a McKinsey report on digitalization.
He led technology strategy and procurement of a telco while reporting to the CEO. He has also led commercial growth of deep tech company Hypatos that reached a 7 digit annual recurring revenue and a 9 digit valuation from 0 within 2 years. Cem's work in Hypatos was covered by leading technology publications like TechCrunch and Business Insider.
Cem regularly speaks at international technology conferences. He graduated from Bogazici University as a computer engineer and holds an MBA from Columbia Business School.
To stay up-to-date on B2B tech & accelerate your enterprise:
Follow on
Comments
Your email address will not be published. All fields are required.